Abstract
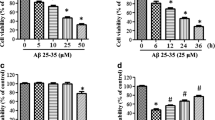
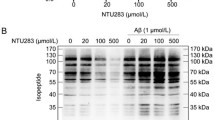
The primary features of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) are extracellular amyloid plaques consisting mainly of deposits of amyloid β (Aβ) peptides and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs). Sets of evidence suggest that interleukin-5 (IL-5) is involved in the pathogenesis of AD. Herein, we investigated the protective role of IL-5 in PC12 cells, to provide new insights into understanding this disease. Western blot was employed to assess the protein levels of Bax and phospho-tau as well as phospho-JAK2; MTT assay was performed to decipher cell viability. Treatment of IL-5 decreased Aβ25–35-induced tau phosphorylation and apoptosis, effects blunted by JAK2 inhibition. IL-5 prevents Aβ25–35-evoked tau protein hyperphosphorylation and apoptosis through JAK2 signaling.







Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Ashenafi S, Fuente A, Criado JM, Riolobos AS, Heredia M, Yajeya J (2005) Beta-amyloid peptide25-35 depresses excitatory synaptic transmission in the rat basolateral amygdala “in vitro”. Neurobiol Aging 26:419–428
Bloom GS (2014) Amyloid-β and tau: the trigger and bullet in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. JAMA Neurol 71:505–508
Buckingham SD, Jones AK, Brown LA, Sattelle DB (2009) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor signalling: roles in Alzheimer’s disease and amyloid neuroprotection. Pharmacol Rev 61:39–61
Chiba T, Yamada M, Sasabe J, Terashita K, Shimoda M, Matsuoka M, Aiso S (2009) Amyloid-beta causes memory impairment by disturbing the JAK2/STAT3 axis in hippocampal neurons. Mol Psychiatry 14:206–222
Darvin P, Joung YH, Yang YM (2013) JAK2-STAT5B pathway and osteoblast differentiation. JAKSTAT 2:e24931
Delacourte A, Defossez A (1986) Alzheimer’s disease: tau proteins, the promoting factors of microtubule assembly, are major components of paired helical filaments. J Neurol Sci 76:173–186
Essa MM, Subash S, Akbar M, Al-Adawi S, Guillemin GJ (2015) Long-term dietary supplementation of pomegranates, figs and dates alleviate neuroinflammation in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 10:e0120964
Han Y, Xu J, Li Z, Yang Z (2013) Neuroprotective effect of leukemia inhibitory factor on antimycin A-induced oxidative injury in differentiated PC12 cells. J Mol Neurosci 50:577–585
Hofmann H-D, Kirsch M (2012) JAK2-STAT3 signaling: a novel function and a novel mechanism. JAKSTAT 1:191–193
Hoppenot D, Malakauskas K, Lavinskiene S, Sakalauskas R (2015) p-STAT6, PU.1, and NF-κB are involved in allergen-induced late-phase airway inflammation in asthma patients. BMC Pulm Med 15:122
Immune regulatory and neuroprotective properties of preimplantation factor: from newborn to adult 2015 1;156:10–25.
Lins C, Borojevic R (2001) Interleukin-5 receptor alpha chain expression and splicing during brain development in mice. Growth Factors 19:145–152
Lopez AF, Hercus TR, Ekert P, Littler DR, Guthridge M, Thomas D, Ramshaw HS, Stomski F, Perugini M, D’Andrea R, Grimbaldeston M, Parker MW (2010) Molecular basis of cytokine receptor activation. IUBMB Life 62:509–518
Mrak RE, Sheng JG, Griffin WS (1995) Glial cytokines in Alzheimer’s disease: review and pathogenic implications. Hum Pathol 26:816–823
Pardanani A, Gotlib JR, Jamieson C, Cortes JE, Talpaz M, Stone RM, Silverman MH, Gilliland G, Shorr J, Tefferi A (2011) Safety and efficacy of TG101348, a selective JAK2 inhibitor, in myelofibrosis. J Clin Oncol 29:789–796
Quelle FW, Sato N, Witthuhn BA, Inhorn RC, Eder M, Miyajima A, Griffin JD, Ihle JN (1994) JAK2 associates with the beta c chain of the receptor for granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and its activation requires the membrane-proximal region. Mol Cell Biol 14:4335–4341
Roberson ED, Scearce-Levie K, Palop JJ, Yan F, Cheng IH, Wu T, Gerstein H, Yu GQ, Mucke L (2007) Reducing endogenous tau ameliorates amyloid beta-induced deficits in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Science 316:750–754
Sheikh AM, Nagai A, Wakabayashi K, Narantuya D, Kobayashi S, Yamaguchi S, Kim SU (2011) Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation modulates neuroinflammation in focal cerebral ischemia: contribution of fractalkine and IL-5. Neurobiol Dis 41:717–724
Takashima A, Honda T, Yasutake K, Michel G, Murayama O, Murayama M, Ishiguro K, Yamaguchi H (1998) Activation of tau protein kinase I/glycogen synthase kinase-3beta by amyloid beta peptide (25-35) enhances phosphorylation of tau in hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Res 31:317–323
Verma A, Kambhampati S, Parmar S, Platanias LC (2003) Jak family of kinases in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 22:423–434
Winter PS, Sarosiek KA, Lin KH, Meggendorfer M, Schnittger S, Letai A, Wood KC (2014) RAS signaling promotes resistance to JAK inhibitors by suppressing BAD-mediated apoptosis. Sci Signal 7:ra122–ra122
Yankner BA, Duffy LK, Kirschner DA (1990) Neurotrophic and neurotoxic effects of amyloid beta protein: reversal by tachykinin neuropeptides. Science 250:279–282
Zambrano A, Otth C, Mujica L, Concha II, Maccioni RB (2007) Interleukin-3 prevents neuronal death induced by amyloid peptide. BMC Neurosci 8:82
Zambrano A, Otth C, Maccioni RB, Concha II (2010) IL-3 controls tau modifications and protects cortical neurons from neurodegeneration. Curr Alzheimer Res 7:615–624
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Yuanyuan Zhou and Chaoyan Li contributed equally and thus share the first authorship
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary data 1
(PPTX 750 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Li, C., Li, D. et al. IL-5 blocks apoptosis and tau hyperphosphorylation induced by Aβ25–35 peptide in PC12 cells. J Physiol Biochem 73, 259–266 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-017-0550-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-017-0550-8