Abstract
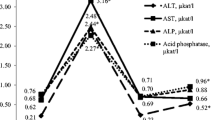
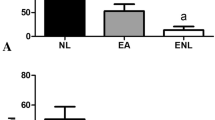
The liposomal form of silibinin was obtained, and its antihepatotoxic activity in mice was studied using a model of acute toxic hepatitis caused by injection of carbon tetrachloride or paracetamol. It was shown that the use of the drug in therapy or prevention regimens leads to normalization of levels of transaminases and total protein in the blood of experimental animals. The results of the study showed that liposomal silibinin when administered intravenously shows a more pronounced hepatoprotective effect compared to intragastric administration of free silibinin. Thus, the effectiveness of the therapeutic action of silibinin can be significantly increased by using its liposomal form. Liposomal drug, in contrast to native silibinin, can be injected directly into the blood that significantly increases its bioavailability.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saller, R., Meier, R., & Brignoli, R. (2001). The use of silymarin in the treatment of liver diseases. Drugs, 61, 2035–2063. https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200161140-00003.
Pradhan, S. C., & Girish, C. (2006). Hepatoprotective herbal drug, silymarin from experimental pharmacology to clinical medicine. The Indian Journal of Medical Research, 124, 491–504.
Abenavoli, L., Capasso, R., Milic, N., & Capasso, F. (2010). Milk thistle in liver diseases: past, present, future. Phytotherapy Research, 24, 1423–1432. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.3207.
Vargas-Mendoza, N., Madrigal-Santillán, E., Morales-González, A., Esquivel-Soto, J., Esquivel-Chirino, C., García-Luna, Y., González-Rubio, M., Gayosso-de-Lucio, J. A., & Morales-González, J. A. (2014). Hepatoprotective effect of silymarin. World Journal of Hepatology, 6, 144–149. https://doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v6.i3.144.
Wu, J. W., Lin, L. C., Hung, S. C., Chi, C. W., & Tsai, T. H. (2007). Analysis of silibinin in rat plasma and bile for hepatobiliary excretion and oral bioavailability application. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 45, 635–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2007.06.026.
Bozzuto, G., & Molinari, A. (2015). Liposomes as nanomedical devices. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 10, 975–999. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S68861.
Daraee, H., Etemadi, A., Kouhi, M., Alimirzalu, S., & Akbarzadeh, A. (2016). Application of liposomes in medicine and drug delivery. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol, 44, 381–391. https://doi.org/10.3109/21691401.2014.953633.
Qian, S., Li, C., & Zuo, Z. (2012). Pharmacokinetics and disposition of various drug loaded liposomes. Current Drug Metabolism, 13, 372–395. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920012800166562.
Elmowafy, M., Viitala, T., Ibrahim, H. M., Abu-Elyazid, S. K., Samy, A., Kassem, A., & Yliperttula, M. (2013). Silymarin loaded liposomes for hepatic targeting: in vitro evaluation and HepG2 drug uptake. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 50, 161–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2013.06.012.
El-Samaligy, M. S., Afifi, N. N., & Mahmoud, E. A. (2006). Increasing bioavailability of silymarin using a buccal liposomal delivery system: preparation and experimental design investigation. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 308, 140–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2005.11.006.
Ochi, M. M., Amoabediny, G., Rezayat, S. M., Akbarzadeh, A., & Ebrahimi, B. (2016). In vitro co-delivery evaluation of novel pegylated nano-liposomal herbal drugs of silibinin and glycyrrhizic acid (nano-phytosome) to hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Journal, 18, 135–148. https://doi.org/10.22074/cellj.2016.4308.
Wang, M., Xie, T., Chang, Z., Wang, L., Xie, X., Kou, Y., Xu, H., & Gao, X. (2015). A new type of liquid silymarin proliposome containing bile salts: its preparation and improved hepatoprotective effects. PLoS One, 10, e0143625. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0143625.
Dube, D., Khatri, K., Goyal, A. K., Mishra, N., & Vyas, S. P. (2010). Preparation and evaluation of galactosylated vesicular carrier for hepatic targeting of silibinin. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 36, 547–555. https://doi.org/10.3109/03639040903325560.
Maheshwari, H., Agarwal, R., Patil, C., & Katare, O. P. (2003). Preparation and pharmacological evaluation of silibinin liposomes. Arzneimittel-Forschung, 53, 420–427. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0031-1297130.
Kumar, N., Rai, A., Reddy, N. D., Raj, P. V., Jain, P., Deshpande, P., Mathew, G., Kutty, N. G., Udupa, N., & Rao, C. M. (2014). Silymarin liposomes improves oral bioavailability of silybin besides targeting hepatocytes, and immune cells. Pharmacological Reports, 66, 788–798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2014.04.007.
Jillavenkatesa, A., Dapkunas, S. J., & Lum, L.-S. H. (2001). Particle size characterization. Washington: National Institute of Standards and Technology.
Reitman, S., & Frankel, S. (1957). A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxalacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. American Journal of Clinical Pathology, 28, 56–63.
Lubran, M. M. (1978). The measurement of total serum proteins by the Biuret method. Annals of Clinical and Laboratory Science, 8, 106–110.
Szoka, F., & Papahadjopoulos, D. (1978). Procedure for preparation of liposomes with large internal aqueous space and high capture by reverse-phase evaporation. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA, 75, 4194–4198. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.75.9.4194.
Jaeschke, H., Gores, G. J., Cederbaum, A. I., Hinson, J. A., Pessayre, D., & Lemasters, J. J. (2002). Mechanisms of hepatotoxicity. Toxicological Sciences, 65(2), 166–176. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/65.2.166.
Ben-Shachar, R., Chen, Y., Luo, S., Hartman, C., Reed, M., & Nijhout, H. F. (2012). The biochemistry of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity and rescue: a mathematical model. Theoretical Biology & Medical Modelling, 9, 55. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-4682-9-55.
Kamiyama, T., Sato, C., Liu, J., Tajiri, K., Miyakawa, H., & Marumo, F. (1993). Role of lipid peroxidation in acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity: comparison with carbon tetrachloride. Toxicology Letters, 66(1), 7–12.
Baer-Dubowska, W., Szaefer, H., & Krajka-Kuzniak, V. (1998). Inhibition of murine hepatic cytochrome P450 activities by natural and synthetic phenolic compounds. Xenobiotica, 28(8), 735–743.
Surai, P. F. (2015). Silymarin as a natural antioxidant: an overview of the current evidence and perspectives. Antioxidants (Basel), 4(1), 204–247. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox4010204.
Allen, T. M., & Cullis, P. R. (2004). Drug delivery systems: entering the mainstream. Science, 303(5665), 1818–1822. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1095833.
Acknowledgements
The work is performed according to the Russian Government Program of Competitive Growth of I.M. Sechenov First Moscow State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All animal experiments were approved by the All-Russian Research Institute of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants Bioethics Committee.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lutsenko, S.V., Gromovykh, T.I., Krasnyuk, I.I. et al. Antihepatotoxic Activity of Liposomal Silibinin. BioNanoSci. 8, 581–586 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-018-0512-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-018-0512-9