Abstract
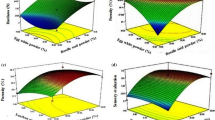
Response surface methodology was used to analyze effects of the amounts of pregelatinized potato flour (PGPF), hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC), egg white protein (EWP), and water on the dough fermentation and physical properties of gluten-free (GF) steamed bread based on potato flour. The results showed that PGPF, HPMC, EWP, and water at the appropriate amounts improved the maximum dough height (Hm), specific volume (SV) and hardness, as well as Hm correlated with SV (R2 = 0.6993) and hardness (R2 = 0.7273). Moreover, the optimal formulation contained 4.84 g/100 g PGPF, 1.68 g/100 g HPMC, 5.87 g/100 g EWP, and 69.69 g/100 g water, potato flour basis. Furthermore, the dietary fiber, total polyphenol content, antioxidant activity, and estimated glycemic index of the steamed GF bread were, respectively, 3.17-, 1.56-, 1.44-, and 0.75-fold of those of steamed wheat bread. The optimized steamed GF bread was found to be acceptable according to the results of sensory analysis. Information collected within this study may provide further insight for optimizing the formulation of steamed GF bread based on potato flour.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez-Jubete L, Auty M, Arendt EK, Gallagher E (2010) Baking properties and microstructure of pseudocereal flours in gluten-free bread formulations. Eur Food Res Technol 230(3):437–445
AACC (2000) Approved methods of the American Association of Cereal Chemists. American Association of Cereal Chemists, St. Paul, Minnesota
Cai J, Chiang JH, Tan MYP, Saw LK, Xu Y, Ngan-Loong MN (2016) Physicochemical properties of hydrothermally treated glutinous rice flour and xanthan gum mixture and its application in gluten-free noodles. J Food Eng 186:1–9
Cappa C, Lucisano M, Mariotti M (2013) Influence of Psyllium, sugar beet fibre and water on gluten-free dough properties and bread quality. Carbohydr Polym 98(2):1657–1666
de la Hera E, Rosell CM, Gomez M (2014) Effect of water content and flour particle size on gluten-free bread quality and digestibility. Food Chem 151:526–531
Ezekiel R, Singh N, Sharma S, Kaur A (2013) Beneficial phytochemicals in potato—a review. Food Res Int 50:487–496
Fasano A, Catassi C (2012) Celiac disease. N Engl J Med 367(25):2419–2426
Granfeldt Y, Bjorck I, Drews A, Tovar J (1992) An in vitro procedure based on chewing to predict metabolic response to starch in cereal and legume products. Eur J Clin Nutr 46:649–660
Gujral HS, Singh N (1999) Effect of additives on dough development, gaseous release and bread making properties. Food Res Int 32(10):691–697
Gumul D, Ziobro R, Ivanišová E, Korus A, Árvay J, Tóth T (2017) Gluten-free bread with an addition of freeze-dried red and purple potatoes as a source of phenolic compounds in gluten-free diet. Int J Food Sci Nutr 68(1):43–51
Hager AS, Arendt EK (2013) Influence of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC), xanthan gum and their combination on loaf specific volume, crumb hardness and crumb grain characteristics of gluten-free breads based on rice, maize, teff and buckwheat. Food Hydrocoll 32(1):195–203
Han A, Romero HM, Nishijima N, Ichimura T, Handa A, Xu C, Zhang Y (2019) Effect of egg white solids on the rheological properties and bread making performance of gluten-free batter. Food Hydrocoll 87:287–296
Huang W, Kim Y, Li X, Rayas-Duarte P (2008) Rheofermentometer parameters and bread specific volume of frozen sweet dough influenced by ingredients and dough mixing temperature. J Cereal Sci 48(3):639–646
Jafari M, Koocheki A, Milani E (2018) Physicochemical and sensory properties of extruded sorghum–wheat composite bread. J Food Meas Charact 2(1):1–8
Kaur A, Shevkani K, Singh N, Sharma P, Kaur S (2015) Effect of guar gum and xanthan gum on pasting and noodle-making properties of potato, corn and mung bean starches. J Food Sci Technol 52(12):8113–8121
Kittisuban P, Ritthiruangdej P, Suphantharika M (2014) Optimization of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose, yeast β-glucan, and whey protein levels based on physical properties of gluten-free rice bread using response surface methodology. LWT Food Sci Technol 57(2):738–748
Kiumarsi M, Shahbazi M, Yeganehzad S, Majchrzak D, Lieleg O, Winkeljann B (2019) Relation between structural, mechanical and sensory properties of gluten-free bread as affected by modified dietary fibers. Food Chem 277:664–673
Kumar CTM, Sabikhi L, Singh K, Raju PN, Kumar R, Sharm R (2019) Effect of incorporation of sodium caseinate, whey protein concentrate and transglutaminase on the properties of depigmented pearl millet based gluten free pasta. LWT Food Sci Technol 103:19–26
Li J, Zhu Y, Yadav MP, Li J (2019) Effect of various hydrocolloids on the physical and fermentation properties of dough. Food Chem 271:165–173
Liu XL, Mu TH, Sun HN, Zhang M, Chen JW, Fauconnier ML (2018) Influence of different hydrocolloids on dough thermo-mechanical properties and in vitro starch digestibility of gluten-free steamed bread based on potato flour. Food Chem 239:1064–1074
Marco C, Rosell CM (2008) Functional and rheological properties of protein enriched gluten free composite flours. J Food Eng 88(1):94–103
Mariotti M, Pagani MA, Lucisano M (2013) The role of buckwheat and HPMC on the breadmaking properties of some commercial gluten-free bread mixtures. Food Hydrocoll 30(1):393–400
Masih J (2018) Study on parameters of consumer preferences for alternative wheat products (gluten-free foods) in USA and India. Agric Sci 9:385–396
McCarthy DF, Gallagher E, Gormley TR, Schober TJ, Arendt EK (2005) Application of response surface methodology in the development of gluten-free bread. Cereal Chem 82(5):609–615
Mezaize S, Chevallier S, Le Bail A, De Lamballerie M (2009) Optimization of gluten-free formulations for French-style breads. J Food Sci 74(3):E140–E146
Morreale F, Benavent-Gil Y, Rosell CM (2019) Inulin enrichment of gluten free breads: interaction between inulin and yeast. Food Chem 278:545–551
Naqash F, Gani A, Gani A, Masoodi FA (2017) Gluten-free baking: combating the challenges—a review. Trends Food Sci Technol 66:98–107
Pongjaruvat W, Methacanon P, Seetapan N, Fuongfuchat A, Gamonpilas C (2014) Influence of pregelatinised tapioca starch and transglutaminase on dough rheology and quality of gluten-free jasmine rice breads. Food Hydrocoll 36:143–150
Ronda F, Oliete B, Gómez M, Caballero PA, Pando V (2011) Rheological study of layer cake batters made with soybean protein isolate and different starch sources. J Food Eng 102(3):272–277
Rosell CM, Rojas JA, De Barber CB (2001) Influence of hydrocolloids on dough rheology and bread quality. Food Hydrocoll 15(1):75–81
Segura MEM, Rosell CM (2011) Chemical composition and starch digestibility of different gluten-free breads. Plant Food Hum Nutr 66(3):224–230
Singh N, Kaur SP, Kaur L, Sodhi NS (2005) Physico-chemical, rheological and chapati making properties of flours from some Indian potato cultivars. J Food Sci Technol Mysore 42(4):344–348
Tan LZ, Kwok SC, Ooi CY (2015) Coeliac disease in Chinese children. J Paediatr Child Health 51(5):566–570
Witczak M, Korus J, Ziobro R, Juszczak L (2019) Waxy starch as dough component and anti-staling agent in gluten-free bread. LWT Food Sci Technol 99:476–482
Zettel V, Krämer A, Hecker F, Hitzmann B (2015) Influence of gel from ground chia (Salvia hispanica L.) for wheat bread production. Eur Food Res Technol 40(3):655–662
Zhang C, Zhang H, Wang L (2007) Effect of carrot (Daucus carota) anti-freeze proteins on the fermentation capacity of frozen dough. Food Res Int 40(6):763–769
Zhu F, Sakulnak R, Wang S (2016) Effect of black tea on antioxidant, textural, and sensory properties of Chinese steamed bread. Food Chem 194:1217–1223
Acknowledgements
This scientific study was financed by the Natural Science Foundation of China (31801578), and the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (Y2016PT21). We thank the University of Liège-Gembloux Agro-Bio Tech and more specifically the research platform AgricultureIsLife for the funding of the scientific stay in Belgium that made this paper possible.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Mu, T., Sun, H. et al. Effect of ingredients on the quality of gluten-free steamed bread based on potato flour. J Food Sci Technol 56, 2863–2873 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03730-9
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03730-9