Abstract
Objectives
Previous studies have shown that negative perfectionism is a critical predictor of suicidal ideation. However, few studies have explored the mechanisms underlying the effects of negative perfectionism on suicidal ideation. Therefore, the current study aims to explore the longitudinal relationship between negative perfectionism and suicidal ideation among Chinese adolescents, the mediating roles of intolerance of uncertainty and anxiety symptoms, and the moderating role of trait mindfulness.
Method
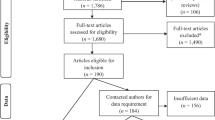
A total of 1665 Chinese middle school students (45% males; Mage = 15.84 years, SD = 1.56) completed questionnaires. The investigation was conducted twice, with an interval of 6 months.
Results
Negative perfectionism was positively correlated with suicidal ideation, intolerance of uncertainty, and anxiety symptoms. After controlling for gender and baseline suicidal ideation, negative perfectionism exacerbated suicidal ideation through increasing intolerance of uncertainty and anxiety symptoms. Additionally, trait mindfulness buffered the association between anxiety symptoms and suicidal ideation, as well as the association between intolerance of uncertainty and anxiety symptoms.
Conclusions
These results demonstrated the longitudinal relationship among negative perfectionism, intolerance of uncertainty, anxiety symptoms, and suicidal ideation and expand our understanding of the development of suicidal ideation. Moreover, the protective role of trait mindfulness implies that promoting trait mindfulness may be useful for interventions and preventions of suicidal ideation.
Preregistration
This study is not preregistered.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdollahi, A., & Carlbring, P. (2017). Coping style as a moderator of perfectionism and suicidal ideation among undergraduate students. Journal of Rational-Emotive & Cognitive-Behavior Therapy, 35(3), 223–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10942-016-0252-0
Afshar, H., Roohafza, H., Sadeghi, M., Saadaty, A., Salehi, M., Motamedi, M., Matinpour, M., Isfahani, H. N., & Asadollahi, G. (2011). Positive and negative perfectionism and their relationship with anxiety and depression in Iranian school students. Journal of Research in Medical Science, 16(1), 79–86.
Aldahadha, B. (2018). The psychometric properties of perfectionism scale and its relation to depression and anxiety. Cogent Psychology, 5(1), 1524324. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311908.2018.1524324
Allan, N. P., Volarov, M., Koscinski, B., Pizzonia, K. L., Potter, K., Accorso, C., Saulnier, K. G., Ashrafioun, L., Stecker, T., Suhr, J., & Allan, D. M. (2021). Lonely, anxious, and uncertain: Critical risk factors for suicidal desire during the COVID-19 pandemic. Psychiatry Research, 304, 114144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2021.114144
Baer, R. A., Smith, G. T., Hopkins, J., Krietemeyer, J., & Toney, L. (2006). Using self-report assessment methods to explore facets of mindfulness. Assessment, 13(1), 27–45. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073191105283504
Baker, A., Simon, N., Keshaviah, A., Farabaugh, A., Deckersbach, T., Worthington, J. J., Hoge, E., Fava, M., & Pollack, M. P. (2019). Anxiety Symptoms Questionnaire (ASQ): Development and validation. General Psychiatry, 32(6), e100144. https://doi.org/10.1136/gpsych-2019-100144
Baumeister, R. F. (1990). Suicide as escape from self. Psychological Review, 97, 90–113. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.97.1.90
Beck, A. T., Brown, G. K., & Steer, R. A. (1997). Psychometric characteristics of the scale for suicide ideation with psychiatric outpatients. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 35(11), 1039–1046. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-7967(97)00073
Beevers, C. G., & Miller, I. W. (2004). Perfectionism, cognitive bias, and hopelessness as prospective predictors of suicidal ideation. Suicide & Life-Threatening Behavior, 34(2), 126–137. https://doi.org/10.1521/suli.34.2.126.32791
Brennan-Wydra, E., Chung, H. W., Angoff, N., ChenFeng, J., Phillips, A., Schreiber, J., Young, C., & Wilkins, K. (2021). Maladaptive perfectionism, impostor phenomenon, and suicidal ideation among medical students. Academic Psychiatry, 45(6), 708–715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40596-021-01503-1
Brown, K. W., & Ryan, R. M. (2003). The benefits of being present: Mindfulness and its role in psychological well-being. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 84(4), 822–848. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.84.4.822
Buhr, K., & Dugas, M. J. (2006). Investigating the construct validity of intolerance of uncertainty and its unique relationship with worry. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 20(2), 222–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2004.12.004
Carleton, R. N., Norton, M., & Asmundson, G. J. (2007). Fearing the unknown: A short version of the intolerance of uncertainty scale. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 21(1), 105–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2006.03.014
Carleton, R. N., Mulvogue, M. K., Thibodeau, M. A., McCabe, R. E., Antony, M. M., & Asmundson, G. J. (2012). Increasingly certain about uncertainty: Intolerance of uncertainty across anxiety and depression. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 26(3), 468–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2012.01.011
Chambers, R., Gullone, E., & Allen, N. B. (2009). Mindful emotion regulation: An integrative review. Clinical Psychology Review, 29(6), 560–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2009.06.005
Chang, E. C. (2013). Perfectionism and loneliness as predictors of depressive and anxious symptoms in Asian and European Americans: Do self-construal schemas also matter? Cognitive Therapy and Research, 37(6), 1179–1188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10608-013-9549-9
Ciarrochi, J., Said, T., & Deane, F. P. (2005). When simplifying life is not so bad: The link between rigidity, stressful life events, and mental health in an undergraduate population. British Journal of Guidance & Counseling, 33(2), 185–197. https://doi.org/10.1080/03069880500132540
Duan, W., & Guan, Y. (2020). Questionnaire data on perfectionism, flourishing and negative emotion symptoms of Chinese adolescents. Data in Brief, 29, 105379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2020.105379
Dugas, M. J., Gagnon, F., Ladouceur, R., & Freeston, M. H. (1998). Generalized anxiety disorder: A preliminary test of a conceptual model. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 36(2), 215–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-7967(97)00070-3
Feldman, G., Hayes, A., Kumar, S., Greeson, J., & Laurenceau, J. P. (2007). Mindfulness and emotion regulation: The development and initial validation of the Cognitive and Affective Mindfulness Scale-Revised (CAMS-R). Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 29, 177–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-006-9035-8
Flamenbaum, R., & Holden, R. R. (2007). Psychache as a mediator in the relationship between perfectionism and suicidality. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 54(1), 51–61. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0167.54.1.51
Gillett, C. B., Bilek, E. L., Hanna, G. L., & Fitzgerald, K. D. (2018). Intolerance of uncertainty in youth with obsessive-compulsive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder: A transdiagnostic construct with implications for phenomenology and treatment. Clinical Psychology Review, 60, 100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2018.01.007
Graham, J. W. (2009). Missing data analysis: Making it work in the real world. Annual Review of Psychology, 60, 549–576. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.58.110405.085530
Graham, J. R., West, L. M., & Roemer, L. (2013). The experience of racism and anxiety symptoms in an African-American sample: Moderating effects of trait mindfulness. Mindfulness, 4, 332–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-012-0133-2
Guo, J., Gao, Q., Wu, R., Ying, J., & You, J. (2021). Parental psychological control, parent-related loneliness, depressive symptoms, and regulatory emotional self-efficacy: A moderated serial mediation model of nonsuicidal self-injury. Archives of Suicide Research, 26(3), 1462–1477. https://doi.org/10.1080/13811118.2021.1922109
Heo, M., Kim, N., & Faith, M. S. (2015). Statistical power as a function of Cronbach alpha of instrument questionnaire items. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 15, 86. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-015-0070-6
Julien, D., O’Connor, K., & Aardema, F. (2016). The inference-based approach to obsessive-compulsive disorder: A comprehensive review of its etiological model, treatment efficacy, and model of change. Journal of Affective Disorders, 202, 187–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2016.05.060
Kabat-Zinn, J. (1994). Wherever you go, there you are: Mindfulness meditation in everyday life. Hyperion Books.
Karyadi, K. A., & Cyders, M. A. (2015). Elucidating the association between trait mindfulness and alcohol use behaviors among college students. Mindfulness, 6(6), 1242–1249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-015-0386-7
Kawamoto, T., & Furutani, K. (2018). The mediating role of intolerance of uncertainty on the relationships between perfectionism dimensions and psychological adjustment/maladjustment among mothers. Personality and Individual Differences, 122, 62–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2017.10.008
Kawamura, K. Y., Hunt, S. L., Frost, R. O., & DiBartolo, P. M. (2001). Perfectionism, anxiety, and depression: Are the relationships independent? Cognitive Therapy and Research, 25(3), 291–301. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010736529013
Kim, M. K., Lee, K. S., Kim, B., Choi, T. K., & Lee, S. (2016). Impact of mindfulness-based cognitive therapy on intolerance of uncertainty in patients with panic disorder. Psychiatry Investigation, 13(2), 196–202. https://doi.org/10.4306/pi.2016.13.2.196
Kline, R. B. (2016). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling (4th ed.). Guilford Press.
Liu, X. C., Chen, H., Liu, Z. Z., Wang, J. Y., & Jia, C. X. (2019). Prevalence of suicidal behaviour and associated factors in a large sample of Chinese adolescents. Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences, 28(3), 280–289. https://doi.org/10.1017/S2045796017000488
Mahoney, A. E. J., & McEvoy, P. M. (2012). Changes in intolerance of uncertainty during cognitive behavior group therapy for social phobia. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 43(2), 849–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbtep.2011.12.004
Martin, K. P., Blair, S., Clark, G. I., Rock, A. J., & Hunter, K. R. (2018). Trait mindfulness moderates the relationship between early maladaptive schemas and depressive symptoms. Mindfulness, 9(1), 140–150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-017-0753-7
Nock, M. K., Park, J. M., Finn, C. T., Deliberto, T. L., Dour, H. J., & Banaji, M. R. (2010). Measuring the suicidal mind: Implicit cognition predicts suicidal behavior. Psychological Science, 21(4), 511–517. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797610364762
Norton, P. J., Temple, S. R., & Pettit, J. W. (2008). Suicidal ideation and anxiety disorders: Elevated risk or artifact of comorbid depression? Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 39(4), 515–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbtep.2007.10.010
O’Neil Rodriguez, K. A., & Kendall, P. C. (2014). Suicidal ideation in anxiety-disordered youth: Identifying predictors of risk. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 43(1), 51–62. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374416.2013.843463
Park, E. H., Hong, N., Jon, D. I., Hong, H. J., & Jung, M. H. (2017). Past suicidal ideation as an independent risk factor for suicide behaviors in patients with depression. International Journal of Psychiatry in Clinical Practice, 21(1), 24–28. https://doi.org/10.1080/13651501.2016.1249489
Rasmussen, K. A., Slish, M. L., Wingate, L. R., Davidson, C. L., & Grant, D. M. (2012). Can perceived burdensomeness explain the relationship between suicide and perfectionism? Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior, 42(2), 121–128. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1943-278X.2011.00074.x
Reuther, E. T., Davis, T. E., III., Rudy, B. M., Jenkins, W. S., Whiting, S. E., & May, A. C. (2013). Intolerance of uncertainty as a mediator of the relationship between perfectionism and obsessive-compulsive symptom severity. Depression and Anxiety, 30(8), 773–777. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.22100
Shikatani, B., Antony, M. M., Cassin, S. E., & Kuo, J. R. (2016). Examining the role of perfectionism and intolerance of uncertainty in postevent processing in social anxiety disorder. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 38(2), 297–306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-015-9516-8
Smith, M. M., Sherry, S. B., Chen, S., Saklofske, D. H., Mushquash, C., Flett, G. L., & Hewitt, P. L. (2018). The perniciousness of perfectionism: A meta-analytic review of the perfectionism–suicide relationship. Journal of Personality, 86(3), 522–542. https://doi.org/10.1111/jopy.12333
Sun, R., Ren, Y., Li, X., Jiang, Y., Liu, S., & You, J. (2020). Self-compassion and family cohesion moderate the association between suicide ideation and suicide attempts in Chinese adolescents. Journal of Adolescence, 79, 103–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2019.12.010
Terry-Short, L. A., Owens, R. G., Slade, P. D., & Dewey, M. E. (1995). Positive and negative perfectionism. Personality and Individual Differences, 18(5), 663–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/0191-8869(94)00192-U
Tomlinson, E. R., Yousaf, O., Vittersø, A. D., & Jones, L. (2018). Dispositional mindfulness and psychological health: A systematic review. Mindfulness, 9(1), 23–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-017-0762-6
Wang, K., Shi, H. S., Geng, F. L., Zou, L. Q., Tan, S. P., Wang, Y., Neumann, D. L., Shum, D. H., & Chan, R. C. (2016). Cross-cultural validation of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scale-21 in China. Psychological Assessment, 28(5), e88–e100. https://doi.org/10.1037/pas0000207
World Health Organization [WHO]. (2020). Suicide worldwide in 2019: Global health estimates. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240026643
Ying, J., You, J., & Guo, J. (2020). The protective effects of youth assets on the associations among academic stress, regulatory emotional self-efficacy, and suicidal risk: A moderated mediation model. Children and Youth Services Review, 119, 105660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2020.105660
Zerach, G., & Levi-Belz, Y. (2019). Intolerance of uncertainty moderates the association between potentially morally injurious events and suicide ideation and behavior among combat veterans. Journal of Traumatic Stress, 32(3), 424–436. https://doi.org/10.1002/jts.22366
Zhang, W. J., Yan, C., Shum, D., & Deng, C. P. (2020). Responses to academic stress mediate the association between sleep difficulties and depressive/anxiety symptoms in Chinese adolescents. Journal of Affective Disorders, 263, 89–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2019.11.157
Zhao, H., Gong, X., Huebner, E. S., Yang, X., & Zhou, J. (2022). Cyberbullying victimization and nonsuicidal self-injury in adolescents: Testing a moderated mediating model of emotion reactivity and dispositional mindfulness. Journal of Affective Disorders, 299, 256–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2021.11.070
Zhou, X., Zhu, H., Zhang, B., & Cai, T. (2013). Perceived social support as moderator of perfectionism, depression, and anxiety in college students. Social Behavior and Personality, 41(7), 1141–1152. https://doi.org/10.2224/sbp.2013.41.7.1141
Zhou, X., Wu, S., Zhu, H., & Cai, T. (2016). Reliability and validity of the positive and negative perfectionism scale among Chinese college students. Social Behavior and Personality, 44(5), 727–736. https://doi.org/10.2224/sbp.2016.44.5.727
Zhou, S., Wang, L., Qi, M., Yang, X., Gao, L., Zhang, S., Zhang, L., Yang, R., & Chen, J. (2021). Depression, anxiety, and suicidal ideation in Chinese university students during the COVID-19 pandemic. Frontiers in Psychology, 12, 669833. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.669833
Zhou, X. (2012). Research on the relationship among parenting style, college students’ perfectionism and mental health, Ph.D. Doctoral Dissertation, China: Central South University. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CDFD1214&filename=1012474396.nh
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31771228), the National Social Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 19ZDA360), and the Special Funds for the Cultivation of Guangdong College Students’ Scientific and Technological Innovation (“Climbing Program” Special Funds) (Grant No. pdjh2021b0145).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xinglin Zhou and Danrui Chen: conceived of the study, conducted the statistical analysis, and drafted the manuscript. Huijiao Wu and Jiefeng Ying: participated in data collection and helped revise the manuscript. Yunhong Shen and Qixin Zhu: participated in data collection and managed the literature searches. Lurong Zheng: managed the literature searches and checked the manuscript. Min-Pei Lin and Jianing You: participated in the design of the study and helped revise the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This study was approved by the South China Normal University Research Ethics Board.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Chen, D., Wu, H. et al. The Protective Effect of Trait Mindfulness on the Associations Between Negative Perfectionism and Suicidal Ideation Among Chinese Adolescents: A Longitudinal Moderated Mediation Model. Mindfulness 14, 395–405 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-023-02069-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-023-02069-9