Abstract
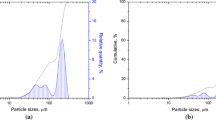
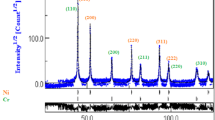
Nanocrystalline Al6063 powders were synthesized by high-energy mechanical milling of gas-atomized powders for 22.5 h. The powders were uniaxially compacted at various compaction pressures ranging 200–1325 MPa and then were sintered at temperatures between 550 and 650 °C for 1 h. The densification and microstructural evolutions during both solid phase sintering and supersolidus liquid phase sintering are studied. Ultrafine-grained (UFG) Al alloy compacts show superior sinterability compared with coarse-grained (CG) compacts due to the higher defect density and larger specific surface area of the mechanically-milled powders. The densification parameter and hardness of both CG and UFG Al6063 compacts enhances as the compaction pressure increases. Nevertheless, applying high compaction pressures has an adverse effect on the sintered density and results in the swelling of compacts. The results point out an optimum sintering temperature at ~600 °C for achieving the highest sintered density and hardness with minimal grain coarsening and slumping.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daver E M, Ullrich W J, and Patel K B, Key Eng Mater 29–31 (1989) 401.
Stevenson R W, P/M Lightweight Metals, ASM Handbook, ASM, Metals Park, USA (1984) 9th Ed., p 741.
Schaffer G B, Sercombe T B, and Lumley R N, Mater Chem Phys 67 (2001) 85.
Jha A K, Prasad S V, and Upadhyaya G S, Powder Metall Int 20 (1988) 18.
Martin J M, and Castro F, J Mater Process Technol 143–144 (2003) 814.
Padmavathi C, Upadhyaya A, and Agrawal D, Mater Res Innov 15 (2011) 294.
Lumley R N, Sercombe T B, and Schaffer G B, Metall Mater Trans A 30 (1999) 457.
Kondoh K, Kimura A, and Watanabe R, Powder Metall 44 (2001) 161.
Padmavathi C, Upadhyaya A, and Agrawal D, Mater Chem Phys 130 (2011) 449.
Sercombe T B, and Schaffer G B, Mater Sci Eng A 268 (1999) 32.
Schaffer G B, and Huo S H, Powder Metall 42 (1999) 219.
Schaffer G B, Huo S H, Drennan J, and Auchterlonie G J, Acta Mater 49 (2001) 2671.
German R M, Int J Powder Metall 26 (1990) 35.
Ziani A, and Pelletier S, Int J Powder Metall 35 (1999) 49.
Youseffi M, and Showaiter N, Powder Metall 49 (2006) 240.
Asgharzadeh H, and Simchi A, Powder Metall 52 (2009) 28.
Rodriguez J A, Gallardo J M, and Herrera E J, J Mater Sci 32 (1997) 3535.
Shanmugasundaram T, Heilmaier M, Murty B S, and Subramanya Sarma V, Mater Sci Eng A 527 (2010) 7821.
Choi H J, Shin J H, Min B H, and Bae D H, Compos A 41 (2010) 327.
Asgharzadeh H, Simchi A, and Kim H S, Mater Sci Eng A 528 (2011) 3981.
Ahn B, Mitra R, Lavernia E J, and Nutt S R, J Mater Sci 45 (2010) 4790.
Kumar Rana J, Sivaprahasam D, Seetharama Raju K, and Subramanya Sarma V, Mater Sci Eng A 527 (2009) 292.
Cintas J, Cuevas F G, Montes J M, and Herrera E J, Scr Mater 52 (2005) 341.
Cintas J, Montes J M, Cuevas F G, and Herrera E J, J Mater Sci 40 (2005) 3911.
Abdoli H, Asgharzadeh H, and Salahi E, J Alloys Compd 473 (2009) 116.
Khan A S, Farrokh B, and Takacs L, Mater Sci Eng A 489 (2008) 77.
Fuentes J J, Rodriguez J A, and Herrera E J, J Alloys Compd 484 (2009) 806.
Asgharzadeh H, and McQueen H J, Mater Sci Technol 31 (2015) 1016.
Asgharzadeh H, Simchi A, and Kim H S, Mater Sci Eng A 527 (2010) 4897.
Fogagnolo J B, Robert M H, and Torralba J M, Mater Sci Eng A 426 (2006) 85.
Zebarjad S M, and Sajjadi S A, Mater Des 27 (2006) 684.
Williamson G K, and Hall W H, Acta Metall 1 (1953) 22.
Zhang D L, Prog Mater Sci 49 (2004) 537.
Abdoli H, Ghanbari M, and Baghshahi S, Mater Sci Eng A 528 (2011) 6702.
Qi W H, Phys B 368 (2005) 46.
Panigrahi B B, Mater Sci Eng A 460–461 (2007) 7.
Asgharzadeh H, Simchi A, and Kim H S, Metall Mater Trans A 42 (2011) 816.
Sakoori Oskooie M, Asgharzadeh H, and Kim H S, J Alloys Compd 632 (2015) 540.
Asgharzadeh H, Simchi A, and Kim H S, Mater Charact 75 (2013) 108.
Abdoli H, Farnoush H R, Asgharzadeh H, and Sadrnezhaad S K, Powder Metall 54 (2011) 24.
Asgharzadeh H, Simchi A, and Kim H S, Powder Technol 211 (2011) 215.
German R M, Int J Powder Metall 26 (1990) 23.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks the University of Tabriz for all of the support provided. The author wish to thank A. Tarasi and P. Pishva for assistance in performing the tests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asgharzadeh, H. Sintering Behavior of Nanocrystalline Al6063 Powders Prepared by High-Energy Mechanical Milling. Trans Indian Inst Met 69, 1359–1368 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-015-0693-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-015-0693-7