Abstract
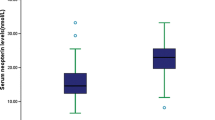
Ninjurin-1 is a novel adhesion molecule which is involved in many inflammatory diseases. Functional blockage of Ninjurin-1 has exerted an atheroprotective effect. The aim of the study is to explore the association between serum Ninjurin-1 and the risk of large artery atherosclerotic acute ischemic stroke. From August 2020 through December 2021, patients with large artery atherosclerotic acute ischemic stroke (LAA-AIS) admitted to the First Hospital Affiliated to Soochow University, and age- and sex-matched controls free of ischemic stroke were recruited. Serum Ninj1 was measured with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Multivariable logistic regression models were used to calculate the odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals of LAA-AIS associated with serum Ninj1 levels, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were performed to assess the improvement value of Ninj1 for the prediction of LAA-AIS after adding Ninj1 to established risk factors. Of the 110 patients and 110 age- and sex-matched controls free of ischemic stroke enrolled, serum Ninj1 levels in LAA-AIS patients were significantly higher than that in control group (142.70 ng/ml [IQR: 110.41–163.44] vs 101.62 ng/ml [IQR: 86.63–120.86], p < 0.001). In multivariable analysis, Ninj1 levels were expressed as continuous variable and ordinal variable (tertiles), and it turned out that Ninj1 levels were positively associated with increased risk of LAA-AIS, especially in tertile3 compared with tertile1 (adjusted OR = 12.567, 95%CI: 5.148–30.678, p < 0.001), and the adjusted odds OR per 10 ng/ml increment was 1.541, 95%CI: 1.348–1.763, p < 0.001. Furthermore, adding Ninj1 to a multivariate logistic model including conventional risk factors associated LAA-AIS improved the area under ROC curves from 0.787 to 0.874. Elevated circulating levels of Ninj1 were associated with increased risk of LAA-AIS, indicating that serum Ninj1 may act as a predictor independent of established conventional risk factors.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AIS:
-
Acute ischemic stroke
- LAA-AIS:
-
Large artery atherosclerotic acute ischemic stroke
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic curve
- ASCVD:
-
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
- CAD:
-
Coronary artery disease
- TOAST criteria:
-
Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment criteria
- AUC:
-
Area under receiver operating characteristic curve
References
Björkegren JLM, Lusis AJ. Atherosclerosis: Recent developments. Cell. 2022;185(10):1630–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2022.04.004.
Roth GA, Mensah GA, Johnson CO, Addolorato G, Ammirati E, Baddour LM, Barengo NC, Beaton AZ, Benjamin EJ, Benziger CP, Bonny A, Brauer M, Brodmann M, Cahill TJ, Carapetis J, Catapano AL, Chugh SS, Cooper LT, Coresh J, Criqui M, DeCleene N, Eagle KA, Emmons-Bell S, Feigin VL, Fernández-Solà J, Fowkes G, Gakidou E, Grundy SM, He FJ, Howard G, Hu F, Inker L, Karthikeyan G, Kassebaum N, Koroshetz W, Lavie C, Lloyd-Jones D, Lu HS, Mirijello A, Temesgen AM, Mokdad A, Moran AE, Muntner P, Narula J, Neal B, Ntsekhe M, Moraes de Oliveira G, Otto C, Owolabi M, Pratt M, Rajagopalan S, Reitsma M, Ribeiro ALP, Rigotti N, Rodgers A, Sable C, Shakil S, Sliwa-Hahnle K, Stark B, Sundström J, Timpel P, Tleyjeh IM, Valgimigli M, Vos T, Whelton PK, Yacoub M, Zuhlke L, Murray C, Fuster V, GBD-NHLBI-JACC Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases Writing Group. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update From the GBD 2019 Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76(25):2982–3021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010.
Fiolet ATL, Opstal TSJ, Mosterd A, Eikelboom JW, Jolly SS, Keech AC, Kelly P, Tong DC, Layland J, Nidorf SM, Thompson PL, Budgeon C, Tijssen JGP, Cornel JH. Efficacy and safety of low-dose colchicine in patients with coronary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(28):2765–75. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehab115.
Araki T, Milbrandt J. Ninjurin, a novel adhesion molecule, is induced by nerve injury and promotes axonal growth. Neuron. 1996;17(2):353–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80166-x.
Ahn BJ, Le H, Shin MW, Bae SJ, Lee EJ, Wee HJ, Cha JH, Lee HJ, Lee HS, Kim JH, Kim CY, Seo JH, Lo EH, Jeon S, Lee MN, Oh GT, Yin GN, Ryu JK, Suh JK, Kim KW. Ninjurin1 deficiency attenuates susceptibility of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(6):3328–38. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.498212.
Ifergan I, Kebir H, Terouz S, Alvarez JI, Lécuyer MA, Gendron S, Bourbonnière L, Dunay IR, Bouthillier A, Moumdjian R, Fontana A, Haqqani A, Klopstein A, Prinz M, López-Vales R, Birchler T, Prat A. Role of Ninjurin-1 in the migration of myeloid cells to central nervous system inflammatory lesions. Ann Neurol. 2011;70(5):751–63. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22519.
Jennewein C, Sowa R, Faber AC, Dildey M, von Knethen A, Meybohm P, Scheller B, Dröse S, Zacharowski K. Contribution of Ninjurin1 to Toll-like receptor 4 signaling and systemic inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015;53(5):656–63. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2014-0354OC.
Jang YS, Kang JH, Woo JK, Kim HM, Hwang JI, Lee SJ, Lee HY, Oh SH. Ninjurin1 suppresses metastatic property of lung cancer cells through inhibition of interleukin 6 signaling pathway. Int J Cancer. 2016;139(2):383–95. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.30021.
Choi S, Woo JK, Jang YS, Kang JH, Hwang JI, Seong JK, Yoon YS, Oh SH. Ninjurin1 plays a crucial role in pulmonary fibrosis by promoting interaction between macrophages and alveolar epithelial cells. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):17542. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35997-x.
Kang JH, Woo JK, Jang YS, Oh SH. Radiation Potentiates Monocyte Infiltration into Tumors by Ninjurin1 Expression in Endothelial Cells. Cells. 2020;9(5):1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051086.
Kayagaki N, Kornfeld OS, Lee BL, Stowe IB, O’Rourke K, Li Q, Sandoval W, Yan D, Kang J, Xu M, Zhang J, Lee WP, McKenzie BS, Ulas G, Payandeh J, Roose-Girma M, Modrusan Z, Reja R, Sagolla M, Webster JD, Cho V, Andrews TD, Morris LX, Miosge LA, Goodnow CC, Bertram EM, Dixit VM. NINJ1 mediates plasma membrane rupture during lytic cell death. Nature. 2021;591(7848):131–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03218-7.
Wang Y, Shao F. NINJ1, rupturing swollen membranes for cataclysmic cell lysis. Mol Cell. 2021;81(7):1370–1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2021.03.005.
Jeon S, Kim TK, Jeong SJ, Jung IH, Kim N, Lee MN, Sonn SK, Seo S, Jin J, Kweon HY, Kim S, Shim D, Park YM, Lee SH, Kim KW, Cybulsky MI, Shim H, Roh TY, Park WY, Lee HO, Choi JH, Park SH, Oh GT. Anti-inflammatory actions of soluble Ninjurin-1 ameliorate atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2020;142(18):1736–51. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.046907.
Tan X, Zhang Y, Shao H. Healthy China 2030, a breakthrough for improving health. Glob Health Promot. 2019;26(4):96–9. https://doi.org/10.1177/1757975917743533.
Gimbrone MA Jr, García-Cardeña G. Endothelial cell dysfunction and the pathobiology of atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 2016;118(4):620–36. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306301.
Ridker PM. From CANTOS to CIRT to COLCOT to Clinic: will all atherosclerosis patients soon be treated with combination lipid-lowering and inflammation-inhibiting agents? Circulation. 2020;141(10):787–9. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.045256.
Ridker PM, Everett BM, Thuren T, MacFadyen JG, Chang WH, Ballantyne C, Fonseca F, Nicolau J, Koenig W, Anker SD, Kastelein JJP, Cornel JH, Pais P, Pella D, Genest J, Cifkova R, Lorenzatti A, Forster T, Kobalava Z, Vida-Simiti L, Flather M, Shimokawa H, Ogawa H, Dellborg M, Rossi PRF, Troquay RPT, Libby P, Glynn RJ, CANTOS Trial Group. Antiinflammatory therapy with canakinumab for atherosclerotic disease. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(12):1119–31. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1707914.
Deftereos SG, Beerkens FJ, Shah B, Giannopoulos G, Vrachatis DA, Giotaki SG, Siasos G, Nicolas J, Arnott C, Patel S, Parsons M, Tardif JC, Kovacic JC, Dangas GD. Colchicine in cardiovascular disease: In-Depth Review. Circulation. 2022;145(1):61–78. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.056171.
Araki T, Zimonjic DB, Popescu NC, Milbrandt J. Mechanism of homophilic binding mediated by ninjurin, a novel widely expressed adhesion molecule. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(34):21373–80. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.34.21373.
Lee HJ, Ahn BJ, Shin MW, Jeong JW, Kim JH, Kim KW. Ninjurin1 mediates macrophage-induced programmed cell death during early ocular development. Cell Death Differ. 2009;16(10):1395–407. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2009.78.
Choi H, Bae SJ, Choi G, Lee H, Son T, Kim JG, An S, Lee HS, Seo JH, Kwon HB, Jeon S, Oh GT, Surh YJ, Kim KW. Ninjurin1 deficiency aggravates colitis development by promoting M1 macrophage polarization and inducing microbial imbalance. FASEB J. 2020;34(6):8702–20. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201902753R.
Woo JK, Jang YS, Kang JH, Hwang JI, Seong JK, Lee SJ, Jeon S, Oh GT, Lee HY, Oh SH. Ninjurin1 inhibits colitis-mediated colon cancer development and growth by suppression of macrophage infiltration through repression of FAK signaling. Oncotarget. 2016;7(20):29592–604. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.9020.
Jeon S, Oh GT. Response by Jeon and Oh to Letter Regarding Article. Anti-inflammatory actions of soluble Ninjurin-1 ameliorate atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2021;143(19):e921–2. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.053671.
Lee HK, Kim ID, Lee H, Luo L, Kim SW, Lee JK. Neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of a dodecamer peptide harboring Ninjurin 1 cell adhesion motif in the postischemic brain. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(7):6094–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0810-1.
Wang X, Qin J, Zhang X, Peng Z, Ye K, Wu X, Yang X, Shi H, Zhao Z, Guo X, Liu X, Yin M, Lu X. Functional blocking of Ninjurin1 as a strategy for protecting endothelial cells in diabetes mellitus. Clin Sci (Lond). 2018;132(2):213–29. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20171273.
Funding
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (82071300), Suzhou Science and Technology Development Plan (SYSD2020073), The Stroke Team of Professor Fang Qi from the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University (SZYQTD202106); a follow-up study of cognitive impairment combined with depression in stroke patients (SYSD2020073); Suzhou Industrial Park Jinji Lake Health Talents (202110).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QF conceived and designed the research. ND analyzed the data and drafted the manuscript. ND, XW, TH, XS, XG, HW, LY, and HZ collected the data and performed the research. All authors reviewed and edited the manuscript and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics Approval
The protocol of the study conforms to the ethical guidelines mentioned in the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Hospital Affiliated to Soochow University (No. 2021–07-01). Written informed consent for participation was not required for this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, N., Wu, X., Hong, T. et al. Elevated Serum Ninjurin-1 Is Associated with a High Risk of Large Artery Atherosclerotic Acute Ischemic Stroke. Transl. Stroke Res. 14, 465–471 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-022-01077-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-022-01077-6