Abstract
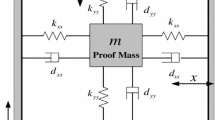
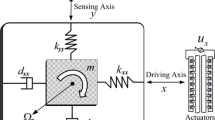
In this paper, a dynamic global proportional integral derivative (PID) sliding mode controller based on an adaptive radial basis function (RBF) neural estimator is developed to guarantee the stability and robustness in the presence of a lumped uncertainty for a micro electromechanical systems (MEMS) gyroscope. This approach gives a new dynamic global PID sliding mode manifold, which not only enables system trajectory to run on the global sliding mode surface at the start point more quickly and eliminates the reaching phase of the conventional sliding mode control, but also restrains the steady-state error and reduces the chattering via a dynamic PID sliding surface. A RBF neural network (NN) system is employed to estimate the lumped uncertainty and eliminate the chattering phenomenon at the same time. Additionally, adaptive laws and dynamic global PID sliding control gains that ensure the asymptotic stability of the close-loop system are proposed, together with the techniques for deciding which kind of basis function should be selected. Finally, simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of RBFNN dynamic global PID sliding mode control method, meanwhile some comparisons are made to verify the good properties of the suggested control approach.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batur C, Sreeramreddy T (2006) sliding mode control of a simulated MEMS gyroscope. ISA T 45(1):99–108
Sung W, Lee Y (2009) On the mode-matched control of MEMS vibratory gyroscope via phase-domain analysis and design. IEEE ASME T MECH 14(4):446–455
Fei J, Zhou J (2012) Robust adaptive control of MEMS triaxial gyroscope using fuzzy compensator. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 2(6):1599–1607
Chang H, Xue L, Jiang C et al (2012) Combining numerous uncorrelated MEMS gyroscopes for accuracy improvement based on an optimal kalman filter. IEEE T Instrum Meas 61(11):3084–3093
Fei J, Xin M (2013) Adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control of MEMS gyroscope sensor using fuzzy switching approach. In: 2013 Proceedings of SICE Annual Conference (SICE), pp 1479–1484
Liu L, Han Z, Li W (2009) Global sliding mode control and application in chaotic systems. Nonlinear Dynam 56(1–2):193–198
Efimov D, Fridman L (2011) Global sliding-mode observer with adjusted gains for locally lipschitz systems. Automatica 47(3):565–570
Men W, Guo C, Liu Y, Yang Y (2012) Global sliding mode based adaptive neural network path following control for underactuated surface vessels with uncertain dynamics. In: 2012 Third International Conference on Intelligent Control and Information Processing (ICICIP), pp 40–45
Liu J, Sun F (2006) Fuzzy global sliding mode control for a servo system with lugre friction model. In: The Sixth World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, pp 1933–1936
Chu Y, Fei J (2014) Global sliding mode control of MEMS gyroscope based on neural network. In: 2014 IEEE 13th International Workshop on Advanced Motion Control (AMC), pp 575–580
Li Y, Xu Q (2010) Adaptive sliding mode control with perturbation estimation and PID sliding surface for motion tracking of a piezo-driven micromanipulator. IEEE T Contr Syst T 18(4):798–810
Jafarov E, Parlakci M, Istefanopulos Y (2005) A new variable structure PID-controller design for robot manipulators. IEEE T Contr Syst T 13(1):122–130
Li Y, Wang Z, Zhu L (2010) Adaptive neural network PID sliding mode dynamic control of nonholonomic mobile robot. In: 2010 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation (ICIA), pp 753–757
Fayez F (2013) Adaptive dynamic sliding-mode control system using recurrent RBFN for high-performance induction motor servo drive. IEEE T Ind Inform 9(4):1922–1936
Yang J, Su J, Li S, Yu X (2014) High-order mismatched disturbance compensation for motion control systems via a continuous dynamic sliding-mode approach. IEEE T Ind Inform 10(1):604–614
Lin F, Chen S, Shyu K (2009) Robust dynamic sliding-mode control using adaptive RENN for magnetic levitation system. IEEE T Neural Netw 20(6):938–951
Iqbal M, Bhatti A, Khan Q (2009) Dynamic sliding modes control of uncertain nonlinear MIMO three tank system. In: IEEE 13th International Multitopic Conference (INMIC2009), pp 1–7
Wang X (2015) Uncertainty in learning from big data-editorial. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 28(5):2329–2330
Wang X, Ashfaq R, Fu A (2015) Fuzziness based sample categorization for classifier performance improvement. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 29(3):1185–1196
Lu S, Wang X, Zhang G, Zhou X (2015) Effective algorithms of the moore-penrose inverse matrices for extreme learning machine. Intell Data Analysis 19(4):743–760
He Y, Wang X, Huang J (2016) Fuzzy nonlinear regression analysis using a random weight network. Inf Sci. doi:10.1016/j.ins.01.037
Ashfaq R, Wang X, Huang J, Abbas H, He Y (2016) Fuzziness based semi-supervised learning approach for intrusion detection system (IDS). Inf Sci. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2016.04.019
Dai S, Wang C, Wang M (2014) Dynamic learning from adaptive neural network control of a class of nonaffine nonlinear systems. IEEE T Neur Net Lear 25(1):111–123
Tuan N, Su S, Nguyen H (2014) Neural network based diagonal decoupling control of powered wheelchair systems. IEEE T Neur Sys Rezh 22(2):371–378
Li X, Cheah C (2014) Adaptive neural network control of robot based on a unified objective bound. IEEE T Contr Syst T 22(3):1032–1043
Wai R, Huang Y, Yang Z, Shih C (2010) Adaptive fuzzy-neural-network velocity sensorless control for robot manipulator position tracking. IET Control Theory A 4(6):1079–1093
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers for their useful comments that improved the quality of the paper. This work is partially supported by National Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 61374100; Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province under Grant No. BK20131136. The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant No. 2014B04014
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, Y., Fang, Y. & Fei, J. Adaptive neural dynamic global PID sliding mode control for MEMS gyroscope. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 8, 1707–1718 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-016-0543-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-016-0543-x