Abstract
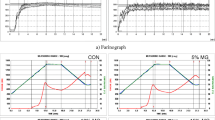
Effect of spinach powder on the physico-chemical, rheological, nutritional and sensory characteristics on chapati premixes was studied by incorporating spinach powder at different concentrations from 1 % to 10 % based on wheat flour. Addition of 5 % of spinach powder to wheat flour was found to be optimum for chapati preparation. Effect of incorporation of spinach powder on the alveo-consistographic, mixographic and pasting characteristics were studied. It was observed that peak viscosity, breakdown viscosity significantly decreases whereas, peak time, tenacity increases with the increase in the concentration of spinach powder from 1 % to 10 % in chapati premixes. Addition of spinach powder also significantly affects the textural qualities of the chapaties. Premixes and prepared chapaties were also studied for chlorophyll content, total carotenoids,vitamins and minerals.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACC (2000) Approved methods of the AACC, 10th edn. The Association, St Paul MN
Allen LDE, Benoist B, Dart O, Hurrel RF (2006) In: Guidelines on food fortification with micronutrients. Geneva, World Health Organisation and Food and Agricultural Organisation of the United Nations
AOAC (1980) Official methods of analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 13th edn. The Association, Washington, DC
Arya SS, Vidyasagar K, Parihar DB (1977) Preservation of chapaties. Lebensm-Wiss-u-Technol 10:2008–2010
Bedekar BR (2001) Chapati-Indian bakery product of the 21st century. Indian Food Ind 20:21–24
Dachana KB, Jyotsna R, Indrani D, Jamuna P (2010) Effect of dried moringa (Moringa Oleifera Lam) leaves on rheological, microbiological, nutritional, textural and organoleptic characteristics of cookies. J Food Qual 33:660–667
Dengate HN, Meredith P (1984) The pasting characteristics of various sizes of starch granules from wheat. Starch / Strake 36:305–309
Ghufran Saeed SM, Saqib A, Mubarak A, Rashida A, Fred S (2009) Influence of rice bran on rheological properties of dough and in the new product development. J Food Sci Technol 46:62–65
Gomez M, Ronda F, Carlos A, Pedro B, Cballero A, Apesteguia A (2003) Effect of dietary fibre on dough rheology and bread quality. Eur Food Res Technol 216:51–56
Gupta S, Prakash J (2011) Nutritional and sensory quality of micronutrient-rich traditional products incorporated with green leafy vegetables. Int Food Res J 18:667–675
Larmond E (1977) Laboratory methods for sensory evaluation of food. Canada Department of Agriculture Publication, Ottawa, pp 234–257
Lee MH, Hettiarachchy NS, Mcnew RW, Gnanasanbandam R (1995) Physico-chemical properties of calcium fortified rice. Cereal Chem 72:352–355
Lee S, Inglett GE, Carriere CJ (2004) Effect of nutrim oat bran and flaxseed on rheological properties of cakes. Cereal Chem 81:637–643
Premavalli KS, Majumdar TK, Madhura CV (2001) Processing effect on colour and vitamins of green leafy vegetables. J Food Sci Technol 38:79–81
Ranganna S (1986) Handbook of analysis and quality control for fruit and vegetable products, 2nd edn. Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi
Reddy V, Urooj A, Kumar A (2000) Evaluation of antioxidant activity of some plant extracts and their application in biscuits. Food Chem 90:317–321
Shirpa B, Jyothi Lakshmi A, Indrani D (2012) Effect of barley, banana and soy protein isolate on rheological, microstructural and nutritional characteristics of North Indian Parotta. J Texure Stud 43:246–256
Singh G, Kawatra A (2006) Development and nutritional evaluation of recipes prepared using fresh and dried amaranthus leaves. J Food Sci Technol 33:509–511
Snedecor GW, Cochran WG (1968) Statistical methods, 6th edn. Oxford and IBH Pub Co, New Delhi
Symons LJ, Brennan CS (2004) The effect of barley β-glucan fiber fractions on starch gelatinization and pasting characteristics. J Food Sci 69:257–261
Yadav DN, Patki PE, Sharma GK, Bawa AS (2008) Effect of microwave heating of wheat grains on the browning of dough and quality of chapaties. Int J Food Sci Technol 43:1217–1225
Yadav DN, Patki PE, Sharma GK, Harila PT, Bawa AS (2009) Studies on the prevention of dough discolouration by chemical additives. J Food Sci Technol 46:149–152
Yuan G, Bo S, Yuan J, Wang Q (2009) Effects of different cooking methods on health-promoting compounds of broccoli. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 10:580–588
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M.A., Mahesh, C., Semwal, A.D. et al. Effect of spinach powder on physico-chemical, rheological, nutritional and sensory characteristics of chapati premixes. J Food Sci Technol 52, 2359–2365 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-013-1198-1
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-013-1198-1