Abstract
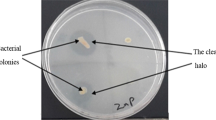
Zinc plays a key role in plant nutrition at low levels; however, at higher concentrations Zn ions can be highly phytotoxic and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria can be used to reduce such metal toxicity. In the present investigation we had reported the zinc biosorption and molecular characterization of plant growth-promoting zinc-tolerant bacteria. Initially, thirty bacteria having zinc solubilizing ability were screened for MIC against zinc ion and displayed high value of MIC ranging from 2.5 to 62.5 mM. Biochemically, all the 30 isolates showed significant difference in the 6 biochemical tests performed. The molecular diversity studies based on the repetitive DNA PCR viz, REP, ERIC and BOX elements showed significant genetic diversity among these 30 zinc-tolerant bacteria. These ZTB strains also showed multiple PGP activities and all ZTB strains were found positive for production of IAA, GA3 and ammonia, whereas 24 were found positive for ACC deaminase activity, 8 showed siderophore production and 9 ZTB isolates were positive for HCN production. Out of 30 isolates, 24 showed phosphorus solubilization activity, 30 showed potash solubilization, 15 showed silica solubilization and 27 showed phytase production activities. All the 30 ZTB stains showed zinc solubilization up to 0.25% insoluble ZnO in the medium, whereas at 2% ZnO in MSM only 12 isolates showed solubilization which were further selected for zinc biosorption and pot studies. The heavy metal removal studies revealed that ZTB stains were able to remove zinc ions effectively from the medium efficiently and the highest zinc biosorption (< 90%) was recorded with the bacterial strain Z-15. Further, the inoculation of ZTB strains under zinc stress conditions (pot containing 1000 mg/kg Zn) resulted in significant increase of shoot length, root length and total chlorophyll content in maize seedlings compared with the uninoculated control. The partial 16S rDNA sequence of the potential ZTB isolates viz. Z-15, Z-24, Z-28 and Z-29 revealed their identity as Serratia sp. The ability of these zinc-tolerant bacteria to tolerate the toxic level of zinc may serve as suitable candidates for developing microbial formulations for the growth of crop plants in Zn-contaminated areas.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ZTB:
-
Zinc-tolerant bacteria
- Zn:
-
Zinc
- MIC:
-
Minimum inhibitory concentration
- AAS:
-
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy
- ERIC:
-
Enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus
- REP:
-
Repetitive extragenic palindromic
- BOX:
-
BOX-A1R-based repetitive extragenic palindromic
- UPGMA:
-
Unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean
- PGPR:
-
Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Aneja KR (2003) Experiments in microbiology plant pathology and biotechnology. New Age International (P) Ltd, New Delhi
Ayangbenro AS, Babalola OO (2017) A new strategy for heavy metal polluted environments: a review of microbial biosorbents. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14(1):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14010094
Bautista-Hernández DA, Ramírez-Burgos LI, Duran-Páramo E, Fernández-Linares L (2012) Zinc and lead biosorption by Delftia tsuruhatensis: a bacterial strain resistant to metals isolated from mine tailings. J Water Resour Prot 4:207–216
Bilung LM, Pui CF, Su’ut L, Apun K (2018) Evaluation of BOX-PCR and ERIC-PCR as molecular typing tools for pathogenic Leptospira. Dis Markers 18:1–9
Buszewski B, Rogowska A, Pomastowski P, Złoch M, Railean-Plugaru V (2017) Identification of microorganisms by modern analytical techniques. J AOAC Int 100(6):1–17
Cole JR, Wang Q, Fish JA, Chai B, McGarrell DM, SunY Brown CT, Porras-Alfaro A, Kuske CR, Tiedje JM (2014) Ribosomal database project: data and tools for high throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 42( (Database issue)):D633–D642
Costerousse B, Mauclaire LS, Frossard E, Thonar C (2018) Identification of heterotrophic zinc mobilization processes among bacterial strains isolated from wheat rhizosphere (Triticum aestivum L.). Appl Environ Microbiol 84(1):1–16
Dinesh R, Srinivasan V, Hamza S, Sarathambal C, Gowda SJ, Ganeshamurthy AN, Gupta SB, Nair AV, Subila KP, Lijina A, Divya VC (2018) Isolation and characterization of potential Zn solubilizing bacteria from soil and its effects on soil Zn release rates, soil available Zn and plant Zn content. Geoderma 321:173–186
Dombek PE, Johnson LK, Zimmerley ST, Sadowsky MJ (2000) Use of Repetitive DNA sequences and the PCR to differentiate Escherichia coli isolates from human and animal sources. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(6):2572–2577
Goteti PK, Emmanuel LDA, Desai S, Shaik MHA (2013) Prospective zinc solubilising bacteria for enhanced nutrient uptake and growth promotion in Maize (Zea mays L.). Int J Microbiol 4(12):1–7
Haroun AA, Kamaluddeen KK, Alhaji I, Magaji Y, Oaikhena EE (2017) Evaluation of heavy metal tolerance level and bioremediation potentials of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from Makera Kakuri industrial drain in Kaduna, Nigeria. Euro J Exp Bio 5(28):1–4
Hrynkiewicz K, Baum C (2014) Application of microorganisms in bioremediation of environment from heavy metals. In: Malik A, Grohmann E, Akhtar R (eds) Environmental deterioration and human health. Springer, Dordrecht
Igiri BE, Okoduwa SIR, Idoko GO, Akabuogu EP, Adeyi AO, Ejiogu IK (2018) Toxicity and bioremediation of heavy metals contaminated ecosystem from tannery wastewater: a review. J Toxicol 2018:16. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2568038
Jain D, Sunda SD, Sanadhya S, Nath DN, Khandelwal SK (2017) Molecular characterization and PCR-based screening of cry genes from Bacillus thuringiensis strains. 3 Biotech 7:4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-016-0583-7
Kamran S, Shahid I, Baig DN, Rizwan M, Malik KA, Mehnaz S (2018) Contribution of zinc solubilizing bacteria in growth promotion and zinc content of wheat. Front Microbiol 8:1–14
Koeuth T, Versalovic J, Lupski JR (1995) Differential subsequence conservation of interspersed repetitive Streptococcus pneumonia BOX elements in diverse bacteria. Genome Res 5(4):408–418
Krishna MP, Varghese R, Babu VA, Jyothy S, Hatha AA (2013) Bioremediation of zinc using Bacillus sp isolated from metal-contaminated industrial zone. In: Sabu A, Augustine A (eds) Prospects in bioscience: addressing the issues. Springer, New Delhi
Kumar P, Dubey RC, Maheshwari DK (2012) Bacillus strains isolated from rhizosphere showed plant growth promoting and antagonistic activity against phytopathogens. Microbiol Res 167:493–499
Kumar V, Singh P, Jorquera MA, Sangwan P, Kumar P, Verma AK, Agrawal S (2013) Isolation of phytase-producing bacteria from Himalayan soils and their effect on growth and phosphorus uptake of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea). World J Microbiol Biotechnol 8(5):45–58
Li XL, Christie P (2001) Changes in soil solution Zn and pH and uptake of Zn by arbuscular mycorrhizal red clover in Zn-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 42:201–207
Louws FJ, Rademaker JL, deBruijn FJ (1999) The three Ds of PCR-based genomic analysis of phytobacteria: diversity, detection and disease diagnosis. Annu Rev Phytopathol 37:81–125
Luli GW, Talnagi JW, Strohl WR, Pfister RM (1983) Hexavalent chromium resistant bacteria isolated from river sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 46(4):846–854
Marzan LW, Hossain M, Mina SA, Akter Y, Chowdhury MA (2017) Isolation and biochemical characterization of heavy-metal resistant bacteria from tannery effluent in Chittagong city, Bangladesh: bioremediation view point. Egypt J Aquat Res 43(1):65–74
Mihdhir AA, Assaeed SA, Abulreesh HH, Osman EH (2016) Detection, identification and characterization of some heavy metals tolerant bacteria. J Microb Biochem Technol 8(3):226–230
Naureen Z, Aqeel M, Hassan MN, Gilani SA, Bouqellah N, Mabood F, Hussain J, Hafeez FY (2015) Isolation and screening of silicate bacteriafrom various habitats for biological control of phytopathogenic fungi. Am J Plant Sci 6:2850–2859
Pandya ND, Desai PV (2014) Screening and characterization of GA3 producing Pseudomonas monteilii and its impact on plant growth promotion. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 3(5):110–115
Park Y, Mun B, Kang S, Hussain A, Shahzad R, Seo C, Kim A, Lee S, Oh KY, Lee DY, Lee I, Yun B (2017) Bacillus aryabhattai SRB02 tolerates oxidative and nitrosative stress and promotes the growth of soybean by modulating the production of phytohormones. PLoS ONE 12(3):1–28
Pramanik K, Mitra S, Sarkar A, Soren T, Maiti TM (2017) Characterization of cadmium-resistant Klebsiella pneumonia MCC 3091 promoted rice seedling growth by alleviating phytotoxicity of cadmium. Environ Sci Pollut Res 17:23–30
Rohlf FJ (1998) NTSYSpc Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system version 2.0 user guide. Applied Biostatistics Inc, Setauket, New York
Rohomania T, Saha ML, Hossain A, Rahman MS (2015) Morphological and biochemical characterization of bacteria isolated from fresh and salted Hilsa, Tenualosailisha (Hamilton, 1822). Bangladesh J Microbiol 32(2):7–13
Saravanan VS, Madhaiyan M, Thangaraju M (2007) Solubilization of zinc compounds by the diazotrophic, plant growth promoting bacterium Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus. Chemosphere 66:1794–1798
Sedlakova-Kadukova J, Kopcakova A, Gresakova L, Godany A, Pristas P (2019) Bioaccumulation and biosorption of zinc by a novel Streptomyces K11 strain isolated from highly alkaline aluminium brown mud disposal site. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 167:204–211
Sen M, Joshi H (2016) Determination of minimum inhibitory concentration and antibiotic susceptibility of zinc tolerant bacteria isolated from mine soil of zawar mine. Indian J Fund Appl Life Sci 6(2):23–29
Shaikh SS, Saraf MS (2017) Optimization of growth conditions for zinc solubilizing plant growth associated bacteria and fungi. J Adv Res Biotechnol 2(1):1–9
Sheng X, Xia J, Jiang C, He L, Qian M (2008) Characterization of heavy metal-resistant endophytic bacteria from rape (Brassica napus) roots and their potential in promoting the growth and lead accumulation of rape. Environ Pollut 156:1164–1170
Singh KK, Hasan HS, Talat M, Singh VK, Gangwar SK (2009) Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using wheat bran. Chem Eng J 151:113–121
Tirry N, Joutey NT, Sayel H, Kouchou A, Bahafid W, Asri M, Ghachtouli NE (2018) Screening of plant growth promoting traits in heavy metals resistant bacteria: prospects in phytoremediation. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 16:613–619
Trindade LC, Lima MF, Marisa AS, Ferreira V (2004) Molecular characterization of Brazilian strains of Xanthomonas campestris pv. viticola by rep-PCR Fingerprinting. Fitopatol Bras 30:46–54
Vasanthi N, Saleena LM, Anthoni SR (2013) Evaluation of media for isolation and screening of silicate solubilising bacteria. Int J Curr Res 5:406–408
Versalovic J, Koeuth T, Lupski JR (1991) Distribution of repetitive DNA sequences in eubacteria and application to fingerprinting of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 19(24):6823–6831
Vidyashree DN, Muthuraju R, Panneerselvam P, Saritha B, Ganeshamurthy AN (2016) Isolation and characterization of zinc solubilizing bacteria from stone quarry dust powder. Int J Agr Sci 8(56):3078–3085
Wani PA, Khan MS, Zaidi A (2007) Impact of zinc-tolerant plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on lentil grown in zinc-amended soil. Agron Susta Dev 28:449–455
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Xie X, Fu J, Wang H, Liu J (2010) Heavy metal resistance by two bacteria strains isolated from a copper mine tailing in China. Afr J Biotechnol 9(26):4055–4066
Zaidi S, Usmani S, Singh BR, Musarrat J (2006) Significance of Bacillus subtilis strain SJ-101 as a bioinoculant for concurrent plant growth promotion and nickel accumulation in Brassica juncea. Chemosphere 64:991–997
Acknowledgements
The financial assistance from All India Network Project on soil biodiversity and biofertilizers and Rastriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) are highly acknowledged. Ms. Suman Sanadhaya thanks CSIR for the award of Senior Research Fellowships. The support from Dean, RCA and Director of Research, MPUAT is also greatfully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DJ and SRM designed the research. RK, AAB, AS, SS, HS performed the experiments and interpreted the data. GJ performed soil and AAS analysis. DJ, SRM and AS wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kour, R., Jain, D., Bhojiya, A.A. et al. Zinc biosorption, biochemical and molecular characterization of plant growth-promoting zinc-tolerant bacteria. 3 Biotech 9, 421 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1959-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1959-2