Abstract
In this report, Pseudomonas putida SJTE1 isolated from an enrichment culture of sludge was confirmed to degrade natural estrogens (17β-estradiol, estrone, estriol), estrogenic chemicals (naphthalene and phenanthrene) and testosterone. The strain completely degraded 1 mg/L 17β-estradiol in 24 h and transformed it into estrone; 90% and 75% of 50 mg/L and 100 mg/L 17β-estradiol were utilized in 7 days, respectively. The transformation efficiency of this strain against natural estrogens was much higher than that against other estrogenic chemicals. Organic carbon sources, lipopolysaccharide and surfactants could enhance the degradation efficiency of strain SJTE-1 against 17β-estradiol. The adsorption of 17β-estradiol onto the biomass was the premise for transmembrane and cellular utilization of this chemical. This work has the potential to bioremediate the environmental estrogens.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The data supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article and additional file. The estrogen-degrading P. putida SJTE-1 has been deposited to CGMCC with No. 6585.
References
Alizadeh S, Prasher SO, ElSayed E, Qi Z, Patel RM (2018) Effect of biochar on fate and transport of manure-borne estrogens in sandy soil. J Environ Sci (China) 73:162–176
Clouzot L, Marrot B, Doumenq P, Roche N (2008) 17a-Ethinylestradiol: an endocrine disrupter of great concern. Analytical methods and removal processes applied to water purification. A review. Environ Prog 27:383–396
Combalbert S, Hernandez-Raquet G (2010) Occurrence, fate, and biodegradation of estrogens in sewage and manure. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:1671–1692
Futoshi K, Maki O, Satoshi S, Yamazoe A, Yagi O (2010) Degradation of natural estrogen and identification of the metabolites produced by soil isolates of Rhodococcus sp. and Sphingomonas sp. J Biosci Bioeng 109:576–582
Giese C, Miethe N, Schlenker G (2007) Biodegradation of estrogens in stream water. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr 120:141–147
Gu L, Huang B, Xu Z, Ma X, Pan X (2016) Dissolved organic matter as a terminal electron acceptor in the microbial oxidation of steroid estrogen. Environ Pollut 218:26–33
Gu L, Huang B, Lai C, Xu Z, He H, Pan X (2018) The microbial transformation of 17βestradiol in an anaerobic aqueous environment is mediated by changes in the biological properties of natural dissolved organic matter. Sci Total Environ 631–632:641–648
Haiyan R, Shulan J, ud din Ahmad N, Dao W, Cheng C (2007) Degradation characteristics and metabolic pathway of 17alpha-ethynylestradiol by Sphingobacterium sp. JCR5. Chemosphere 66:340–346
He H, Huang B, Fu G, Xiong D, Xu Z, Wu X, Pan X (2018) Electrochemically modified dissolved organic matter accelerates the combining photodegradation and biodegradation of 17α-ethinylestradiol in natural aquatic environment. Water Res 137:251–261
Holt J, Krieg N, Sneath P, Staley J, Williams S, Wilkins W (1994) International edition: Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore
Horinouchi M, Hayashi T, Kudo T (2012) Steroid degradation in Comamonas testosteroni. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 129:4–14
Huang B, Wang B, Ren D, Jin W, Liu J, Peng J, Pan X (2013) Occurrence, removal and bioaccumulation of steroid estrogens in Dianchi Lake catchment, China. Environ Int 59:262–273
Huang B, Sun W, Li X, Liu J, Li Q, Wang R, Pan X (2015) Effects and bioaccumulation of 17β-estradiol and 17α-ethynylestradiol following long-term exposure in crucian carp. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 112:169–176
Lee K, Park JW, Ahn IS (2003) Effect of additional carbon source on naphthalene biodegradation by Pseudomonas putida G7. J Hazard Mater 105:157–167
Liu JL, Wang RM, Huang B, Lin C, Wang Y, Pan XJ (2011) Distribution and bioaccumulation of steroidal and phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals in wild fish species from Dianchi lake. China Environ Pollut 159:2815–2822
Liu JL, Wang RM, Huang B, Lin C, Wang Y, Pan XJ (2012) Biological effects and bioaccumulation of steroidal and phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals in high-back crucian carp exposed to wastewater treatment plant effluents. Environ Pollut 162:325–331
Matsumura Y, Hosokawa C, Sasaki-Mori M, Akahira A, Fukunaga K, Ikeuchi T, Oshiman K, Tsuchido T (2009) Isolation and characterization of novel bisphenol-A degrading bacteria from soils. Biocontrol Sci 14:161–169
Masuda M, Yamasaki Y, Ueno S, Inoue A (2007) Isolation of bisphenol A-tolerant/degrading Pseudomonas monteilii strain N-502. Extremophiles 11:355–362
McAdam EJ, Bagnall JP, Koh YK, Chiu TY, Pollard S, Scrimshaw MD, Lester JN, Cartmell E (2010) Removal of steroid estrogens in carbonaceous and nitrifying activated sludge processes. Chemosphere 8:11–16
Mita L, Grumiro L, Rossi S, Bianco C, Defez R, Gallo P, Mita DG, Diano N (2015) Bisphenol A removal by a Pseudomonas aeruginosa immobilized on granular activated carbon and operating in a fluidized bed reactor. J Hazard Mater 2015, 291:129–135
Pauwels B, Wille K, Noppe H, De Brabander H, Van de Wiele T, Verstraete W, Boon N (2008) 17alpha-ethinylestradiol cometabolism by bacteria degrading estrone, 17beta-estradiol and estriol. Biodegradation 19:683–693
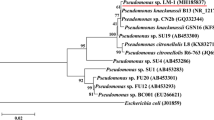
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Shi J, Fujisawa S, Nakai S, Hosomi M (2004) Biodegradation of natural and synthetic estrogens by nitrifying activated sludge and ammonia-oxidizing bacterium Nitrosomonas europaea. Water Res 38:2322–2329
Tay M, Roizman D, Cohen Y, Tolker-Nielsen T, Givskov M, Yang L (2014) Draft Genome sequence of the model naphthalene-utilizing organism Pseudomonas putida OUS82. Genome Announc 2:e01161–e01113
Tilghman SL, Nierth-Simpson EN, Wallace R, Burow ME, McLachlan JA (2010) Environmental hormones: Multiple pathways for response may lead to multiple disease outcomes. Steroids 75:520–523
Ting YF, Praveena SM (2017) Sources, mechanisms, and fate of steroid estrogens in wastewater treatment plants: a mini review. Environ Monit Assess 189:178
Weber S, Leuschner P, Kampfer P, Dott W, Hollender J (2005) Degradation of estradiol and ethinyl estradiol by activated sludge and by a defined mixed culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 6:7106–7112
Yin GG, Kookana RS, Ru YJ (2002) Occurrence and fate of hormone steroids in the environment. Environ Int 28:545–551
Ying G, Kookana RS, Dillon P (2003) Sorption and degradation of selected five endocrine disrupting chemicals in aquifer material. Water Res 37:3785–3791
Yoshimoto T, Nagai F, Fujimoto J, Watanabe K, Mizukoshi H, Makino T, Kimura K, Saino H, Sawada H, Omura H (2004) Degradation of estrogens by Rhodococcus zopfii and Rhodococcus equi isolates from activated sludge in wastewater treatment plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5283–5289
Yu CP, Roh H, Chu KH (2007) 17beta-estradiol-degrading bacteria isolated from activated sludge. Environ Sci Technol 41:486–492
Yu CP, Deeb RA, Chu KH (2013) Microbial degradation of steroidal estrogens. Chemosphere 91:1225–1235
Zeng Q, Li Y, Gu G, Zhao J, Zhang C, Luan J (2009) Sorption and biodegradation of 17b-estradiol by acclimated aerobic activated sludge and isolation of the bacterial strain. Environ Engin Sci 26:783–790
Zhang ZH, Feng YJ, Gao P, Wang C, Ren NQ (2011) Occurrence and removal efficiencies of eight EDCs and estrogenicity in a STP. J Environ Monit 13:1366–1373
Zhang Y, Dong S, Wang H, Tao S, Kiyama R (2016) Biological impact of environmental polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (ePAHs) as endocrine disruptors. Environ Pollut 213:809–824
Zheng D, Wang X, Wang P, Peng W, Ji N, Liang R (2016) Genome sequence of Pseudomonas citronellolis SJTE-3, an estrogen- and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium. Genome Announc 4:e01373–e01316
Funding
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 31370152, 31570099).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RL designed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. DZ and PW performed the experiments. XW assisted the experiments. All the authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Zheng, D. & Liang, R. Isolation and characterization of an estrogen-degrading Pseudomonas putida strain SJTE-1. 3 Biotech 9, 61 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1537-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1537-z