Abstract
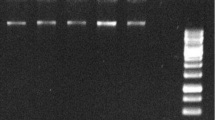
Isolation of high-quality RNA from weed plants such as Parthenium hysterophorus is a difficult task due to the hindrance caused by numerous secondary metabolites. Such metabolites not only affect the quality and yield of RNA, but also limit the quality of downstream applications. Therefore, the present study was undertaken to design a protocol for yielding RNA with better quality and quantity from P. hysterophorus leaf which could be suitable for functional genomics. To achieve the objective, four different important RNA extraction protocols, viz. acid guanidinium thiocyanate–phenol–chloroform, phenol–LiCl precipitation, TRIzol®, and PVP–ethanol were tested. The PVP–ethanol method proved to be best among the tested protocols. This method was further modified for obtaining improved quality and yield of RNA. The modified method successfully enhanced the yield of RNA from 280 to 334 µg g−1 fresh weight. The absorbance ratio (A 260/A 280) was in the purity range of 1.9 that indicated the good quality of RNA. To prove the feasibility of the extracted RNA in PCR-based cDNA synthesis, actin transcripts were targeted and successfully amplified using suitable primers. The improved protocol thus not only improved the yield and quality of RNA, but also gave better results in reverse transcriptase PCR.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Accerbi M, Schmidt SA, Paoli E, Park S, Jeong DH, Green PJ (2009) Methods for isolation of total RNA to recover miRNAs and other small RNAs from diverse species. In: Meyers BC, Green PJ (eds) Plant micro RNAs, methods in molecular biology. Humana Press, New York, pp 31–50. doi:10.1007/978-1-60327-005-2_3
Ahmad J, Bashir H, Bagheri R, Baig A, Huqail A, Ibrahim MM, Qureshi MI (2017) Drought and salinity induced changes in ecophysiology and proteomic profile of Parthenium hysterophorus. PLoS ONE (Under Production). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0185118
Boyer JS (1982) Plant productivity and environment. Science 218(4571):443–448. doi:10.1126/science.218.4571.443
Boyer JS, Westgate ME (2004) Grain yields with limited water. J Exp Bot 55(407):2385–2394. doi:10.1093/jxb/erh219
Chafe Z (2005) Bioinvasions. State of the world 2005: redefining global security. W.W. Norton and Company, New York, pp 60–61
Chan CX, Teo SSHOCL, Othman RY, Phang SM (2004) Optimisation of RNA extraction from Gracilaria changii (Gracilariales, Rhodophyta). J Appl Phycol 16(4):297–301
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162(1):156–159. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(87)90021-2
Ding LW, Sun QY, Wang ZY, SunYB XuZF (2008) Using silica particles to isolate total RNA from plant tissues recalcitrant to extraction in guanidine thiocyanate. Anal Biochem 374(2):426–428. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2007.11.030
Jordon-Thaden IE, Chanderbali AS, Gitzendanner MA, Soltis DE (2015) Modified CTAB and TRIzol protocols improve RNA extraction from chemically complex Embryophyta. Appl Plant Sci. doi:10.3732/apps.1400105
Kolosova N, Miller B, Ralph S, Ellis BE, Douglas C, Ritland K, Bohlmann J (2004) Isolation of high-quality RNA from gymnosperm and angiosperm trees. Nat Rev Genet 2:353–359
Kumar A (2014) Parthenium hysterophorus L. and its impact on living world. Indian J Sci Res 4(1):8–14
Lavoie M, Abou ES (2008) Yeast ribonuclease III uses a network of multiple hydrogen bonds for RNA binding and cleavage. Biochemistry 47(33):8514–8526. doi:10.1021/bi800238u
Ma Z, Huang B, Xu S, Chen Y, Li S, Lin S (2015) Isolation of high-quality total RNA from Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb.) Hook). PLoS ONE 10(6):e0130234. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0130234
Maishi AI, Ali PKS, Chaghtai SA, Khan G (1998) A proving of Parthenium hysterophorus, L. Br Homoeopath J 87:17–21. doi:10.1016/S0007-0785(98)80005-7
Patel S (2011) Harmful and beneficial aspects of Parthenium hysterophorus: an update. 3 Biotech 1(1):19
Rubio-Piña JA, Zapata-Pérez O (2011) Isolation of total RNA from tissues rich in polyphenols and polysaccharides of mangrove plants. Electron J Biotechnol 14(5):11. doi:10.2225/vol14-issue5-fulltext-8
Sajeevan RS, Shivanna MB, Nataraja KN (2014) An efficient protocol for total RNA isolation from healthy and stressed tissues of mulberry (Morus sp) and other species. Am J Plant Sci. doi:10.4236/ajps.2014.513221
Salzman RA, Fujita T, Zhu-Salzman K, Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA (1999) An improved RNA isolation method for plant tissues containing high levels of phenolic compounds or carbohydrates. Plant Mol Biol Rep 17:11–17. doi:10.1023/A:1007520314478
Sambrook J, Fritschi EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Shojaie N, Ghaffari MS, Safari Z (2014) Simultaneous Extraction of DNA and RNA from animal cells by a modified Laemmli Buffer. Protocol Exchange 2014 https://www.scientificprotocols.org/protocols. doi:10.1038/protex.2014.036
Singh HP, Batish DR, Pandher JK, Kohli RK (2003) Assessment of allelopathic properties of Parthenium hysterophorus residues. Agric Ecosys Environ 9:537–541. doi:10.1016/S0167-8809(02)00202-5
Sokolovsky V, Kaldenhoff R, Ricci M, Russo VEA (1990) Fast and reliable mini-prep RNA extraction from Neurospora crassa. Neurospora Newslett 37:41–43
Wu J, Xiao Q, Xu JLIM, Pan J, Yang M (2008) Natural products from true mangrove flora: source, chemistry and bioactivities. Nat Prod Res 25(5):955–981. doi:10.1039/b807365a
Yockteng R, Almeida AM, Yee S, Andre T, Hill C, Specht CD (2013) A method for extracting high-quality RNA from diverse plants for next-generation sequencing and gene expression analyses. Appl Plant Sci. doi:10.3732/apps.1300070
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for supporting this work through research group no. RGP 231.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, J., Baig, M.A., Ali, A.A. et al. Comparative assessment of four RNA extraction methods and modification to obtain high-quality RNA from Parthenium hysterophorus leaf. 3 Biotech 7, 373 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-1003-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-1003-3