Abstract
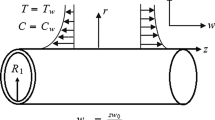
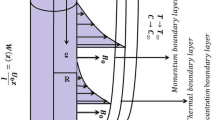
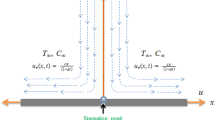
This paper investigates the aspects of magnetic field and chemical reaction in Oldroyd-B nanofluid influenced by a stretching cylinder. The properties of mixed convection, nonlinear radiation and heat sink/source are incorporated. By means of noteworthy conversions, the nonlinear PDEs are altered into nonlinear ODEs and elucidated via homotopic approach. The influence of countless variables for velocity, temperature and concentration fields in addition to local Nusselt and Sherwood numbers are portrayed and conferred. These upshots portray that the liquid velocity enhances for intensifying value of mixed convection parameter whereas, it diminish for magnetic parameter. Moreover, the Brownian motion parameter and radiation parameter enhances the liquid temperature of Oldroyd-B nanofluid. For the endorsement of current upshots an assessment values in restrictive circumstances is also presented.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel MS, Tawade JV, Nandeppanavar MM (2012) MHD flow and heat transfer for the upper convected Maxwell fluid over a stretching sheet. Meccanica 47:385–393
Ahmed J, Khan M, Ahmad L (2019) Transient thin-film spin-coating flow of chemically reactive and radiative Maxwell nanofluid over a rotating disk. Appl Phys A. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2424-0
Alshomrani AS, Irfan M, Salem A, Khan M (2018) Chemically reactive flow and heat transfer of magnetite Oldroyd-B nanofluid subject to stratifications. Appl Nanosci 8:1743–1754
Anjalidevi SP, Kandasamy R (1999) Effects of chemical reaction, heat and mass transfer on laminar flow along a semi-infinite horizontal plate. Heat Mass Transf 35:465–467
Anwar MS, Rasheed A (2017) Simulations of a fractional rate type nanofluid flow with non-integer Caputo time derivatives. Comput Math Appl 74:2485–2502
Choi SUS (1995) Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. ASME Int Mech Eng 66:99–105
Ellahi R (2018) Special issue on recent developments of nanofluids. Appl Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8020192
Haq RU, Rashid I, Khan ZA (2017) Effects of aligned magnetic field and CNTs in two different base fluids over a moving slip surface. J Mol Liq 243:682–688
Haq RU, Soomro FA, Öztop HF, Mekkaoui T (2019) Thermal management of water-based carbon nanotubes enclosed in a partially heated triangular cavity with heated cylindrical obstacle. Int J Heat Mass Transf 131:724–736
Hayat T, Rashid M, Alsaedi A (2017a) MHD convective flow of magnetite-Fe3O4 nanoparticles by curved stretching sheet. Result Phys 7:3107–3115
Hayat T, Khan MI, Waqas M, Alsaedi A (2017b) Newtonian heating effect in nanofluid flow by a permeable cylinder. Results Phys 7:256–262
Hayat T, Waqas M, Khan MI, Alsaedi A (2017c) Impacts of constructive and destructive chemical reactions in magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) flow of Jeffrey liquid due to nonlinear radially stretched surface. J Mol Liq 225:302–310
Hayat T, Rashid M, Alsaedi A (2018) Three dimensional radiative flow of magnetite-nanofluid with homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions. Results Phys 8:268–275
Irfan M, Khan M, Khan WA, Ayaz M (2018a) Modern development on the features of magnetic field and heat sink/source in Maxwell nanofluid subject to convective heat transport. Phys Lett A 382:1992–2002
Irfan M, Khan M, Khan WA, Sajid M (2018b) Thermal and solutal stratifications in flow of Oldroyd-B nanofluid with variable conductivity. Appl Phys A. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2086-3
Irfan M, Khan M, Khan WA, Sajid M (2019a) Consequence of convective conditions for flow of Oldroyd-B nanofluid by a stretching cylinder. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-019-1604-3
Irfan M, Khan M, Khan WA (2019b) Impact of Non-uniform heat sink/source and convective condition in radiative heat transfer to Oldroyd-B nanofluid: a revised proposed relation. Phys Lett A 383:376–382
Khan M, Irfan M, Khan WA (2017) Impact of nonlinear thermal radiation and gyrotactic microorganisms on the Magneto-Burgers nanofluid. Int J Mech Sci 130:375–382
Kumar KG, Haq RU, Rudraswamy NG, Gireesha BJ (2017) Effects of mass transfer on MHD three dimensional flow of a Prandtl liquid over a flat plate in the presence of chemical reaction. Results Phys 7:3465–3471
Kumar RVMSSK, Raju CSK, Mahanthesh B, Gireesha BJ, Varma SVK (2018) Chemical reaction effects on nano Carreau liquid flow past a cone and a wedge with Cattaneo-Christov heat flux model. Int J Chem Reactor Eng. https://doi.org/10.1515/ijcre-2017-0108
Mahanthesh B, Gireesha BJ, Gorla RSR, Abbasi FM, Shehzad SA (2016) Numerical solutions for magnetohydrodynamicflow of nanofluid over a bidirectional non-linear stretching surface with prescribed surface heat flux boundary. J Mag Mag Mater 417:189–196
Mahanthesh B, Gireesha BJ, Prasannakumara BC, Kumar PBS (2017a) Magneto-Thermo-Marangoni convective flow of Cu-H2O nanoliquid past an infinite disk with particle shape and exponential space based heat source effects. Results Phys 7:2990–2996
Mahanthesh B, Mabood F, Gireesha BJ, Gorla RSR (2017b) Effects of chemical reaction and partial slip on the three-dimensional flow of a nanofluid impinging on an exponentially stretching surface. Eur Phys J Plus. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2017-11389-8
Meghed AM (2013) Variable fluid properties and variable heat flux effects on the flow and heat transfer in a non-Newtonian Maxwell fluid over an unsteady stretching sheet with slip velocity. Chin Phys B 22:094701
Mustafa M, Khan JA, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2015) Analytical and numerical solutions for axisymmetric flow of nanofluid due to non-linearly stretching sheet. Int J Non-Linear Mech 71:22–29
Rashid M, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2019) Entropy generation in Darcy–Forchheimer flow of nanofluid with five nanoarticles due to stretching cylinder. Appl Nanosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-00961-2
Rehman FU, Nadeem S, Haq RU (2017) Heat transfer analysis for three-dimensional stagnation-point flow over an exponentially stretching surface. Chin J Phys 55:1552–1560
Sheikholeslami M, Oztop HF (2017) MHD free convection of nanofluid in a cavity with sinusoidal walls by using CVFEM. Chin J Phys 55:2291–2304
Sheikholeslami M, Haq RU, Shafee A, Li Z, Elaraki YG, Tlili I (2019) Heat transfer simulation of heat storage unit with nanoparticles and fins through a heat exchanger. Int J Heat Mass Transf 135:470–478
Sreedevi P, Reddy PS, Chamkha AJ (2017) Heat and mass transfer analysis of nanofluid over linear and non-linear stretching surfaces with thermal radiation and chemical reaction. Powder Technol 315:194–204
Waqas M, Khan MI, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2017a) Numerical simulation for magneto Carreau nanofluid model with thermal radiation: a revised model. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 324:640–653
Waqas M, Khan MI, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2017b) Stratified flow of an Oldroyd-B nanoliquid with heat generation. Result Phys 7:2489–2496
Zhang C, Zheng L, Zhang X, Chen G (2015) MHD flow and radiation heat transfer of nanofluids in porous media with variable surface heat flux and chemical reaction. Appl Math Model 39:165–181
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Irfan, M., Khan, M., Gulzar, M.M. et al. Chemically reactive and nonlinear radiative heat flux in mixed convection flow of Oldroyd-B nanofluid. Appl Nanosci 10, 3133–3141 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01052-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01052-y