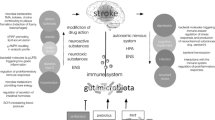
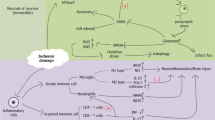
Abstract
Ischemic stroke, a disease with high mortality and disability rate worldwide, currently has no effective treatment. The systemic inflammation response to the ischemic stroke, followed by immunosuppression in focal neurologic deficits and other inflammatory damage, reduces the circulating immune cell counts and multiorgan infectious complications such as intestinal and gut dysfunction dysbiosis. Evidence showed that microbiota dysbiosis plays a role in neuroinflammation and peripheral immune response after stroke, changing the lymphocyte populations. Multiple immune cells, including lymphocytes, engage in complex and dynamic immune responses in all stages of stroke and may be a pivotal moderator in the bidirectional immunomodulation between ischemic stroke and gut microbiota. This review discusses the role of lymphocytes and other immune cells, the immunological processes in the bidirectional immunomodulation between gut microbiota and ischemic stroke, and its potential as a therapeutic strategy for ischemic stroke.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- 5-HT:
-
5-Hydroxytryptamine
- ABX:
-
Antibiotics
- ACTH:
-
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
- ANS:
-
Autonomic nervous system
- GBMA:
-
Gut-brain-microbiota axis
- CAN:
-
Central autonomic network
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CRH/CRF:
-
Corticotropin-releasing hormone/factor
- DA:
-
Dopamine
- DAMPs:
-
Damage-associated molecular patterns
- DCs:
-
Dendritic cells
- dMCAO:
-
Distal middle cerebral artery occlusion
- DNTs:
-
Double-negative T cells
- EAE:
-
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- ENS:
-
Enteric nervous system
- EVs:
-
Extracellular vesicles
- fMCAO:
-
Filamentous middle cerebral artery occlusion
- FMT:
-
Fecal microbiota transfer
- FOXP3:
-
Forkhead box P3
- GBMA:
-
Gut-brain-microbiome axis
- GF:
-
Germ-free
- HDAC:
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors
- HMGB1:
-
High-mobility group box 1 protein
- HPA:
-
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis
- HSP:
-
Heat shock protein
- IBD:
-
Inflammatory bowel disease
- IFN-γ:
-
Interferon-γ
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- IS:
-
Ischemic stroke
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- MCAO:
-
Middle cerebral artery occlusion
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- MS:
-
Maternal separation
- NE:
-
Norepinephrine
- NPY:
-
Neuropeptide Y
- pMCAO:
-
Permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion
- PP:
-
Peyer’s patches
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SCFAs:
-
Short-chain fatty acids
- SFB:
-
Segmented filamentous bacteria
- SIID:
-
Stroke-induced immunodepression
- SP:
-
Substance P
- SPF:
-
Specific pathogen-free
- TMAO:
-
Trimethylamine-N-oxide
- tMCAO:
-
Transient middle cerebral artery occlusion
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
- tPA:
-
Tissue plasminogen activator
- Treg:
-
Regulatory T cells
- VIP:
-
Vasoactive intestinal peptide
References
Katan M, Luft A. Global burden of stroke. Semin Neurol. 2018;38:208–11.
DeGregorio-Rocasolano N, Martí-Sistac O, Gasull T. Deciphering the iron side of stroke: neurodegeneration at the crossroads between iron dyshomeostasis, excitotoxicity, and ferroptosis. Front Neurosci. 2019;13:85.
Fukuta T, Asai T, Yanagida Y, Namba M, Koide H, Shimizu K, Oku N. Combination therapy with liposomal neuroprotectants and tissue plasminogen activator for treatment of ischemic stroke. Faseb j. 2017;31:1879–90.
Xing C, Arai K, Lo EH, Hommel M. Pathophysiologic cascades in ischemic stroke. Int J Stroke. 2012;7:378–85.
Chamorro Á, Lo EH, Renú A, van Leyen K, Lyden PD. The future of neuroprotection in stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2021;92:129–35.
Seifert HA, Pennypacker KR. Molecular and cellular immune responses to ischemic brain injury. Transl Stroke Res. 2014;5:543–53.
Stuckey SM, Ong LK, Collins-Praino LE, Turner RJ. Neuroinflammation as a key driver of secondary neurodegeneration following stroke? Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:13101.
Mao R, Zong N, Hu Y, Chen Y, Xu Y. Neuronal death mechanisms and therapeutic strategy in ischemic stroke. Neurosci Bull. 2022;38:1229–47.
Iadecola C, Buckwalter MS, Anrather J. Immune responses to stroke: mechanisms, modulation, and therapeutic potential. J Clin Investig. 2020;130:2777–88.
Gu L, Jian Z, Stary C, Xiong X. T cells and cerebral ischemic stroke. Neurochem Res. 2015;40:1786–91.
Gill D, Veltkamp R. Dynamics of T cell responses after stroke. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2016;26:26–32.
Petrovic-Djergovic D, Goonewardena SN, Pinsky DJ. Inflammatory disequilibrium in stroke. Circ Res. 2016;119:142–58.
Liesz A, Suri-Payer E, Veltkamp C, Doerr H, Sommer C, Rivest S, Giese T, Veltkamp R. Regulatory T cells are key cerebroprotective immunomodulators in acute experimental stroke. Nat Med. 2009;15:192–9.
Jiang C, Kong W, Wang Y, Ziai W, Yang Q, Zuo F, Li F, Wang Y, Xu H, Li Q, et al. Changes in the cellular immune system and circulating inflammatory markers of stroke patients. Oncotarget. 2017;8:3553–67.
Passarelli JP, Nimjee SM, Townsend KL. Stroke and neurogenesis: bridging clinical observations to new mechanistic insights from animal models. Transl Stroke Res. 2022.
Liesz A, Hagmann S, Zschoche C, Adamek J, Zhou W, Sun L, Hug A, Zorn M, Dalpke A, Nawroth P, Veltkamp R. The spectrum of systemic immune alterations after murine focal ischemia: immunodepression versus immunomodulation. Stroke. 2009;40:2849–58.
Haeusler KG, Schmidt WU, Föhring F, Meisel C, Helms T, Jungehulsing GJ, Nolte CH, Schmolke K, Wegner B, Meisel A, et al. Cellular immunodepression preceding infectious complications after acute ischemic stroke in humans. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2008;25:50–8.
Wu F, Liu Z, Zhou L, Ye D, Zhu Y, Huang K, Weng Y, Xiong X, Zhan R, Shen J. Systemic immune responses after ischemic stroke: from the center to the periphery. Front Immunol. 2022;13:911661.
Poisson SN, Johnston SC, Josephson SA. Urinary tract infections complicating stroke: mechanisms, consequences, and possible solutions. Stroke. 2010;41:e180-184.
Liu DD, Chu SF, Chen C, Yang PF, Chen NH, He X. Research progress in stroke-induced immunodepression syndrome (SIDS) and stroke-associated pneumonia (SAP). Neurochem Int. 2018;114:42–54.
Stanley D, Mason LJ, Mackin KE, Srikhanta YN, Lyras D, Prakash MD, Nurgali K, Venegas A, Hill MD, Moore RJ, Wong CH. Translocation and dissemination of commensal bacteria in post-stroke infection. Nat Med. 2016;22:1277–84.
Ghelani DP, Kim HA, Zhang SR, Drummond GR, Sobey CG, De Silva TM. Ischemic stroke and infection: a brief update on mechanisms and potential therapies. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;193:114768.
Al Omran Y, Aziz Q. The brain-gut axis in health and disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;817:135–53.
Margolis KG, Cryan JF, Mayer EA. The microbiota-gut-brain axis: from motility to mood. Gastroenterology. 2021;160:1486–501.
Zhao L, Xiong Q, Stary CM, Mahgoub OK, Ye Y, Gu L, Xiong X, Zhu S. Bidirectional gut-brain-microbiota axis as a potential link between inflammatory bowel disease and ischemic stroke. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15:339.
Collins SM, Surette M, Bercik P. The interplay between the intestinal microbiota and the brain. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012;10:735–42.
Chang Y, Woo HG, Jeong JH, Kim GH, Park KD, Song TJ. Microbiota dysbiosis and functional outcome in acute ischemic stroke patients. Sci Rep. 2021;11:10977.
Adnan S, Nelson JW, Ajami NJ, Venna VR, Petrosino JF, Bryan RM Jr, Durgan DJ. Alterations in the gut microbiota can elicit hypertension in rats. Physiol Genomics. 2017;49:96–104.
Yang T, Santisteban MM, Rodriguez V, Li E, Ahmari N, Carvajal JM, Zadeh M, Gong M, Qi Y, Zubcevic J, et al. Gut dysbiosis is linked to hypertension. Hypertension. 2015;65:1331–40.
Ganesh BP, Nelson JW, Eskew JR, Ganesan A, Ajami NJ, Petrosino JF, Bryan RM Jr, Durgan DJ. Prebiotics, probiotics, and acetate supplementation prevent hypertension in a model of obstructive sleep apnea. Hypertension. 2018;72:1141–50.
Liu Z, Dai X, Zhang H, Shi R, Hui Y, Jin X, Zhang W, Wang L, Wang Q, Wang D, et al. Gut microbiota mediates intermittent-fasting alleviation of diabetes-induced cognitive impairment. Nat Commun. 2020;11:855.
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini V, Mardis ER, Gordon JI. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature. 2006;444:1027–31.
Passos M, Moraes-Filho JP. Intestinal microbiota in digestive diseases. Arq Gastroenterol. 2017;54:255–62.
Nishida A, Inoue R, Inatomi O, Bamba S, Naito Y, Andoh A. Gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2018;11:1–10.
Gomaa EZ. Human gut microbiota/microbiome in health and diseases: a review. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2020;113:2019–40.
Guinane CM, Cotter PD. Role of the gut microbiota in health and chronic gastrointestinal disease: understanding a hidden metabolic organ. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2013;6:295–308.
Kalbermatter C, Fernandez Trigo N, Christensen S, Ganal-Vonarburg SC. Maternal microbiota, early life colonization and breast milk drive immune development in the newborn. Front Immunol. 2021;12.
Zhang C, Li L, Jin B, Xu X, Zuo X, Li Y, Li Z. The effects of delivery mode on the gut microbiota and health: state of art. Front Microbiol 2021;12.
Bokulich NA, Chung J, Battaglia T, Henderson N, Jay M, Li H, Lieber AD, Wu F, Perez-Perez GI, Chen Y, et al. Antibiotics, birth mode, and diet shape microbiome maturation during early life. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8:343ra382-343ra382.
Jost T, Lacroix C, Braegger CP, Rochat F, Chassard C. Vertical mother-neonate transfer of maternal gut bacteria via breastfeeding. Environ Microbiol. 2014;16:2891–904.
Yee AL, Das P, Salas Garcia MC, Buschmann MM, Gilbert JA: Chapter 2 - microbiome establishment and maturation: early life environmental factors. In The Developing Microbiome. Edited by Claud EC: Acade Press 2020;21–41
Ma Q, Xing C, Long W, Wang HY, Liu Q, Wang R-F. Impact of microbiota on central nervous system and neurological diseases: the gut-brain axis. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;16:53.
Qin J, Li R, Raes J, Arumugam M, Burgdorf KS, Manichanh C, Nielsen T, Pons N, Levenez F, Yamada T, et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature. 2010;464:59–65.
Jandhyala SM, Talukdar R, Subramanyam C, Vuyyuru H, Sasikala M, Nageshwar Reddy D. Role of the normal gut microbiota. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:8787–803.
Fan Y, Pedersen O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021;19:55–71.
Barrett KE, Wu GD. Influence of the microbiota on host physiology - moving beyond the gut. J Physiol. 2017;595:433–5.
Valdes AM, Walter J, Segal E, Spector TD. Role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. BMJ. 2018;361:k2179.
Chung H-J, Nguyen TTB, Kim H-J, Hong S-T. Gut microbiota as a missing link between nutrients and traits of human. Front Microbiol 2018;9.
Heiss CN, Olofsson LE. Gut microbiota-dependent modulation of energy metabolism. J Innate Immun. 2018;10:163–71.
Xiao H, Kang S. The role of the gut microbiome in energy balance with a focus on the gut-adipose tissue axis. Front Genet 2020;11.
Oliphant K, Allen-Vercoe E. Macronutrient metabolism by the human gut microbiome: major fermentation by-products and their impact on host health. Microbiome. 2019;7:91.
Takiishi T, Fenero CIM, Câmara NOS. Intestinal barrier and gut microbiota: shaping our immune responses throughout life. Tissue Barriers. 2017;5:e1373208.
Antonini M, Lo Conte M, Sorini C, Falcone M. How the interplay between the commensal microbiota, gut barrier integrity, and mucosal immunity regulates brain autoimmunity. Front Immunol. 2019;10.
De Vadder F, Grasset E, Mannerås Holm L, Karsenty G, Macpherson AJ, Olofsson LE, Bäckhed F. Gut microbiota regulates maturation of the adult enteric nervous system via enteric serotonin networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2018;115:6458–63.
Lu J, Lu L, Yu Y, Cluette-Brown J, Martin CR, Claud EC. Effects of intestinal microbiota on brain development in humanized gnotobiotic mice. Sci Rep. 2018;8:5443.
Bergot AS, Giri R, Thomas R. The microbiome and rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2019;33:101497.
Han H, Li Y, Fang J, Liu G, Yin J, Li T, Yin Y. Gut microbiota and type 1 diabetes. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19.
Singh R, Zogg H, Wei L, Bartlett A, Ghoshal UC, Rajender S, Ro S. Gut microbial dysbiosis in the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal dysmotility and metabolic disorders. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021;27:19–34.
Ahmed I, Roy BC, Khan SA, Septer S, Umar S. Microbiome, metabolome and inflammatory bowel disease. Microorganisms. 2016;4.
Lee YT, Mohd Ismail NI, Wei LK. Microbiome and ischemic stroke: a systematic review. PLoS One. 2021;16:e0245038.
Li H, Zhang X, Pan D, Liu Y, Yan X, Tang Y, Tao M, Gong L, Zhang T, Woods CR, et al. Dysbiosis characteristics of gut microbiota in cerebral infarction patients. Transl Neurosci. 2020;11:124–33.
Li N, Wang X, Sun C, Wu X, Lu M, Si Y, Ye X, Wang T, Yu X, Zhao X, et al. Change of intestinal microbiota in cerebral ischemic stroke patients. BMC Microbiol. 2019;19:191–191.
Huang L, Wang T, Wu Q, Dong X, Shen F, Liu D, Qin X, Yan L, Wan Q. Analysis of microbiota in elderly patients with acute cerebral infarction. PeerJ. 2019;7:e6928.
Haak BW, Westendorp WF, van Engelen TSR, Brands X, Brouwer MC, Vermeij JD, Hugenholtz F, Verhoeven A, Derks RJ, Giera M, et al. Disruptions of anaerobic gut bacteria are associated with stroke and post-stroke infection: a prospective case-control study. Transl Stroke Res. 2021;12:581–92.
Yin J, Liao SX, He Y, Wang S, Xia GH, Liu FT, Zhu JJ, You C, Chen Q, Zhou L, et al. Dysbiosis of gut microbiota with reduced trimethylamine-N-oxide level in patients with large-artery atherosclerotic stroke or transient ischemic attack. J Am Heart Assoc 2015;4.
Mariat D, Firmesse O, Levenez F, Guimarăes V, Sokol H, Doré J, Corthier G, Furet JP. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio of the human microbiota changes with age. BMC Microbiol. 2009;9:123.
Spychala MS, Venna VR, Jandzinski M, Doran SJ, Durgan DJ, Ganesh BP, Ajami NJ, Putluri N, Graf J, Bryan RM, McCullough LD. Age-related changes in the gut microbiota influence systemic inflammation and stroke outcome. Ann Neurol. 2018;84:23–36.
Zhou P, Zhang XS, Xu ZB, Gao SX, Zheng QW, Xu MZ, Shen L, Yu F, Guan JC. Staphylococcal enterotoxin B administration in pregnant rats alters the splenic lymphocyte response in adult offspring rats. BMC Microbiol. 2017;17:1.
Everard A, Cani PD. Diabetes, obesity and gut microbiota. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2013;27:73–83.
Chen Y, Liang J, Ouyang F, Chen X, Lu T, Jiang Z, Li J, Li Y, Zeng J. Persistence of gut microbiota dysbiosis and chronic systemic inflammation after cerebral infarction in cynomolgus monkeys. Front Neurol. 2019;10:661–661.
Singh V, Roth S, Llovera G, Sadler R, Garzetti D, Stecher B, Dichgans M, Liesz A. Microbiota dysbiosis controls the neuroinflammatory response after stroke. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci. 2016;36:7428–40.
Sherman MP, Zaghouani H, Niklas V. Gut microbiota, the immune system, and diet influence the neonatal gut–brain axis. Pediatr Res. 2015;77:127–35.
Powley TL, Jaffey DM, McAdams J, Baronowsky EA, Black D, Chesney L, Evans C, Phillips RJ. Vagal innervation of the stomach reassessed: brain-gut connectome uses smart terminals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019;1454:14–30.
Wang FB, Powley TL. Vagal innervation of intestines: afferent pathways mapped with new en bloc horseradish peroxidase adaptation. Cell Tissue Res. 2007;329:221–30.
Yu CD, Xu QJ, Chang RB. Vagal sensory neurons and gut-brain signaling. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2020;62:133–40.
Travagli RA, Hermann GE, Browning KN, Rogers RC. Brainstem circuits regulating gastric function. Annu Rev Physiol. 2006;68:279–305.
Yuan PQ, Taché Y. Abdominal surgery induced gastric ileus and activation of M1-like macrophages in the gastric myenteric plexus: prevention by central vagal activation in rats. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017;313:G320-g329.
Yip JLK, Balasuriya GK, Spencer SJ, Hill-Yardin EL. The role of intestinal macrophages in gastrointestinal homeostasis: heterogeneity and implications in disease. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;12:1701–18.
Cai PY, Bodhit A, Derequito R, Ansari S, Abukhalil F, Thenkabail S, Ganji S, Saravanapavan P, Shekar CC, Bidari S, et al. Vagus nerve stimulation in ischemic stroke: old wine in a new bottle. Front Neurol. 5:107.
Mravec B. The role of the vagus nerve in stroke. Auton Neurosci Basic Clin. 158:8–12
Bercik P, Park AJ, Sinclair D, Khoshdel A, Lu J, Huang X, Deng Y, Blennerhassett PA, Fahnestock M, Moine D, et al. The anxiolytic effect of Bifidobacterium longum NCC3001 involves vagal pathways for gut-brain communication. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2011;23:1132–9.
Benakis C, Liesz A. The gut-brain axis in ischemic stroke: its relevance in pathology and as a therapeutic target. Neurol Res Pract. 2022;4:57.
Keck ME. Corticotropin-releasing factor, vasopressin and receptor systems in depression and anxiety. Amino Acids. 2006;31:241–50.
Jiang Y, Peng T, Gaur U, Silva M, Little P, Chen Z, Qiu W, Zhang Y, Zheng W. Role of corticotropin releasing factor in the neuroimmune mechanisms of depression: examination of current pharmaceutical and herbal therapies. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:290.
Slominski AT, Zmijewski MA, Zbytek B, Tobin DJ, Theoharides TC, Rivier J. Key role of CRF in the skin stress response system. Endocr Rev. 2013;34:827–84.
Koch F, Thom U, Albrecht E, Weikard R, Nolte W, Kuhla B, Kuehn C. Heat stress directly impairs gut integrity and recruits distinct immune cell populations into the bovine intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116:10333–8.
Grosheva I, Zheng D, Levy M, Polansky O, Lichtenstein A, Golani O, Dori-Bachash M, Moresi C, Shapiro H, Del Mare-Roumani S, et al. High-throughput screen identifies host and microbiota regulators of intestinal barrier function. Gastroenterology. 2020;159:1807–23.
Shaler CR, Parco AA, Elhenawy W, Dourka J, Jury J, Verdu EF, Coombes BK. Psychological stress impairs IL22-driven protective gut mucosal immunity against colonising pathobionts. Nat Commun. 2021;12:6664.
Pohjasvaara T, Vataja R, Leppävuori A, Kaste M, Erkinjuntti T. Depression is an independent predictor of poor long-term functional outcome post-stroke. Eur J Neurol. 2001;8:315–9.
Caso JR, Hurtado O, Pereira MP, García-Bueno B, Menchén L, Alou L, Gómez-Lus ML, Moro MA, Lizasoain I, Leza JC. Colonic bacterial translocation as a possible factor in stress-worsening experimental stroke outcome. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009;296:R979–85.
Allen AP, Dinan TG, Clarke G, Cryan JF. A psychology of the human brain-gut-microbiome axis. Soc Personal Psychol Compass. 2017;11:e12309.
Yamashiro K, Kurita N, Urabe T, Hattori N. Role of the gut microbiota in stroke pathogenesis and potential therapeutic implications. Ann Nutr Metab. 2021;77(Suppl 2):36–44.
Cani PD, Bibiloni R, Knauf C, Waget A, Neyrinck AM, Delzenne NM, Burcelin R. Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Diabetes. 2008;57:1470–81.
Santisteban MM, Qi Y, Zubcevic J, Kim S, Yang T, Shenoy V, Cole-Jeffrey CT, Lobaton GO, Stewart DC, Rubiano A, et al. Hypertension-linked pathophysiological alterations in the gut. Circ Res. 2017;120:312–23.
Pendlebury ST, Rothwell PM. Prevalence, incidence, and factors associated with pre-stroke and post-stroke dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8:1006–18.
Zhou L, Wang T, Yu Y, Li M, Sun X, Song W, Wang Y, Zhang C, Fu F. The etiology of poststroke-depression: a hypothesis involving HPA axis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;151:113146.
Du Y, Liang H, Zhang L, Fu F. Administration of Huperzine A exerts antidepressant-like activity in a rat model of post-stroke depression. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2017;158:32–8.
Luo F, Fang C. Association between gut microbiota and post-stroke depression in Chinese population: a meta-analysis. Heliyon. 2022;8:e12605.
Louveau A, Smirnov I, Keyes TJ, Eccles JD, Rouhani SJ, Peske JD, Derecki NC, Castle D, Mandell JW, Lee KS, et al. Structural and functional features of central nervous system lymphatic vessels. Nature. 2015;523:337–41.
Negi N, Das BK. CNS: Not an immunoprivilaged site anymore but a virtual secondary lymphoid organ. Int Rev Immunol. 2018;37:57–68.
Papadopoulos Z, Herz J, Kipnis J. Meningeal lymphatics: from anatomy to central nervous system immune surveillance. J Immunol. 2020;204:286–93.
Iadecola C, Buckwalter MS, Anrather J. Immune responses to stroke: mechanisms, modulation, and therapeutic po tential. J Clin Investig. 130:2777–2788
Arya AK, Hu B. Brain-gut axis after stroke. Brain circulation. 2018;4:165–73.
Strandwitz P. Neurotransmitter modulation by the gut microbiota. Brain Res. 2018;1693:128–33.
Huang F, Wu X. Brain neurotransmitter modulation by gut microbiota in anxiety and depression. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9.
Aresti Sanz J, El Aidy S. Microbiota and gut neuropeptides: a dual action of antimicrobial activity and neuroimmune response. Psychopharmacology. 2019;236:1597–609.
Holzer P, Farzi A. Neuropeptides and the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;817:195–219.
Rooks MG, Garrett WS. Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016;16:341–52.
Man AWC, Zhou Y, Xia N, Li H. Involvement of gut microbiota, microbial metabolites and interaction with polyphenol in host immunometabolism. Nutrients. 2020;12:3054.
Silva YP, Bernardi A, Frozza RL. The role of short-chain fatty acids from gut microbiota in gut-brain communication. Front Endocrinol 2020;11.
Tan C, Wu Q, Wang H, Gao X, Xu R, Cui Z, Zhu J, Zeng X, Zhou H, He Y, Yin J. Dysbiosis of gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids in acute ischemic stroke and the subsequent risk for poor functional outcomes. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2021;45:518–29.
Chen R, Xu Y, Wu P, Zhou H, Lasanajak Y, Fang Y, Tang L, Ye L, Li X, Cai Z, Zhao J. Transplantation of fecal microbiota rich in short chain fatty acids and butyric acid treat cerebral ischemic stroke by regulating gut microbiota. Pharmacol Res. 2019;148:104403.
Vogt NM, Romano KA, Darst BF, Engelman CD, Johnson SC, Carlsson CM, Asthana S, Blennow K, Zetterberg H, Bendlin BB, Rey FE. The gut microbiota-derived metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide is elevated in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2018;10:124.
Nam HS. Gut microbiota and ischemic stroke: the role of trimethylamine N-oxide. J Stroke. 2019;21:151–9.
Skye SM, Zhu W, Romano KA, Guo C-J, Wang Z, Jia X, Kirsop J, Haag B, Lang JM, DiDonato JA, et al. Microbial transplantation with human gut commensals containing CutC Is sufficient to transmit enhanced platelet reactivity and thrombosis po tential. Circulation Res 123:1164–1176.
Planas AM. Role of immune cells migrating to the ischemic brain. Stroke. 2018;49:2261–7.
Zhang D, Ren J, Luo Y, He Q, Zhao R, Chang J, Yang Y, Guo Z-N. T cell response in ischemic stroke: from mechanisms to translational insights. Front Immunol. 2021;12:707972–707972.
Jayaraj RL, Azimullah S, Beiram R, Jalal FY, Rosenberg GA. Neuroinflammation: friend and foe for ischemic stroke. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;16:142–142.
Kolaczkowska E, Kubes P. Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13:159–75.
Zhang Q, Liao Y, Liu Z, Dai Y, Li Y, Li Y, Tang Y. Interleukin-17 and ischaemic stroke. Immunology. 2021;162:179–93.
Perez-de-Puig I, Miró-Mur F, Ferrer-Ferrer M, Gelpi E, Pedragosa J, Justicia C, Urra X, Chamorro A, Planas AM. Neutrophil recruitment to the brain in mouse and human ischemic stroke. Acta Neuropathol. 2015;129:239–57.
Nian K, Harding IC, Herman IM, Ebong EE. Blood-brain barrier damage in ischemic stroke and its regulation by endothelial mechanotransduction. Front Physiol. 2020;11.
Benakis C, Brea D, Caballero S, Faraco G, Moore J, Murphy M, Sita G, Racchumi G, Ling L, Pamer EG, et al. Commensal microbiota affects ischemic stroke outcome by regulating intestinal γδ T cells. Nat Med. 2016;22:516–23.
Wang J, Zhong Y, Zhu H, Mahgoub OK, Jian Z, Gu L, Xiong X. Different gender-derived gut microbiota influence stroke outcomes by mitigating inflammation. J Neuroinflammation. 2022;19:245.
Pantoni L. Cerebral small vessel disease: from pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9:689–701.
Thion MS, Ginhoux F, Garel S. Microglia and early brain development: an intimate journey. Science. 2018;362:185–9.
Abdel-Haq R, Schlachetzki JCM, Glass CK, Mazmanian SK. Microbiome-microglia connections via the gut-brain axis. J Exp Med. 2019;216:41–59.
Erny D, Hrabě de Angelis AL, Jaitin D, Wieghofer P, Staszewski O, David E, Keren-Shaul H, Mahlakoiv T, Jakobshagen K, Buch T, et al. Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat Neurosci. 2015;18:965–77.
Singh V, Sadler R, Heindl S, Llovera G, Roth S, Benakis C, Liesz A. The gut microbiome primes a cerebroprotective immune response after stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2018;38:1293–8.
Han H, Safe S, Jayaraman A, Chapkin RS. Diet-host-microbiota interactions shape aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand production to modulate intestinal homeostasis. Annu Rev Nutr. 2021;41:455–78.
Mezö C, Mossad O, Erny D, Blank T. The gut-brain axis: microglia in the spotlight. Neuroforum. 2019;25:205–12.
Fan X, Wang S, Hu S, Yang B, Zhang H. Host-microbiota interactions: the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the acute and chronic phases of cerebral ischemia. Front Immunol. 2022;13.
Sadler R, Cramer JV, Heindl S, Kostidis S, Betz D, Zuurbier KR, Northoff BH, Heijink M, Goldberg MP, Plautz EJ, et al. Short-chain fatty acids improve poststroke recovery via immunological mechanisms. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci. 2020;40:1162–73.
Ludewig P, Gallizioli M, Urra X, Behr S, Brait VH, Gelderblom M, Magnus T, Planas AM. Dendritic cells in brain diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) - Mol Basis Dis. 2016;1862:352–67.
Hatterer E, Davoust N, Didier-Bazes M, Vuaillat C, Malcus C, Belin M-F, Nataf S. How to drain without lymphatics? Dendritic cells migrate from the cerebrospinal fluid to the B-cell follicles of cervical lymph nodes. Blood. 2006;107:806–12.
Scott CL, Aumeunier AM, Mowat AM. Intestinal CD103+ dendritic cells: master regulators of tolerance? Trends Immunol. 2011;32:412–9.
Honarpisheh P, d'Aigle J, Mobley AS, Won WW, Bautista Garrido JJ, Blixt F, Miranda-Sohrabji DF, Blasco Conesa MP, Chauhan A, Lee J, et al. Abstract TP108: dendritic cells mediate the detrimental effects of age -related gut dysbiosis after stroke. Stroke. 51.
Jung Y-J, Chung W-S. Phagocytic roles of glial cells in healthy and diseased brains. Biomol Ther. 2018;26:350–7.
Giovannoni F, Quintana FJ. The role of astrocytes in CNS inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2020;41:805–19.
Rothhammer V, Quintana FJ. Control of autoimmune CNS inflammation by astrocytes. Semin Immunopathol. 2015;37:625–38.
Rothhammer V, Mascanfroni ID, Bunse L, Takenaka MC, Kenison JE, Mayo L, Chao C-C, Patel B, Yan R, Blain M, et al. Type I interferons and microbial metabolites of tryptophan modulate astrocyte activity and central nervous system inflammation via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Nat Med. 2016;22:586–97.
Chen W-C, Chang L-H, Huang S-S, Huang Y-J, Chih C-L, Kuo H-C, Lee Y-H, Lee IH. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor modulates stroke-induced astrogliosis and neurogenesis in the adult mouse brain. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;16:187.
Chen Y-L, Bai L, Dilimulati D, Shao S, Qiu C, Liu T, Xu S, Bai X-B, Du L-J, Zhou L-J, et al. Periodontitis salivary microbiota aggravates ischemic stroke through I L-17A. Front Neurosci. 16:876582.
Rayasam A, Hsu M, Kijak JA, Kissel L, Hernandez G, Sandor M, Fabry Z. Immune responses in stroke: how the immune system contributes to damage and healing after stroke and how this knowledge could be translated to better cures? Immunology. 2018;154:363–76.
Yilmaz G, Arumugam TV, Stokes KY, Granger DN. Role of T lymphocytes and interferon-gamma in ischemic stroke. Circulation. 2006;113:2105–12.
Hurn PD, Subramanian S, Parker SM, Afentoulis ME, Kaler LJ, Vandenbark AA, Offner H. T- and B-cell-deficient mice with experimental stroke have reduced lesion size and inflammation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007;27:1798–805.
Jung C, Hugot JP, Barreau F. Peyer’s patches: the immune sensors of the intestine. Int J Inflam. 2010;2010:823710.
Roy-O’Reilly M, McCullough LD. Age and sex are critical factors in ischemic stroke pathology. Endocrinology. 2018;159:3120–31.
Banerjee A, McCullough LD. Sex-specific immune responses in stroke. Stroke. 53:1449–1459.
Li M, Li Z, Yao Y, Jin WN, Wood K, Liu Q, Shi FD, Hao J. Astrocyte-derived interleukin-15 exacerbates ischemic brain injury via propagation of cellular immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114:E396-e405.
Mracsko E, Liesz A, Stojanovic A, Lou WP, Osswald M, Zhou W, Karcher S, Winkler F, Martin-Villalba A, Cerwenka A, Veltkamp R. Antigen dependently activated cluster of differentiation 8-positive T cells cause perforin-mediated neurotoxicity in experimental stroke. J Neurosci. 2014;34:16784–95.
Ahnstedt H, Patrizz A, Chauhan A, Roy-O’Reilly M, Furr JW, Spychala MS, D’Aigle J, Blixt FW, Zhu L, Bravo Alegria J, McCullough LD. Sex differences in T cell immune responses, gut permeability and outcome after ischemic stroke in aged mice. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;87:556–67.
Ritzel RM, Crapser J, Patel AR, Verma R, Grenier JM, Chauhan A, Jellison ER, McCullough LD. Age-associated resident memory CD8 T cells in the central nervous system are primed to potentiate inflammation after ischemic brain injury. J Immunol. 2016;196:3318–30.
Xu C, Zhu H, Qiu P. Aging progression of human gut microbiota. BMC Microbiol. 2019;19:236.
Sun H, Gu M, Li Z, Chen X, Zhou J. Gut microbiota dysbiosis in acute ischemic stroke associated with 3-month unfavorable outcome. Front Neurol. 2021;12:799222.
Golomb MR, Fullerton HJ, Nowak-Gottl U, Deveber G. Male predominance in childhood ischemic stroke: findings from the international pediatric stroke study. Stroke. 2009;40:52–7.
Bots SH, Peters SAE, Woodward M. Sex differences in coronary heart disease and stroke mortality: a global assessment of the effect of ageing between 1980 and 2010. BMJ Glob Health. 2017;2:e000298.
Wexler HM. Bacteroides: the good, the bad, and the nitty-gritty. Clin Microbiol Rev. 20:593–621.
Sadler R, Singh V, Benakis C, Garzetti D, Brea D, Stecher B, Anrather J, Liesz A. Microbiota differences between commercial breeders impacts the post-stroke immune response. Brain Behav Immun. 2017;66:23–30.
Shichita T, Sugiyama Y, Ooboshi H, Sugimori H, Nakagawa R, Takada I, Iwaki T, Okada Y, Iida M, Cua DJ, et al. Pivotal role of cerebral interleukin-17-producing gammadeltaT cells in the delayed phase of ischemic brain injury. Nat Med. 2009;15:946–50.
Zheng Y, Song T, Zhang L, Wei N. Immunomodulatory effects of T helper 17 cells and regulatory T cells on cerebral ischemia. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2018;32:29–35.
Jian Z, Liu R, Zhu X, Smerin D, Zhong Y, Gu L, Fang W, Xiong X. The involvement and therapy target of immune cells after ischemic stroke. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2167–2167.
Wang H, Wang Z, Wu Q, Yuan Y, Cao W, Zhang X. Regulatory T cells in ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021;27:643–51.
Li P, Wang L, Zhou Y, Gan Y, Zhu W, Xia Y, Jiang X, Watkins S, Vazquez A, Thomson AW, et al. C-C chemokine receptor type 5 (CCR5)-mediated docking of transferred tregs protects against early blood-brain barrier disruption after stroke. J Am Heart Assoc 2017;6.
Shi L, Sun Z, Su W, Xu F, Xie D, Zhang Q, Dai X, Iyer K, Hitchens TK, Foley LM, et al. Treg cell-derived osteopontin promotes microglia-mediated white matter repair after ischemic stroke. Immunity. 2021;54:1527-1542.e1528.
Atarashi K, Tanoue T, Ando M, Kamada N, Nagano Y, Narushima S, Suda W, Imaoka A, Setoyama H, Nagamori T, et al. Th17 cell induction by adhesion of microbes to intestinal epithelial cells. Cell. 2015;163:367–80.
Na SY, Mracsko E, Liesz A, Hünig T, Veltkamp R. Amplification of regulatory T cells using a CD28 superagonist reduces brain damage after ischemic stroke in mice. Stroke. 2015;46:212–20.
Jacobse J, Li J, Rings EHHM, Samsom JN, Goettel JA. Intestinal regulatory T cells as specialized tissue-restricted immune cells in intestinal immune homeostasis and disease. Front Immunol. 2021;12.
Smith PM, Howitt MR, Panikov N, Michaud M, Gallini CA, Bohlooly YM, Glickman JN, Garrett WS. The microbial metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, regulate colonic Treg cell homeostasis. Science. 2013;341:569–73.
Lee J, d’Aigle J, Atadja L, Quaicoe V, Honarpisheh P, Ganesh BP, Hassan A, Graf J, Petrosino J, Putluri N, et al. Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids promote poststroke recovery in aged mice. Circ Res. 2020;127:453–65.
Farache J, Koren I, Milo I, Gurevich I, Kim KW, Zigmond E, Furtado GC, Lira SA, Shakhar G. Luminal bacteria recruit CD103+ dendritic cells into the intestinal epithelium to sample bacterial antigens for presentation. Immunity. 2013;38:581–95.
Steimle A, Frick JS. Molecular mechanisms of induction of tolerant and tolerogenic intestinal dendritic cells in mice. J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:1958650.
Hu Y, Zheng Y, Wu Y, Ni B, Shi S. Imbalance between IL-17A-producing cells and regulatory T cells during ischemic stroke. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:813045–813045.
Meng H, Zhao H, Cao X, Hao J, Zhang H, Liu Y, Zhu MS, Fan L, Weng L, Qian L, et al. Double-negative T cells remarkably promote neuroinflammation after ischemic stroke. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116:5558–63.
Benakis C, Poon C, Lane D, Brea D, Sita G, Moore J, Murphy M, Racchumi G, Iadecola C, Anrather J. Distinct commensal bacterial signature in the gut is associated with acute and long-term protection from ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2020;51:1844–54.
Doyle KP, Buckwalter MS. Does B lymphocyte-mediated autoimmunity contribute to post-stroke dementia? Brain Behav Immun. 2017;64:1–8.
Liu Z-J, Chen C, Li F-W, Shen J-M, Yang Y-Y, Leak RK, Ji X-M, Du H-S, Hu X-M. Splenic responses in ischemic stroke: new insights into stroke pathology. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2015;21:320–6.
Kim M, Qie Y, Park J, Kim CH. Gut microbial metabolites fuel host antibody responses. Cell Host Microbe. 2016;20:202–14.
Kim CH. B cell-helping functions of gut microbial metabolites. Microb Cell. 2016;3:529–31.
Liu Y, Luo S, Kou L, Tang C, Huang R, Pei Z, Li Z. Ischemic stroke damages the intestinal mucosa and induces alteration of the intestinal lymphocytes and CCL19 mRNA in rats. Neurosci Lett. 2017;658:165–70.
Camara-Lemarroy CR, Ibarra-Yruegas BE, Gongora-Rivera F. Gastrointestinal complications after ischemic stroke. J Neurol Sci. 2014;346:20–5.
Houlden A, Goldrick M, Brough D, Vizi ES, Lénárt N, Martinecz B, Roberts IS, Denes A. Brain injury induces specific changes in the caecal microbiota of mice via altered autonomic activity and mucoprotein production. Brain Behav Immun. 57:10–20.
Liu Q, Johnson EM, Lam RK, Wang Q, Bo Ye H, Wilson EN, Minhas PS, Liu L, Swarovski MS, Tran S, et al. Peripheral TREM1 responses to brain and intestinal immunogens amplify stroke severity. Nat Immunol. 20:1023–1034.
Tuz AA, Hasenberg A, Hermann DM, Gunzer M, Singh V. Ischemic stroke and concomitant gastrointestinal complications- a fata l combination for patient recovery. Front Immunol. 13:1037330.
Park SY, Lee SP, Kim WJ. Fecal calprotectin is increased in stroke. J Clin Med. 2021;11.
Sherwin E, Dinan TG, Cryan JF. Recent developments in understanding the role of the gut microbiota in brain health and disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018;1420:5–25.
Corrêa-Oliveira R, Fachi JL, Vieira A, Sato FT, Vinolo MAR. Regulation of immune cell function by short-chain fatty acids. Clin Transl Immunol. 5:e73.
Vartanian KB, Stevens SL, Marsh BJ, Williams-Karnesky R, Lessov NS, Stenzel-Poore MP. LPS preconditioning redirects TLR signaling following stroke: TRIF-IRF3 plays a seminal role in mediating tolerance to ischemic injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2011;8:140.
Xia G-H, You C, Gao X-X, Zeng X-L, Zhu J-J, Xu K-Y, Tan C-H, Xu R-T, Wu Q-H, Zhou H-W, et al. Stroke dysbiosis index (SDI) in gut microbiome are associated with brain injury and prognosis of stroke. Front Neurol. 2019;10:397–397.
Crapser J, Ritzel R, Verma R, Venna VR, Liu F, Chauhan A, Koellhoffer E, Patel A, Ricker A, Maas K, et al. Ischemic stroke induces gut permeability and enhances bacterial translocation leading to sepsis in aged mice. Aging. 2016;8:1049–63.
Wen SW, Shim R, Ho L, Wanrooy BJ, Srikhanta YN, Prame Kumar K, Nicholls AJ, Shen SJ, Sepehrizadeh T, de Veer M, et al. Advanced age promotes colonic dysfunction and gut-derived lung infection after stroke. Aging Cell. 2019;18:e12980–e12980.
Vermeij JD, Westendorp WF, Dippel DW, van de Beek D, Nederkoorn PJ. Antibiotic therapy for preventing infections in people with acute stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;1:Cd008530.
Smith CJ, Heal C, Vail A, Jeans AR, Westendorp WF, Nederkoorn PJ, van de Beek D, Kalra L, Montaner J, Woodhead M, Meisel A. Antibiotic class and outcome in post-stroke infections: an individual participant data pooled analysis of VISTA-Acute. Front Neurol. 2019;10:504.
Powell N, Walker MM, Talley NJ. The mucosal immune system: master regulator of bidirectional gut–brain communications. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;14:143–59.
Li M, van Esch B, Wagenaar GTM, Garssen J, Folkerts G, Henricks PAJ. Pro- and anti-inflammatory effects of short chain fatty acids on immune and endothelial cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018;831:52–9.
Chen R, Ovbiagele B, Feng W. Diabetes and stroke: epidemiology, pathophysiology, pharmaceuticals and outcomes. Am J Med Sci. 2016;351:380–6.
Shukla V, Shakya AK, Perez-Pinzon MA, Dave KR. Cerebral ischemic damage in diabetes: an inflammatory perspective. J Neuroinflammation. 2017;14:21.
Li WZ, Stirling K, Yang JJ, Zhang L. Gut microbiota and diabetes: from correlation to causality and mechanism. World J Diabetes. 2020;11:293–308.
Wang J, Zhang H, He J, Xiong X. The role of the gut microbiota in the development of ischemic stroke. Front Immunol. 2022;13:845243.
Chen X, Wu Q, Gao X, Wang H, Zhu J, Xia G, He Y, Song W, Xu K. Gut microbial dysbiosis associated with type 2 diabetes aggravates acute ischemic stroke. mSystems. 2021;6:e0130421.
Wang H, Song W, Wu Q, Gao X, Li J, Tan C, Zhou H, Zhu J, He Y, Yin J. Fecal transplantation from db/db mice treated with sodium butyrate attenuates ischemic stroke injury. Microbiol Spectr. 2021;9:e0004221.
Kurita N, Yamashiro K, Kuroki T, Tanaka R, Urabe T, Ueno Y, Miyamoto N, Takanashi M, Shimura H, Inaba T, et al. Metabolic endotoxemia promotes neuroinflammation after focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2020;40:2505–20.
Hackam DG, Spence JD. Combining multiple approaches for the secondary prevention of vascular events after stroke. Stroke. 38:1881–1885.
Neuman H, Forsythe P, Uzan A, Avni O, Koren O. Antibiotics in early life: dysbiosis and the damage done. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2018;42:489–99.
Rizzatti G, Ianiro G, Gasbarrini A. Antibiotic and modulation of microbiota: a new paradigm? J Clin Gastroenterol 2018, 52 Suppl 1, Proceedings from the 9th Probiotics, Prebiotics and New Foods, Nutraceuticals and Botanicals for Nutrition & Human and Microbiota Health Meeting, held in Rome, Italy from September 10 to 12, 2017;S74-s77.
Gupta S, Allen-Vercoe E, Petrof EO. Fecal microbiota transplantation: in perspective. Ther Adv Gastroenterol. 2016;9:229–39.
Smits LP, Bouter KE, de Vos WM, Borody TJ, Nieuwdorp M. Therapeutic potential of fecal microbiota transplantation. Gastroenterology. 2013;145:946–53.
Louie TJ, Miller MA, Mullane KM, Weiss K, Lentnek A, Golan Y, Gorbach S, Sears P, Shue YK. Fidaxomicin versus vancomycin for Clostridium difficile infection. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:422–31.
Lopez J, Grinspan A. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;12:374–9.
Glassner KL, Abraham BP, Quigley EMM. The microbiome and inflammatory bowel disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;145:16–27.
Tan P, Li X, Shen J, Feng Q. Fecal microbiota transplantation for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: an update. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11.
Natividad JM, Pinto-Sanchez MI, Galipeau HJ, Jury J, Jordana M, Reinisch W, Collins SM, Bercik P, Surette MG, Allen-Vercoe E, Verdu EF. Ecobiotherapy rich in firmicutes decreases susceptibility to colitis in a humanized gnotobiotic mouse model. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015;21:1883–93.
Burrello C, Giuffrè MR, Macandog AD, Diaz-Basabe A, Cribiù FM, Lopez G, Borgo F, Nezi L, Caprioli F, Vecchi M, Facciotti F. Fecal microbiota transplantation controls murine chronic intestinal inflammation by modulating immune cell functions and gut microbiota composition. Cells. 2019;8.
Kristensen NB, Bryrup T, Allin KH, Nielsen T, Hansen TH, Pedersen O. Alterations in fecal microbiota composition by probiotic supplementati on in healthy adults: a systematic review of randomized controlled tri als. Genome med. 8:52.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82171336 and 81870939), Open Project of Sichuan Provincial Key Laboratory for Clinical Immunology Translational Medicine (LCMYZHYX-KFKT202203) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2042022kf1216) to Xiaoxing Xiong.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.P. wrote the initial draft. L.G. contributed to reviewing the literature. Z.H. prepared the figures and table. Z.J. and L.W. collected the literature. X.X. designed the manuscript and prepared the final version. The authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pu, B., Zhu, H., Wei, L. et al. The Involvement of Immune Cells Between Ischemic Stroke and Gut Microbiota. Transl. Stroke Res. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-023-01151-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-023-01151-7