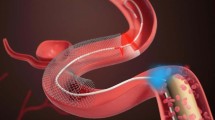
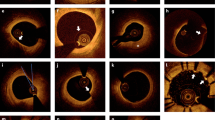
Abstract
Optical coherence tomography (OCT), based on the backscattering or reflection of near-infrared light, enables an ultra-high resolution of up to 10 μm. The successful application of OCT in coronary artery diseases has sparked increasing interest in its implementation in cerebrovascular diseases. OCT has shown promising potential in the atherosclerotic plaque structure characterization, plaque rupture risk stratification, pre-stenting and post-stenting evaluation, and long-term follow-up in extracranial and intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis (ICAS). In hemorrhagic cerebrovascular diseases, OCT plays an important role in the structure evaluation, rupture risk stratification, and healing and occlusion evaluation following initial treatment in intracranial aneurysms (IAs). In this study, we summarized the applications of OCT in the diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of cerebrovascular diseases, especially in ICAS and IAs. The current limitations and future directions of OCT in the endovascular treatment of cerebrovascular diseases were also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data included in this work are available publicly.
References
Huang D, Swanson EA, Lin CP, Schuman JS, Stinson WG, Chang W, et al. Optical coherence tomography. Science. 1991;254(5035):1178–81.
Swanson EA, Izatt JA, Hee MR, Huang D, Lin CP, Schuman JS, et al. In vivo retinal imaging by optical coherence tomography. Opt Lett. 1993;18(21):1864–6.
Mintz GS, Guagliumi G. Intravascular imaging in coronary artery disease. Lancet. 2017;390(10096):793–809.
Rico-Jimenez JJ, Campos-Delgado DU, Buja LM, Vela D, Jo JA. Intravascular optical coherence tomography method for automated detection of macrophage infiltration within atherosclerotic coronary plaques. Atherosclerosis. 2019;290:94–102.
Boi A, Jamthikar AD, Saba L, Gupta D, Sharma A, Loi B, et al. A survey on coronary atherosclerotic plaque tissue characterization in intravascular optical coherence tomography. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2018;20(7):33.
Feske SK. Ischemic Stroke. Am J Med. 2021;134(12):1457–64.
Flaherty ML, Kissela B, Khoury JC, Alwell K, Moomaw CJ, Woo D, et al. Carotid artery stenosis as a cause of stroke. Neuroepidemiology. 2013;40(1):36–41.
Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139(10):e56–528.
Brezinski ME, Tearney GJ, Bouma BE, Izatt JA, Hee MR, Swanson EA, et al. Optical coherence tomography for optical biopsy Properties and demonstration of vascular pathology. Circulation. 1996;93(6):1206–13.
Yabushita H, Bouma BE, Houser SL, Aretz HT, Jang IK, Schlendorf KH, et al. Characterization of human atherosclerosis by optical coherence tomography. Circulation. 2002;106(13):1640–5.
Prabhudesai V, Phelan C, Yang Y, Wang RK, Cowling MG. The potential role of optical coherence tomography in the evaluation of vulnerable carotid atheromatous plaques: a pilot study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2006;29(6):1039–45.
Ghosn MG, Mashiatulla M, Syed SH, Mohamed MA, Larin KV, Morrisett JD. Permeation of human plasma lipoproteins in human carotid endarterectomy tissues: measurement by optical coherence tomography. J Lipid Res. 2011;52(7):1429–34.
Zimarino M, Prati F, Stabile E, Pizzicannella J, Fouad T, Filippini A, et al. Optical coherence tomography accurately identifies intermediate atherosclerotic lesions–an in vivo evaluation in the rabbit carotid artery. Atherosclerosis. 2007;193(1):94–101.
Yoshimura S, Kawasaki M, Hattori A, Nishigaki K, Minatoguchi S, Iwama T. Demonstration of intraluminal thrombus in the carotid artery by optical coherence tomography: technical case report. Neurosurgery. 2010;67(3 Suppl Operative):onsE305; discussion onsE
Kawasaki M, Yoshimura S, Yamada K, Hattori A, Ishihara Y, Nishigaki K, et al. Carotid artery OCT in cerebral infarction. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013;6(11):1215–6.
Saba L, Saam T, Jäger HR, Yuan C, Hatsukami TS, Saloner D, et al. Imaging biomarkers of vulnerable carotid plaques for stroke risk prediction and their potential clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(6):559–72.
Li ZY, Howarth SP, Tang T, Gillard JH. How critical is fibrous cap thickness to carotid plaque stability? A flow-plaque interaction model Stroke. 2006;37(5):1195–9.
Cilingiroglu M, Hakeem A, Feldman M, Wholey M. Optical coherence tomography imaging in asymptomatic patients with carotid artery stenosis. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2013;14(1):53–6.
Shindo S, Fujii K, Shirakawa M, Uchida K, Enomoto Y, Iwama T, et al. Morphologic features of carotid plaque rupture assessed by optical coherence tomography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015;36(11):2140–6.
Shi X, Han Y, Li M, Yin Q, Liu R, Wang F, et al. Superficial calcification with rotund shape is associated with carotid plaque rupture: an optical coherence tomography study. Front Neurol. 2020;11:563334.
Jones MR, Attizzani GF, Given CA 2nd, Brooks WH, Ganocy SJ, Ramsey CN, et al. Intravascular frequency-domain optical coherence tomography assessment of carotid artery disease in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2014;7(6):674–84.
Yang Q, Guo H, Shi X, Xu X, Zha M, Cai H, et al. Identification of symptomatic carotid artery plaque: a three-item scale combined angiography with optical coherence tomography. Front Neurosci. 2021;15:792437.
Bosiers M, de Donato G, Deloose K, Verbist J, Peeters P, Castriota F, et al. Does free cell area influence the outcome in carotid artery stenting? Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2007;33(2):135–41 (discussion 42-3).
Harada K, Oshikata S, Kajihara M. Optical coherence tomography evaluation of tissue prolapse after carotid artery stenting using closed cell design stents for unstable plaque. J Neurointerv Surg. 2018;10(3):229–34.
Harada K, Kajihara M, Sankoda Y, Taniguchi S. Efficacy of post-dilatation during carotid artery stenting for unstable plaque using closed-cell design stent evaluated by optical coherence tomography. J Neuroradiol. 2019;46(6):384–9.
de Donato G, Setacci F, Sirignano P, Galzerano G, Cappelli A, Setacci C. Optical coherence tomography after carotid stenting: rate of stent malapposition, plaque prolapse and fibrous cap rupture according to stent design. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2013;45(6):579–87.
Umemoto T, de Donato G, Pacchioni A, Reimers B, Ferrante G, Isobe M, et al. Optical coherence tomography assessment of newgeneration mesh-covered stents after carotid stenting. EuroIntervention. 2017;13(11):1347–54.
Prati F, Zimarino M, Stabile E, Pizzicannella G, Fouad T, Rabozzi R, et al. Does optical coherence tomography identify arterial healing after stenting? An in vivo comparison with histology, in a rabbit carotid model. Heart. 2008;94(2):217–21.
Yoshimura S, Kawasaki M, Yamada K, Hattori A, Nishigaki K, Minatoguchi S, et al. OCT of human carotid arterial plaques. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011;4(4):432–6.
Pasarikovski CR, Ramjist J, da Costa L, Black SE, Cardinell J, Yang VX. Optical coherence tomography as an adjunct during carotid artery stenting for carotid atherosclerotic disease. Clin Neuroradiol. 2020;30(3):503–9.
Liu R, Jiang Y, Xiong Y, Li M, Ma M, Zhu W, et al. An optical coherence tomography assessment of stent strut apposition based on the presence of lipid-rich plaque in the carotid artery. J Endovasc Ther. 2015;22(6):942–9.
Farb A, Burke AP, Kolodgie FD, Virmani R. Pathological mechanisms of fatal late coronary stent thrombosis in humans. Circulation. 2003;108(14):1701–6.
Yan L, Dmytriw AA, Yang B, Jiao L. Optical coherence tomography of plaque erosion and thrombus in severe vertebral artery stenosis. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021;11(4):638.
Liu R, Yin Q, Li M, Ye R, Zhu W, Liu X. Diagnosis and treatment evaluation of in-stent restenosis of carotid artery stenting using optical coherence tomography. Neurology. 2019;92(2):99–100.
Blackham KA, Kim BS, Jung RS, Badve C, Manjila S, Sila CA, et al. In vivo characterization of carotid neointimal hyperplasia by use of optical coherence tomography: before and after cutting balloon angioplasty. J Neuroimaging. 2015;25(6):1044–6.
Matsumoto H, Yako R, Masuo O, Hirayama K, Uematsu Y, Nakao N. A case of in-stent neoatherosclerosis 10 years after carotid artery stent implantation: observation with optical coherence tomography and plaque histological findings. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2014;54(2):139–44.
Shah PK. Mechanisms of plaque vulnerability and rupture. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;41(4 Suppl S):15s-22s
de Havenon A, Mossa-Basha M, Shah L, Kim SE, Park M, Parker D, et al. High-resolution vessel wall MRI for the evaluation of intracranial atherosclerotic disease. Neuroradiology. 2017;59(12):1193–202.
Jang IK, Bouma BE, Kang DH, Park SJ, Park SW, Seung KB, et al. Visualization of coronary atherosclerotic plaques in patients using optical coherence tomography: comparison with intravascular ultrasound. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;39(4):604–9.
Mathews MS, Su J, Heidari E, Levy EI, Linskey ME, Chen Z. Neuroendovascular optical coherence tomography imaging and histological analysis. Neurosurgery. 2011;69(2):430–9.
Feng Y, Wu T, Wang T, Li Y, Li M, Li L, et al. Correlation between intracranial vertebral artery stenosis diameter measured by digital subtraction angiography and cross-sectional area measured by optical coherence tomography. J Neurointerv Surg. 2021;13(11):1002–6.
Benes V, Netuka D, Mandys V, Vrabec M, Mohapl M, Benes V Jr, et al. Comparison between degree of carotid stenosis observed at angiography and in histological examination. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2004;146(7):671–7.
Given CA 2nd, Ramsey CN 3rd, Attizzani GF, Jones MR, Brooks WH, Bezerra HG, et al. Optical coherence tomography of the intracranial vasculature and Wingspan stent in a patient. J Neurointerv Surg. 2015;7(6):e22.
Ughi GJ, Marosfoi MG, King RM, Caroff J, Peterson LM, Duncan BH, et al. A neurovascular high-frequency optical coherence tomography system enables in situ cerebrovascular volumetric microscopy. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):3851.
Xu X, Li M, Liu R, Yin Q, Shi X, Wang F, et al. Optical coherence tomography evaluation of vertebrobasilar artery stenosis: case series and literature review. J Neurointerv Surg. 2020;12(8):809–13.
Li L, Dmytriw AA, Krings T, Feng Y, Jiao L. Visualization of the human intracranial vasa vasorum in vivo using optical coherence tomography. JAMA Neurol. 2020;77(7):903–5.
Yang B, Feng Y, Ma Y, Wang Y, Chen J, Li L, et al. Frequency-domain optical coherence tomography for intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis: feasibility, safety, and preliminary experience. Front Neurol. 2021;12:678443.
Xu R, Yang B, Li L, Wang T, Lu X, Luo J, et al. Macrocalcification of intracranial vertebral artery may be related to in-stent restenosis: lessons learned from optical coherence tomography. J Neurointerv Surg. 2022;14(5):neurintsurg-2021-017913.
Feigin VL, Lawes CM, Bennett DA, Barker-Collo SL, Parag V. Worldwide stroke incidence and early case fatality reported in 56 population-based studies: a systematic review. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8(4):355–69.
Bamford J, Dennis M, Sandercock P, Burn J, Warlow C. The frequency, causes and timing of death within 30 days of a first stroke: the Oxfordshire Community Stroke Project. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1990;53(10):824–9.
Goulart AC, Bensenor IM, Fernandes TG, Alencar AP, Fedeli LM, Lotufo PA. Early and one-year stroke case fatality in Sao Paulo, Brazil: applying the World Health Organization’s stroke STEPS. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012;21(8):832–8.
Lawton MT, Vates GE. Subarachnoid hemorrhage. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(3):257–66.
Vlak MH, Algra A, Brandenburg R, Rinkel GJ. Prevalence of unruptured intracranial aneurysms, with emphasis on sex, age, comorbidity, country, and time period: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10(7):626–36.
Greving JP, Wermer MJ, Brown RD Jr, Morita A, Juvela S, Yonekura M, et al. Development of the PHASES score for prediction of risk of rupture of intracranial aneurysms: a pooled analysis of six prospective cohort studies. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13(1):59–66.
Nieuwkamp DJ, Setz LE, Algra A, Linn FH, de Rooij NK, Rinkel GJ. Changes in case fatality of aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage over time, according to age, sex, and region: a meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8(7):635–42.
Hoffmann T, Glaßer S, Boese A, Brandstädter K, Kalinski T, Beuing O, et al. Experimental investigation of intravascular OCT for imaging of intracranial aneurysms. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2016;11(2):231–41.
Liu Y, Zheng Y, An Q, Song Y, Leng B. Optical coherence tomography for intracranial aneurysms: a new method for assessing the aneurysm structure. World Neurosurg. 2019;123:e194–201.
Frösen J, Piippo A, Paetau A, Kangasniemi M, Niemelä M, Hernesniemi J, et al. Remodeling of saccular cerebral artery aneurysm wall is associated with rupture: histological analysis of 24 unruptured and 42 ruptured cases. Stroke. 2004;35(10):2287–93.
Kataoka K, Taneda M, Asai T, Kinoshita A, Ito M, Kuroda R. Structural fragility and inflammatory response of ruptured cerebral aneurysms. A comparative study between ruptured and unruptured cerebral aneurysms. Stroke. 1999;30(7):1396–401.
Thorell WE, Chow MM, Prayson RA, Shure MA, Jeon SW, Huang D, et al. Optical coherence tomography: a new method to assess aneurysm healing. J Neurosurg. 2005;102(2):348–54.
Su J, Mathews MS, Nwagwu CI, Edris A, Nguyen BV, Heidari M, et al. Imaging of treated brain aneurysms in vivo using optical coherence tomorgraphy. Proc SPIE. 2008;6847(8). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.766657.
King RM, Marosfoi M, Caroff J, Ughi GJ, Groth DM, Gounis MJ, et al. High frequency optical coherence tomography assessment of homogenous neck coverage by intrasaccular devices predicts successful aneurysm occlusion. J Neurointerv Surg. 2019;11(11):1150–4.
Vardar Z, King RM, Kraitem A, Langan ET, Peterson LM, Duncan BH, et al. High-resolution image-guided WEB aneurysm embolization by high-frequency optical coherence tomography. J Neurointerv Surg. 2021;13(7):669–73.
Tearney GJ, Regar E, Akasaka T, Adriaenssens T, Barlis P, Bezerra HG, et al. Consensus standards for acquisition, measurement, and reporting of intravascular optical coherence tomography studies: a report from the International Working Group for Intravascular Optical Coherence Tomography Standardization and Validation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;59(12):1058–72.
van der Marel K, Gounis MJ, Weaver JP, de Korte AM, King RM, Arends JM, et al. Grading of Regional Apposition after Flow-Diverter Treatment (GRAFT): a comparative evaluation of VasoCT and intravascular OCT. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016;8(8):847–52.
Matsuda Y, Chung J, Lopes DK. Analysis of neointima development in flow diverters using optical coherence tomography imaging. J Neurointerv Surg. 2018;10(2):162–7.
King RM, Brooks OW, Langan ET, Caroff J, Clarençon F, Tamura T, et al. Communicating malapposition of flow diverters assessed with optical coherence tomography correlates with delayed aneurysm occlusion. J Neurointerv Surg. 2018;10(7):693–7.
Guerrero BP, Pacheco CD, Saied A, Joshi K, Rodríguez C, Martínez-Galdámez M, et al. First human evaluation of endothelial healing after a pipeline flex embolization device with shield technology implanted in posterior circulation using optical coherence tomography. Neurointervention. 2018;13(2):129–32.
Martínez-Galdámez M, Escartín J, Pabón B, Diaz C, Martín-Reyes R, Hermosín A, et al. Optical coherence tomography: translation from 3D-printed vascular models of the anterior cerebral circulation to the first human images of implanted surface modified flow diverters. Interv Neuroradiol. 2019;25(2):150–6.
Pasarikovski CR, da Costa L, Pereira VM, Ramjist J, Dobashi Y, Yang VXD. Optical coherence tomography-guided flow diversion for aneurysmal treatment. Neurol Clin Pract. 2020;10(4):e30–2.
Li L, Yongjie M, Dmytriw AA, Jian R, Hongqi Z. Evaluation of vessel wall apposition for stent-assisted coiling in treatment of vertebral artery aneurysms using optical coherence tomography. Clin Neuroradiol. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-021-01070-w.
Monteiro A, Lopes DK, Aghaebrahim A, Hanel R. Optical coherence tomography for elucidation of flow-diversion phenomena: the concept of endothelized mural thrombus behind reversible in-stent stenosis in flow-diverters. Interv Neuroradiol. 2021;27(6):774–80.
Fries F, Maßmann A, Tomori T, Yilmaz U, Kettner M, Simgen A, et al. Accuracy of optical coherence tomography imaging in assessing aneurysmal remnants after flow diversion. J Neurointerv Surg. 2020;12(12):1242–6.
Jones MR, Attizzani GF, Given CA 2nd, Brooks WH, Costa MA, Bezerra HG. Intravascular frequency-domain optical coherence tomography assessment of atherosclerosis and stent-vessel interactions in human carotid arteries. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012;33(8):1494–501.
Pasarikovski CR, Ramjist J, da Costa L, Black SE, Yang V. Optical coherence tomography imaging after endovascular thrombectomy for basilar artery occlusion: report of 3 cases. J Neurosurg. 2019;133(4):1141–6.
Griessenauer CJ, Gupta R, Shi S, Alturki A, Motiei-Langroudi R, Adeeb N, et al. Collar sign in incompletely occluded aneurysms after pipeline embolization: evaluation with angiography and optical coherence tomography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017;38(2):323–6.
Given CA 2nd, Attizzani GF, Jones MR, Ramsey CN 3rd, Brooks WH, Costa MA, et al. Frequency-domain optical coherence tomography assessment of human carotid atherosclerosis using saline flush for blood clearance without balloon occlusion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013;34(7):1414–8.
Yoshimura S, Kawasaki M, Yamada K, Enomoto Y, Egashira Y, Hattori A, et al. Visualization of internal carotid artery atherosclerotic plaques in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients: a comparison of optical coherence tomography and intravascular ultrasound. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012;33(2):308–13.
Secco GG, Cremonesi A, Amor M, Pistis G, Reimers B, Castriota F. Optical coherence tomography during carotid artery stenting: a new niche application? Int J Cardiol. 2015;187:372–3.
de Donato G, Setacci C. New frontiers in the feasibility of optical coherence tomography in carotid arteries. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013;34(7):1419–20.
Bezerra HG, Tahara S, Parikh SA, Costa MA. “Old” problems revisited; imaging the coronary in high resolution. EuroIntervention. 2009;5(5):523–5.
He C, Li Z, Wang J, Huang Y, Yin Y, Li Z. Atherosclerotic plaque tissue characterization: an OCT-based machine learning algorithm with ex vivo validation. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:749.
Gessert N, Lutz M, Heyder M, Latus S, Leistner DM, Abdelwahed YS, et al. Automatic plaque detection in IVOCT pullbacks using convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2019;38(2):426–34.
Abdolmanafi A, Duong L, Dahdah N, Adib IR, Cheriet F. Characterization of coronary artery pathological formations from OCT imaging using deep learning. Biomed Opt Express. 2018;9(10):4936–60.
Abdolmanafi A, Duong L, Dahdah N, Cheriet F. Deep feature learning for automatic tissue classification of coronary artery using optical coherence tomography. Biomed Opt Express. 2017;8(2):1203–20.
Funding
This work was supported by the Beijing Scientific and Technologic Project (Z201100005520019) and Xuanwu Hospital Science Program for Fostering Young Scholars (QNPY2020010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, R., Zhao, Q., Wang, T. et al. Optical Coherence Tomography in Cerebrovascular Disease: Open up New Horizons. Transl. Stroke Res. 14, 137–145 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-022-01023-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-022-01023-6