Abstract
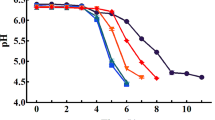
The present study concludes the impact of storage on changes in physico-chemical characteristics of fermented whey cereal (pearl millet and moth bean) beverage. The beverage was prepared by fermented whey (standardised to 4% fat and 18% total solids) supplemented with germinated pearl millet and moth bean slurry & using NCDC-167 as starter culture for 6–8 h at 37 °C. The developed beverage was then stored at 5 °C for 4 weeks. The samples were analysed for physico-chemical characteristics (pH, titrable acidity, viscosity, tyrosine, FFA, wheying off), sensory qualities changes and microbial quality changes (standard plate count, lactic acid bacteria count, coli form counts) at 3 days’ interval for 4 weeks at 4 °C. Control was prepared standardised whey (4% fat and 18% total solids) while treatments were prepared using standardised milk. During storage: acidity, tyrosine values, free fatty acid values and wheying off increased in all the samples The upsurge was on higher side in non nisin treated and non thermised samples compared to control formulation. However, all the samples remained sensorily acceptable upto 12th day of storage. Basic and thermised as well as nisin treated fermented whey cereal products epitomize innovative dairy products with desired functional characteristics with decent shelf life.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be provided, if required. Data supporting the results reported in the article can be found including, where applicable, hyperlinks to publicly archived datasets analysed or generated during the study.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
APHA (1992) Compendium of methods for the microbiological examination of foods. In: Vandergant C, Splittstoesser DF, American Public Health Association, Washington, D.C, Adwan L, (eds) Fermented dairy drinks under pressure (online). Euromonitor international archive. Available from: http://www.euromonitor.com/article.asp?id=1371
AOAC (2007) Official methods of analysis, 18th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington, D.C.
Behare PV, Prajapati JB (2007) Thermization as a method for enhancing the shelf life of cultured buttermilk. Indian J Dairy Sci 60(2):86–93
O’Callaghan YC, Shevade AV, Guinee TP, O’Connor TP, O’Brien NM (2019) Comparison of the nutritional composition of experimental fermented milk:wheat bulgur blends and commercially available kishk and tarhana products. Food Chem 278:110–118
Chavan RS, Shraddha RC, Kumar A, Nalawade T (2015) Whey based beverage: its functionality, formulations, health benefits and applications. J Food Proc Technol 6(10):495
Cronk TC, Steinkraus KH, Hackler LR, Mattick LR (1977) Indonesian tape ketan fermentation. Appl Environ Microbiol 33:1067–1073
Dave RI, Shah NP (1997) Viability of yogurt and probiotic bacteria in yogurt made from commercial starter culture. Int Dairy J 7:31–41
Deeth HC, FitzGerald CH (1976) Lipolysis in dairy products: a review. Aust J Dairy Technol 31(2):53–64
Gupta N, Srivastava AK, Pandey VN (2012) Biodiversity and nutraceutical quality of some Indian millets. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect B Biol Sci 82:265–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-012-0035-z
Hussain SA, Gargh FC, Pal D (2012) Effect of different preservative treatments on the shelf life of sorghum malt based fermented milk beverage. J Food Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-012-0657-4
Khan S, Amin N, Ansari Z, Majumder DR (2015) WHEY: waste to health and wealth. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 2:245–325
Kramer NE, Smid EJ, Kok J, de Kruijff B, Kuipers OP (2004) Resistance of gram positive bacteria to nisin is not determined by lipid ΙΙ levels. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 239:157–161
Kruni´c TZ, Rakin MB (2022) Enriching alginate matrix used for probiotic encapsulation with whey protein concentrate or its trypsin-derived hydrolysate: impact on antioxidant capacity and stability of fermented whey-based beverages. Food Chem 370:130931
Krunic T, Rakin M, Bulatovic M, Zaric D (2018) Chapter 9—the contribution of bioactive peptides of whey to quality of food products. In food processing for increased quality and consumption; grumezescu. In: Holban AM (ed) Handbook of food bioengineering. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 251–285
Modha H, Pal D (2011) Optimisation of rabadi like fermented milk beverage using pearl millet. J Food Sci Technol 48(2):190–196
Oliveira JD, Silva DA, de Paula RCM, Feitosa JPA, Paula HCB (2001) Composition and effect of salt on rheological and gelation properties of enterolobium contortisiliquum gum exudate. Int J Biol Macromol 29:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-8130(01)00151-9
Patel MT (1984) Evaluation of the effects of methods of lactose hydrolysis and post- incubation thermization in relation to manufacture and quality of stirred and frozen yoghurts. Gujrat Agricultural University, Anand campus, Gujrat
Patidar SK, Prajapati JB (1998) Standardization and evaluation of lassi prepared using Lactobacillus acidophilus and Streptococcus thermophilus. J Food Sci Technol 35(5):428–431
Pawar BK, Choudhari DM, Kamble DK (2010) Effect of nisin on shelf life of lassi. Asian J Dairy Food Res 29(2):79–85
Prajapati PS, Gupta GR, Patel AA (1992) Studies on the preparation of Shrikhand by using selected starter. Indian J Dairy Sci 1992:1–5
Rahmawati SI, Suntornsuk W (2016) Effects of fermentation and storage on bioactive activities in milks and yoghurts. Procedia Chem 18:53–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proche.2016.01.010
Ramana BLV, Tiwari BD (1999) Effect of processing variables on sensory and physico-chemical qualities of heat treated lassi. Indian J Dairy Sci 52(5):272–278
Rasic JL, Kurmann JA (1978) Yoghurt: Scientific grounds, technology, manufacture and preparations. Technical Dairy Publishing House, Copenhagen, p 466
Sarkar S (2016) Effect of nisin on technological and microbiological characteristics of stirred yoghurt. J Microbiol Microbial Technol 1(1):01–06
Shaghaghi M, Pourahmad R, Mahdavi Adeli HR (2013) Synbiotic yogurt production by using prebiotic compounds and probiotic lactobacilli. Int Res J Appl Basic Sci 5:839–846
Sharma S, Sreeja V, Prajapati BJ (2016) Development of symbiotic lassi containing honey: studies on probiotic viability, product characteristics and shelf life. Indian J Dairy Sci 69(2):148–153
Snedecor GW, Cochran WG (1994) Statistical methods, 9th edn. Iowa State University Press, Ames, Iowa
Stanton C, Gardiner G, Meehan H, Collins K, Fitzgerald G, Lynch PB, Ross RP (2011) Market potential for probiotics. Am J Clin Nutr 73(2):476S-483S
Stone H, Sidel J, Oliver S, Woosley A, Singleton RC (1974) Sensory evaluation by quantitative descriptive analysis. Food Technol 28:24–34
Strange ED, Benedict RC, Smith JL, Swift CE (1977) Evaluation of rapid test for monitoring alteration in meat quality during storage. J Food Prot 40:843–847
Talwalkar A, Kailasapathy K (2004) A review of oxygen toxicity in probiotic yoghurts: influence on the survival of probiotic bacteria and protective techniques. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 3:117–124
Acknowledgements
Authors are highly thankful to Vice-Chancellor, LUVAS for providing needful facilities in Department of Livestock Products Technology. Authors are also thankful to Department of Science and Technology, India for financial assistance throughout the study.
Funding
Authors are thankful to, LUVAS for providing needful facilities in Department of Livestock Products Technology. Authors are also thankful to Department of Science and Technology, India for financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MR conceived, carried out the experiments and wrote the MS, while RSD supervised the work and SB and GJ corrected the manuscript and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethics approval
Not required.
Consent to participate
I hereby submit my consent for publication of the manuscript to JFST.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rani, M., Dabur, R.S., Bishnoi, S. et al. Influence of storage on physico-chemical physiognomies of fermented whey cereal (pearl millet and moth bean) beverage. J Food Sci Technol 61, 117–128 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-023-05825-w
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-023-05825-w