Abstract
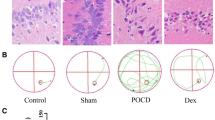
Chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment (CICI) is widely recognized as a frequent adverse side effect following the administration of chemotherapeutic agents. This study aimed to explore the neuroprotective functions and mechanisms of microRNAs (miRNAs) mediated by dexmedetomidine (Dex) on cisplatin-induced CICI. The model rats received 5 mg/kg cisplatin injections once per week for 4 weeks. Dex (30 μg/kg) was administered before cisplatin treatment. The protective effects of Dex were evaluated using Morris water maze, Nissl staining, and transmission electron microscopy. Dex-mediated miRNAs were screened via miRNA sequencing. The effects of Dex and key miRNAs on mitochondrial DNA gene mt-ND1 and caspase-9 expression were tested. Dex exhibited a protective effect against decreased learning memory ability, hippocampal neuronal damage, and mitochondrial damage in CICI rats. Thirty-nine differentially expressed (DE) miRNAs were screened, 13 of which responded positively to Dex treatment. Gene Ontology annotation identified that DE miRNAs were mainly involved in transcription, DNA-templated. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analysis showed that DE miRNAs were mainly involved in neuronal function and brain development-related pathways, such as axon guidance and calcium signaling pathways. Compared to cisplatin treatment, the expression of miR-429-3p responded more strongly to Dex treatment. In cisplatin-treated cultured hippocampal neurons, Dex treatment and miR-429-3p overexpression significantly increased mitochondrial DNA gene mt-ND1expression and decreased caspase-9 expression. Our study suggests that Dex alleviates CICI by modulating miR-429-3p expression in rats. Thus, Dex may be effective in preventing the side effects of cisplatin.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Anthiya S, Griveau A, Loussouarn C, Baril P, Garnett M, Issartel JP, Garcion E (2018) MicroRNA-based drugs for brain tumors. Trends Cancer 4(3):222–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trecan.2017.12.008
Bernstein LJ, McCreath GA, Komeylian Z, Rich JB (2017) Cognitive impairment in breast cancer survivors treated with chemotherapy depends on control group type and cognitive domains assessed: a multilevel meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 83:417–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.10.028
Boese AS, Saba R, Campbell K, Majer A, Medina S, Burton L, Booth TF, Chong P, Westmacott G, Dutta SM, Saba JA, Booth SA (2016) MicroRNA abundance is altered in synaptoneurosomes during prion disease. Mol Cell Neurosci 71:13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2015.12.001
Chanraud S, Zahr N, Sullivan EV, Pfefferbaum A (2010) MR diffusion tensor imaging: a window into white matter integrity of the working brain. Neuropsychol Rev 20(2):209–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-010-9129-7
Chen Y, Gao DY, Huang L (2015) In vivo delivery of miRNAs for cancer therapy: challenges and strategies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 81:128–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2014.05.009
Christie LA, Acharya MM, Parihar VK, Nguyen A, Martirosian V, Limoli CL (2012) Impaired cognitive function and hippocampal neurogenesis following cancer chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 18(7):1954–1965. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2000
Cosar M, Eser O, Fidan H, Sahin O, Buyukbas S, Ela Y, Yagmurca M, Ozen OA (2009) The neuroprotective effect of dexmedetomidine in the hippocampus of rabbits after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Surg Neurol 71(1):54–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2007.08.020(discussion 59)
Dasari S, Tchounwou PB (2014) Cisplatin in cancer therapy: molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol 740:364–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.07.025
Dong H, Hao X, Cui B, Guo M (2017) MiR-429 suppresses glioblastoma multiforme by targeting SOX2. Cell Biochem Funct 35(5):260–268. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbf.3271
Fang H, Li HF, He MH, Yan JY, Yang M, Zhang FX, Wang RR, Wang QY, Zhang JP (2019) Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 sponges microRNA-429 to regulate apoptosis of hippocampal neurons in hypoxic-ischemic brain damage by regulating WNT1. Brain Res Bull 152:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.06.004
Feng X, Wang Z, Fillmore R, Xi Y (2014) MiR-200, a new star miRNA in human cancer. Cancer Lett 344(2):166–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2013.11.004
Filippi M, Agosta F (2016) Diffusion tensor imaging and functional MRI. Handb Clin Neurol 136:1065–1087. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-53486-6.00056-9
Ho GY, Woodward N, Coward JI (2016) Cisplatin versus carboplatin: comparative review of therapeutic management in solid malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 102:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2016.03.014
Hwang L, Choi IY, Kim SE, Ko IG, Shin MS, Kim CJ, Kim SH, Jin JJ, Chung JY, Yi JW (2013) Dexmedetomidine ameliorates intracerebral hemorrhage-induced memory impairment by inhibiting apoptosis and enhancing brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in the rat hippocampus. Int J Mol Med 31(5):1047–1056. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2013.1301
Kumar M, Nerurkar VR (2014) Integrated analysis of microRNAs and their disease related targets in the brain of mice infected with West Nile virus. Virology 452–453:143–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2014.01.004
Lam JK, Chow MY, Zhang Y, Leung SW (2015) siRNA versus miRNA as therapeutics for gene silencing. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 4:e252. https://doi.org/10.1038/mtna.2015.23
Li J, Xiong M, Nadavaluru PR, Zuo W, Ye JH, Eloy JD, Bekker A (2016) Dexmedetomidine attenuates neurotoxicity induced by prenatal propofol exposure. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 28(1):51–64. https://doi.org/10.1097/ANA.0000000000000181
Ling H, Fabbri M, Calin GA (2013) MicroRNAs and other non-coding RNAs as targets for anticancer drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12(11):847–865. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd4140
Lomeli N, Di K, Czerniawski J, Guzowski JF, Bota DA (2017) Cisplatin-induced mitochondrial dysfunction is associated with impaired cognitive function in rats. Free Radic Biol Med 102:274–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.11.046
Pandey A, Singh P, Jauhari A, Singh T, Khan F, Pant AB, Parmar D, Yadav S (2015) Critical role of the miR-200 family in regulating differentiation and proliferation of neurons. J Neurochem 133(5):640–652. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13089
Peng L, Fu J, Ming Y (2018) The miR-200 family: multiple effects on gliomas. Cancer Manag Res 10:1987–1992. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S160945
Podratz JL, Lee H, Knorr P, Koehler S, Forsythe S, Lambrecht K, Arias S, Schmidt K, Steinhoff G, Yudintsev G, Yang A, Trushina E, Windebank A (2017) Cisplatin induces mitochondrial deficits in Drosophila larval segmental nerve. Neurobiol Dis 97(Pt A):60–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2016.10.003
Qin Y, Chen W, Liu B, Zhou L, Deng L, Niu W, Bao D, Cheng C, Li D, Liu S, Niu C (2017) MiR-200c inhibits the tumor progression of glioma via targeting moesin. Theranostics 7(6):1663–1673. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.17886
Reddy PH, Williams J, Smith F, Bhatti JS, Kumar S, Vijayan M, Kandimalla R, Kuruva CS, Wang R, Manczak M, Yin X, Reddy AP (2017) MicroRNAs, aging, cellular senescence, and Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 146:127–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.pmbts.2016.12.009
Rosso SB, Inestrosa NC (2013) WNT signaling in neuronal maturation and synaptogenesis. Front Cell Neurosci 7:103. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2013.00103
Tang CZ, Yang JT, Liu QH, Wang YR, Wang WS (2019) Up-regulated miR-192-5p expression rescues cognitive impairment and restores neural function in mice with depression via the Fbln2-mediated TGF-beta1 signaling pathway. FASEB J 33(1):606–618. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201800210RR
Wefel JS, Kesler SR, Noll KR, Schagen SB (2015) Clinical characteristics, pathophysiology, and management of noncentral nervous system cancer-related cognitive impairment in adults. CA Cancer J Clin 65(2):123–138. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21258
Xiao L, Chen Y, Ji M, Dong J (2011) KIBRA regulates Hippo signaling activity via interactions with large tumor suppressor kinases. J Biol Chem 286(10):7788–7796. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.173468
Yuan L, Hu S, Okray Z, Ren X, De Geest N, Claeys A, Yan J, Bellefroid E, Hassan BA, Quan XJ (2016) The Drosophila neurogenin tap functionally interacts with the Wnt-PCP pathway to regulate neuronal extension and guidance. Development 143(15):2760–2766. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.134155
Zhang C, Zhang J, Hao J, Shi Z, Wang Y, Han L, Yu S, You Y, Jiang T, Wang J, Liu M, Pu P, Kang C (2012) High level of miR-221/222 confers increased cell invasion and poor prognosis in glioma. J Transl Med 10:119. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-10-119
Zhang L, Yang S, Wennmann DO, Chen Y, Kremerskothen J, Dong J (2014) KIBRA: in the brain and beyond. Cell Signal 26(7):1392–1399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.02.023
Zhao C, Ma ZG, Mou SL, Yang YX, Zhang YH, Yao WC (2017) Targeting effect of microRNA on CD133 and its impact analysis on proliferation and invasion of glioma cells. Genet Mol Res 16(1):gmr16019281. https://doi.org/10.4238/gmr16019281
Zheng P, Bin H, Chen W (2019) Inhibition of microRNA-103a inhibits the activation of astrocytes in hippocampus tissues and improves the pathological injury of neurons of epilepsy rats by regulating BDNF. Cancer Cell Int 19:109. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-019-0821-2
Zhou W, Kavelaars A, Heijnen CJ (2016) Metformin prevents cisplatin-induced cognitive impairment and brain damage in mice. PLoS ONE 11(3):e0151890. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0151890
Funding
This study was provided by Science and technology project of education department of Jiangxi province (project no. GJJ190035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and Funding acquisition: GX. Data curation: CL and FD. Formal analysis: JN and BZ. Investigation: CL, JN and WD. Methodology: ZZ and BZ. Writing—original draft: CL, JN and WD. Writing—review and editing: BZ, FD and ZZ. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The animal experiments in this study and all procedures involving the handling and treatment of rat during this study were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University. All the experiments were performed according to the guidelines of the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
13205_2020_2217_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplementary file3 (TIF 120 kb) Quality control results of a representative sample sequence. The horizontal axis indicates the number of bases or the range of bases, the vertical axis displays quality score values; quality scores > 30 revealed the accuracy of mapping to be greater than 99.9%
13205_2020_2217_MOESM4_ESM.tif
Supplementary file4 (TIF 697 kb) Wayne diagrams illustrating predicted DE miRNAs target genes between control and model groups (A), as well as DE miRNA target genes involving the Dex and model groups (B)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Niu, J., Zhou, B. et al. Dexmedetomidine attenuates cisplatin-induced cognitive impairment by modulating miR-429-3p expression in rats. 3 Biotech 10, 244 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02217-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02217-1