Abstract
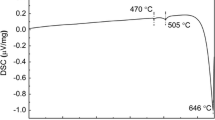
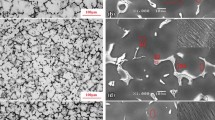
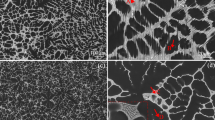
In this paper, the Fe/Si reduction efficiency, Gd/Mn alloying efficiency, and corrosion susceptibility of the Mg-xMn-4.0Gd alloy were investigated. The results reveal that adding Mn gives a more prominent Fe removal effect under the conventional smelting processes. Neither the amount of Gd addition nor excessive Mn addition is sufficient for the continued strengthening of the Fe removal effect. The alloying efficiency of Mn increased and then decreased as a result of adding Mn alone to mixtures of Mn and Gd elements, while the alloying efficiency of Gd elements gradually diminished. An appropriate amount of Mn addition is beneficial for efficiently improving the corrosion resistance of the alloy. The extruded Mg-0.8Mn-4.0Gd alloy has more outstanding corrosion resistance, with a CRWeighet Loss of 4.48 ± 0.33 mg/(cm2·d) and CRHydrogen Evolution of 2.01 ± 0.31 ml/(cm2·d). The corrosion susceptibility of the extruded Mg-xMn-4.0Gd alloy mainly hinges on the grain size, Gd solid solubility, and texture intensity of basal plane I(0002).









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cho D H, Avey T, Nam K H, Dean D, and Luo A A, Acta Biomater 150 (2022) 442.
Sun L X, Bai J, and Xue F, J Mater Res Technol 21 (2022) 3961.
Liu M, Uggowitzer P J, Nagasekhar A V, Schmutz P, Easton M, Song G L, and Atrens A, Corros Sci 51 (2009) 602.
Gu D D, Peng J, Wang J W, Liu Z T, and Pan F S, Acta Metall Sin (Engl Lett) 34 (2021) 1.
Kim J I, Nguyen H N, You B S, and Kim Y M, Scr Mater 162 (2019) 355.
Jiang S Y, Yuan Y, Wang J, Chen T, Wu L, Chen X H, Jiang B, Tang A T, and Pan F S, Calphad 79 (2022) 102503.
Gu D D, Wang J W, Chen Y B, and Peng J, T Nonferr Metal Soc 30 (2020) 2941.
Sun Y H, Wang R C, Peng C Q, and Wang X F, T Nonferr Metal Soc 32 (2022) 2494.
Li L H, Bao J X, Qiao M L, Tian J, Yang Y Q, Sha J C, and Zhang Z Q, Mat Sci Eng A 872 (2023) 144979.
Yuan X C, Liu M N, Wei K W, Li F Z, Li X Y, and Zeng X Y, Mat Sci Eng A 850 (2022) 143572.
Guan F, Jiang W M, Zhang Z, Wang J L, and Li G Y, Mater Charact 200 (2023) 112898.
Gu D D, Peng J, Sun S, and Pan F S, J Mater Res Technol 20 (2022) 2859.
Tong X, You G Q, Wang Y C, Wu H, Liu W L, Li P Q, and Guo W, Mater Sci Eng A 731 (2018) 44.
Guan K, Meng F Z, Qin P F, Yang Q, Zhang D D, Li B S, Sun W, Lv S H, Huang Y D, Hort N, and Meng J, J Mater Sci Technol 35 (2019) 1368.
Wang Q, Master Thesis, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China (2016)
Atrens A, Johnston S, Shi Z M, and Dargusch M S, Scr Mater 154 (2018) 92.
Liu M, and Song G L, Corros Sci 77 (2013) 143.
Aung N N, and Zhou W, Corros Sci 52 (2010) 589.
Xin R L, Li B, Li L, and Liu Q, Mater Design 32 (2011) 4548.
Yang L, Zhou X R, Curioni M, Pawar S, Liu H, Fan Z Y, Scamans G, and Thompson G, J Electrochem Soc 162 (2015) C362.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFB3701100), Scientific research project of Jiangxi Provincial Department of Education (GJJ211038), Jiangxi Students’ Platform for innovation and entrepreneurship training program (S202210419009), and Doctoral research project of Jinggangshan University (JZB2110).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, Dd., Wu, Wx., Xie, Sk. et al. On the Solute Concentration and Corrosion Susceptibility of Mg-xMn-4.0Gd Alloy. Trans Indian Inst Met 77, 627–636 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-023-03149-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-023-03149-z