Abstract
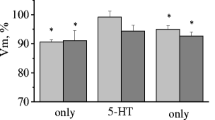
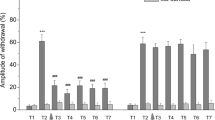
It is shown that after the elaboration of a conditioned reflex in snails, a reliable decrease can be observed in the membrane potential (Vm) of the premotor interneurons at 4 mV, daily injection of serotonin (5-HT) causes a decrease in Vm at 4.5 mV, the same change is observed for Vm in the snails trained after the injection of 5-HT. A single injection of 5-HT causes a depolarization shift of Vm at 5 mV. After the initial stage of training (10–12 pairs) the snails, injected by 5-HT, there is a depolarization at 4.5 mV.

Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Balaban, P. M., Bravarenko, N. I., Maksimova, O. A., Nikitin, E., Ierusalimsky, V. N., Zakharov, I. S. (2001). A single serotoninergic modulatory cell can mediate reinforcement in the withdrawal network of the terrestrial snail. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 75, 30–50. doi:10.1006/nlme.1999.3953.
Dyakonova, V. E. (2007). Behavioral functions of serotonin and octopamin: some paradoxes of comparative physiology. Uspekhi Physiologicheskikh Nauk (Russian), 38, 3–20.
Il-Han, J., Janes, T., Lukowiak, K. (2010). The role of serotonin in the enhancement of long-term memory resulting from predator detection in Lymnaea. The Journal of Experimental Biology, 213, 3603–3614. doi:10.1242/jeb.048256.
Andrianov, V. V., Bogodvid, T. K., Deryabina, I. B., Golovchenko, A. N., Muranova, L. N., Tagirova, R. R., et al. (2015). Modulation of defensive reflex conditioning in snails by serotonin. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 9(Article 279), 1–12. doi:10.3389/fnbeh.2015.00279.
Zakharov, I. S., Ierusalimsky, V. N., Balaban, P. M. (1995). Pedal serotonergic neurons modulate the synaptic input of withdrawal interneurons of Helix. Invertebrate Neuroscience, 1, 41–52. doi:10.1007/BF02331831.
Shevelkin, A. V., Nikitin, V. P., Kozyrev, S. A., Samoilov, M. O., Sherstnev, V. V. (1997). Serotonin imitates several of the neuronal effects of nociceptive sensitization in the common snail. Zhurnal vysshei nervnoi deiatelnosti imeni I. P. Pavlova (Russian), 47, 532–542.
Malyshev, A. Y., Bravarenko, N. I., Pivovarov, A. S., Balaban, P. M. (1997). Effects of serotonin levels on postsynaptically induced potentiation of snail neuron responses. Zhurnal vysshei nervnoi deiatelnosti imeni I. P. Pavlova (Russian), 47, 553–562.
Levenson, J., Byrne, J. H., Eskin, A. (1999). Levels of serotonin in the hemolymph of Aplysia are modulated by light/dark cycles and sensitization training. The Journal of Neuroscience, 19, 8094–8103.
Balaban, P. M. (2002). Cellular mechanisms of behavioral plasticity in terrestrial snail. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 26, 597–630.
Muranova, L. N., Bogodvid, T. K., Andrianov, V. V., Gainutdinov, K. L. (2016). Effects of NO donors and inhibitors of NO synthase and guanylate cyclase on the acquisition of a conditioned defense food aversion response in edible snails. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 160, 414–416. doi:10.1007/s10517-.
Liao, X., Brou, C. G., Walters, E. T. (1999). Limited contributions of serotonin to long-term hyperexcitability of Aplysia sensory neurons. Journal of Neurophysiology, 82, 3223–3235.
Jin, N. G., Tian, L.-M., Crow, T. (2009). 5-HT and GABA modulate intrinsic excitability of type I interneurons in Hermissenda. Journal of Neurophysiology, 102, 2825–2833. doi:10.1152/jn.00477.2009.
Cleary, L. J., Lee, W. L., Byrne, J. H. (1998). Cellular correlates of long-term sensitization in Aplysia. The Journal of Neuroscience, 18, 5988–5998.
Gainutdinov, K. L., Chekmarev, L. Y., Gainutdinova, T. H. (1998). Excitability increase in withdrawal interneurons after conditioning in snail. NeuroReport, 9, 517–520. doi:10.1097/00001756-199802160-00026.
Mozzachiodi, R., Lorenzetti, F. D., Baxter, D. A., Byrne, J. H. (2008). Changes in neuronal excitability serve as a mechanism of long-term memory for operant conditioning. Nature Neuroscience, 11, 1146–1148. doi:10.1038/nn.2184.
Gainutdinov, K. L., Andrianov, V. V., Gainutdinova, T. K. (2011). Changes of the neuronal membrane excitability as cellular mechanisms of learning and memory. Uspekhi Physiologicheskikh Nauk (Russian), 42, 33–52. PMID: 21442956.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the subsidy of the Russian Government to support the Program of Competitive Growth of Kazan Federal University among the World’s Leading Academic Centers (agreement No.02.A03.21.0002) and by Russian Fund of Basic Research (grant No. 15-04-05487_a).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golovchenko, A.N., Andrianov, V.V., Bogodvid, T.K. et al. Serotonin Modulation of Premotor Interneuron Excitability in the Snail during Associative Learning. BioNanoSci. 6, 450–452 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-016-0252-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-016-0252-7