Abstract
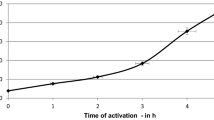
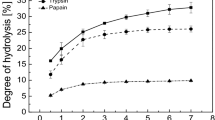
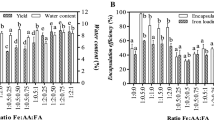
Poor bioavailability of minerals from plant based foods attributing to iron deficiency anemia and zinc deficiency is a cause of concern in the developing world. The investigation was undertaken to prepare casein phosphopeptides (CPP) and check their efficacy in enhancing the bioavailaibility of minerals by in vitro method. Alcalase hydrolysis of casein yielded 28.7 g/100 g CPP. CPP added at ratios of mineral: CPP of 1:2 and 1:3 to ferrous sulphate and zinc sulphate solutions enhanced the bioaccessibility of minerals significantly. Addition of 5–10 g CPP/100 g soya flour enhanced the bioaccessible iron and zinc in native and iron fortified flour to a significant extent. CPP counteracted the inhibitory effect of fortified minerals on bioaccessibillity of native minerals. CPP can definitely be used for enhancing the bioaccessibility of iron and zinc in pure solutions and high phytate foods. CPP can be used in manufacturing food products with enhanced bioaccessibility of minerals for overcoming the deficiencies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ait-Oukhatar N, Bouhallab AP, Maubois JL, Drosdowsky M, Bougle D (1999) Iron tissue storage and hemoglobin levels of deficient rats repleted with iron bound to the caseinophosphopeptide 1–25 of b-casein. J Agric Food Chem 47:2786–2790
Alder–Nissen J (1979) Determination of the degree of hydrolysis of food protein hydrolysates by trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid. J Agric Food Chem 27:1256–1262
Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC) (2000) Official methods of analysis of AOAC inter methods 934.01 and 988.05. AOAC International, Arlington
Bouhallab S, Bougle D (2004) Biopeptides of milk: caseinophosphopeptides and mineral bioavailability. Reprod Nutr Dev 44:493–498
Bouhallab S, Cinga V, Ait-Oukhatar N, Bureau F, Neuville D, Arhan P, Maubois JL, Bougle D (2002) Influence of various phosphopeptides of caseins on iron absorption. J Agric Food Chem 50:7127–7130
Camara F, Amaro MA (2003) Nutral aspects of zinc availability. Int J Food Sci Nutr 54:143–151
Hegde U, Lakshmi JA, Radha C, Kumar RP, Prakash J (2009) Effect of soya protein on the dialysability of exogenous iron and zinc. Food Chem 117:577–581
Hemalatha S, Platel K, Srinivasan K (2007) Influence of heat processing on the bioaccessibility of zinc and iron from cereals and pulses consumed in India. J Trace Elem Med Biol 21:1–7
Iyengar P, Pullakhandam R, Nair M (2010) Dieatry ligands as determinants of iron-zinc interactions at the absorptive enterocyte. J Food Sci 75:H260–H264
Kapil U, Jain K (2011) Magnitude of zinc deficiency among under five children in India. Indian J Ped 78:1069–1072
Lonnerdal B (2000) Dietary factors influencing zinc absorption. J Nutr 130:1378S–1383S
Luten J, Crews H, Flynn A, Dael PV, Kastenmeyer P, Hurrell R, Deelstra H, Shen L, Fairweather Trait S (1996) Interlaboratory trial on the determination of in vitro dialyzability from food. J Sci Food Agric 72:415–424
Meisel H, Fitzgerald RJ (2003) Biofunctional peptides from milk proteins: mineral binding and cytomodulatory effects. Curr Pharma Des 9:1289–1295
Meisel H, Schlimme E (1993) Calcium and iron binding capacity of different fractions from in vitro proteolysis of casein. Kiel Milch Forsch 45:235–243
Miquel E, Gomez JA, Alegria A, Barbera R, Farre R, Recio I (2005) Identification of casein phosphopeptides released after simulated digestion in milk-based infant formulas. J Agric Food Chem 53:3426–3433
Park O, Swaisgood HE, Allen JC (1998) Calcium binding of phosphopeptides derived from hydrolysis of αs-casein and β-casein using immobilized trypsin. J Diary Sci 81:2850–2857
Perales S, Barbera R, Lagarda MJ, Farre R (2007) Availability of iron from milk-based formulas and fruit juices containing milk and cereals estimated by in vitro methods (solubility, dialysability) and uptake and transport by Caco-2 cells. Food Chem 102:1296–1303
Peres JM, Bouhallab S, Petit C, Bureau F, Maubois JL, Arhan P, Bougle D (1998) Improvement of zinc intestinal absorption and reduction of zinc/iron interaction using metal bound to the caseinophosphopeptide 1–25 of b-casein. Rep Nutr Dev 38:465–472
Sato R, Naguchi T, Naito H (1986) Casein phosphopeptide (CPP) enhances calcium absorption from the ligated segment of rat small intestine. J Nutr Sci Vitam 32:67–76
Schlemmer U, Frolich W, Prieto FM, Grases F (2009) Phytate in foods and significance for humans: food sources, processing, intake, bioavailability, protective role and analysis. Mol Nutr Food Res 53:S330–S375
Taussky HH, Shorr E (1953) A micro-colorimetry method for determination of inorganic phosphorous. J Biol Chem 202:675–685
WHO/CDC (World Health Organization/Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2004) Technical consultation assessing the iron status of populations. Switzerland, Geneva
Yeung AC, Glahn RP, Miller DD (2002) Effects of iron source on iron availability from casein and casein phosphopeptides. J Food Sci 67:1271–1275
Zhao L, Wang Z, Xu S (2007) Preparation of casein phosphorylated peptides and casein non-phosphorylated peptides using alcalase. Eur Food Res Technol 225:579–584
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prakash, D., Lakshmi, A.J. Preparation of caseinophosphopeptides and assessing their efficacy in enhancing the bioaccessibility of iron and zinc. J Food Sci Technol 52, 7493–7499 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1864-6
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1864-6