Abstract
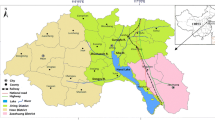
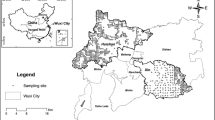
The characteristics of mercury (Hg) emissions from the fault zone can be used to understand the fault activity and evaluate the impact of emissions on the environment. Here, the distribution of soil Hg was investigated at the Daqingliangzi (DQL) site within the active Zemuhe fault zone in Sichuan, China. Total mercury in soil (THg) and total organic carbon (TOC) concentrations were analyzed at depths of 0–80 cm at 11 sampling sites. The THg concentrations showed large variations, ranging from 18 to 123 ng/g, with the higher values (94–113 ng/g) occurring within the fault plane profile. A positive correlation was observed between the THg and TOC concentrations. These correlations indicated that the enrichment of Hg most likely resulted from adsorption onto organic matter. The Hg migration and accumulation in the fault zone was related to the fault structure, and the Hg enrichment was mainly driven by natural emissions from the fault. This result could be useful in future studies of fault emission processes at the Earth’s surface.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiuppa A, Bagnato E, Witt MLI, Mather TA, Parello F, Pyle DM, Martin RS (2007) Real-time simultaneous detection of volcanic Hg and SO2 at La Fossa Crater, Vulcano (Aeolian Islands, Sicily). Geophys Res Lett 34(21):L21307
Bagnato E, Allard P, Parello F, Aiuppa A, Calabrese S, Hammouya G (2009) Mercury gas emissions from La Soufrière Volcano, Guadeloupe Island (Lesser Antilles). Chem Geol 266(3–4):267–273
Bagnato E, Viveiros F, Pacheco JE, D’Agostino F, Silva C, Zanon V (2018) Hg and CO2 emissions from soil diffuse degassing and fumaroles at Furnas Volcano (São Miguel Island, Azores): gas flux and thermal energy output. J Geochem Explor 190:39–57
Bergquist BA, Blum JD (2009) The odds and evens of mercury isotopes: applications of mass-dependent and mass-independent isotope fractionation. Elements 5(6):353–357
Caine JS, Evans JP, Forster CB (1996) Fault zone architecture and permeability structure. Geology 24(11):1025–1028
Ciotoli G, Lombardi S, Annunziatellis A (2007) Geostatistical analysis of soil gas data in a high seismic intermontane basin: Fucino Plain, central Italy. J Geophys Res 112(B5):B05407
Dai Z, Feng X, Zhang C, Wang J, Jiang T, Xiao H, Li Y, Wang X, Qiu G (2013) Assessing anthropogenic sources of mercury in soil in Wanshan Hg mining area, Guizhou, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(11):7560–7569
Faulkner DR, Jackson CAL, Lunn RJ, Schlische RW, Shipton ZK, Wibberley CAJ, Withjack MO (2010) A review of recent developments concerning the structure, mechanics and fluid flow properties of fault zones. J Struct Geol 32(11):1557–1575
Fu C-C, Yang TF, Walia V, Chen C-H (2005) Reconnaissance of soil gas composition over the buried fault and fracture zone in southern Taiwan. Geochem J 39:427–439
Gong Z, Li H, Lao C, Tang L, Luo L (2015) Real-time drilling mud gas monitoring records seismic damage zone from the 2008 Mw 7.9 Wenchuan earthquake. Tectonophysics 639:109–117
Gong Z, Li H, Tang L, Lao C, Zhang L, Li L (2017) Real time drilling mud gas response to small-moderate earthquakes in Wenchuan Earthquake Scientific Drilling Hole-1 in SW China. J Asian Earth Sci 138:416–426
He H, Ren J (2003) Holocene earthquakes on the Zemuhe fault in southwestern China. Ann Geophys 46(5):1035–1051
Hinkle ME (1994) Environmental conditions affecting concentrations of He, CO2, O2 and N2 in soil gases. Appl Geochem 9(1):53–63
Jin Y, Wu Z, Shen C, Wei J, Zhu H (1989) Earthquake prediction through the observation and measurement of mercury content variation in water. J Geochem Explor 33(1–3):195–202
Li Y, Du J, Wang X, Zhou X, Xie C, Cui Y (2013) Spatial variations of soil gas geochemistry in the Tangshan area of northern China. Terr Atmos Ocean Sci 24(3):323–332
Liu J, Feng X, Yin R, Zhu W, Li Z (2011) Mercury distributions and mercury isotope signatures in sediments of Dongjiang, the Pearl River Delta, China. Chem Geol 287(1–2):81–89
Luo L, Ma Y, Zhang S, Wei D, Zhu Y-G (2009) An inventory of trace element inputs to agricultural soils in China. J Environ Manage 90(8):2524–2530
Obrist D, Johnson DW, Lindberg SE, Luo Y, Hararuk O, Bracho R, Battles JJ, Dail DB, Edmonds RL, Monson RK, Ollinger SV, Pallardy SG, Pregitzer KS, Todd DE (2011) Mercury distribution across 14 U.S. forests. Part I: Spatial patterns of concentrations in biomass, litter, and soils. Environ Sci Technol 45(9):3974–3981
Obrist D, Kirk JL, Zhang L, Sunderland EM, Jiskra M, Selin NE (2018) A review of global environmental mercury processes in response to human and natural perturbations: changes of emissions, climate, and land use. Ambio 47(2):116–140
Pastrana-Corral MA, Wakida FT, García-Flores E, Rodriguez-Mendivil DD, Quiñonez-Plaza A, Piñon-Colin TDJ (2016) Soil mercury levels in the area surrounding the Cerro Prieto geothermal complex, MEXICO. Environ Monit Assess 188(8):466
Ren Z, Lin A (2010) Deformation characteristics of co-seismic surface ruptures produced by the 1850 M7.5 Xichang earthquake on the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. J Asian Earth Sci 38(1–2):1–13
Ren Z, Lin A, Rao G (2010) Late Pleistocene-Holocene activity of the Zemuhe Fault on the southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Tectonophysics 495(3–4):324–336
Rodriguez L, Rincón J, Asencio I, Rodríguez-Castellanos L (2007) Capability of selected crop plants for shoot mercury accumulation from polluted soils: phytoremediation perspectives. Int J Phytorem 9(1):1–13
Sherman LS, Blum JD, Nordstrom DK, McCleskey RB, Barkay T, Vetriani C (2009) Mercury isotopic composition of hydrothermal systems in the Yellowstone Plateau volcanic field and Guaymas Basin sea-floor rift. Earth Planet Sci Lett 279(1–2):86–96
Sibson RH (2003) Thickness of the seismic slip zone. Bull Seismol Soc Am 93(3):1169–1178
Smith CN, Kesler SE, Klaue B, Blum JD (2005) Mercury isotope fractionation in fossil hydrothermal systems. Geology 33(10):825–828
Sun X, Si X, Xiang Y, Liu D (2017) Soil mercury spatial variations in the fault zone and corresponding influence factors. Terr Atmos Ocean Sci 28(3):283–294
Varekamp JC, Buseck PR (1984) Changing mercury anomalies in Long Valley, California: indication for magma movement or seismic activity. Geology 12(5):283–286
Wang C-H (2016) Xichang in 2015 rural soil lead, cadmium, mercury, arsenic, chromium pollution survey. China’s Rural Health 6(6) (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang G, Liu C, Wang J, Liu W, Zhang P (2006) The use of soil mercury and radon gas surveys to assist the detection of concealed faults in Fuzhou City, China. Environ Geol 51(1):83–90
Wang H, Li H, Si J, Sun Z, Huang Y (2014) Internal structure of the Wenchuan earthquake fault zone, revealed by surface outcrop and WFSD-1 drilling core investigation. Tectonophysics 619–620:101–114
Wang B, Liu Y, Sun X, Ma Y, Zhang L, Ren H, Fang Z (2018) Hydrogeological and geochemical observations for earthquake prediction research in China: a brief overview. Pure Appl Geophys 175(7):2541–2555
Wen X-Z, Ma S-L, Xu X-W, He Y-N (2008) Historical pattern and behavior of earthquake ruptures along the eastern boundary of the Sichuan-Yunnan faulted-block, southwestern China. Phys Earth Planet Inter 168(1–2):16–36
Williams SN (1985) Soil radon and elemental mercury distribution and relation to magmatic resurgence at Long Valley Caldera. Science 229(4713):551–553
Xie X, Ren T, Sun H (2012) Geochemical atlas of China. Geological Publishing House, Beijing, p 56
Xue W, Kwon SY, Grasby SE, Sunderland EM, Pan X, Sun R, Zhou T, Yan H, Yin R (2019) Anthropogenic influences on mercury in Chinese soil and sediment revealed by relationships with total organic carbon. Environ Pollut 255:113186
Yang D, Zhang L, Liu Y, Ren H, Xie F, Chen G (2015) Mercury indicating inflow zones and ruptures along the Wenchuan Ms 8.0 earthquake fault. Chin J Geochem 34(2):201–207
Yang F, Yang X-Z, Jiang Q-M, Yang Y (2018a) Analysis on the hydrogeologic characteristics of Luoji Mountain core and perimeter areas. Groundwater 40(5):12–14 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang Y, Li Y, Guan Z, Chen Z, Zhang L, Lv CJ, Sun F (2018b) Correlations between the radon concentrations in soil gas and the activity of the Anninghe and the Zemuhe faults in Sichuan, southwestern of China. Appl Geochem 89:23–33
Yu X, Driscoll CT, Warby RAF, Montesdeoca M, Johnson CE (2014) Soil mercury and its response to atmospheric mercury deposition across the northeastern United States. Ecol Appl 24(4):812–822
Zhang P-Z (2013) A review on active tectonics and deep crustal processes of the Western Sichuan region, eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Tectonophysics 584:7–22
Zhang L, He C (2013) Frictional properties of natural gouges from Longmenshan fault zone ruptured during the Wenchuan Mw7.9 earthquake. Tectonophysics 594:149–164
Zhang X-Z, Yang Z-H, Ma Z-S, Tang J-H (2006) Geochemical background and geochemical baseline. Geol Bull China 25(5):626–629 ((in Chinese with English abstract))
Zhang L, Liu Y, Guo L, Yang D, Fang Z, Chen T, Ren H, Yu B (2014) Isotope geochemistry of mercury and its relation to earthquake in the Wenchuan Earthquake Fault Scientific Drilling Project Hole-1 (WFSD-1). Tectonophysics 619–620:79–85
Zhang B, Liu Y, Fang Z, Guan Z, Zhang L, Guo L (2018) Relationship between concentrations of hydrogen and mercury of No.2 hole cores at the Wenchuan Earthquake Scientific Drilling and fault zone structure. Chin J Geophys 61(5):1771–1781 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang L, Liu Y, Bao C, Guo L (2019) Distribution characteristics of soil mercury in Anninghe fault zone. Acta Seismol Sin 41(2):249–258 ((in Chinese with English abstract))
Zhao X, Wang D (2010) Mercury in some chemical fertilizers and the effect of calcium superphosphate on mercury uptake by corn seedlings (Zea mays L.). J Environ Sci 22(8):1184–1188
Zhou X, Du J, Chen Z, Cheng J, Tang Y, Yang L, Xie C, Cui Y, Liu L, Yi L, Yang P, Li Y (2010) Geochemistry of soil gas in the seismic fault zone produced by the Wenchuan Ms 8.0 earthquake, southwestern China. Geochem Trans 11:5
Zhou X, Chen Z, Cui Y (2016) Environmental impact of CO2, Rn, Hg degassing from the rupture zones produced by Wenchuan Ms 8.0 earthquake in western Sichuan, China. Environ Geochem Health 38(5):1067–1082
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Runsheng Yin of the Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Science, for his helpful suggestions. We also thank Yuxiu Li for assistance with the sample analyses. We are particularly grateful to the reviewers’ comments, which improved the quality of the manuscripts. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41703009) and National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2018YFC1503806).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Bao, C., Guo, L. et al. Variations of mercury in soils in the northern segment of Zemuhe fault zone, southwestern China. Environ Earth Sci 80, 798 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-10091-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-10091-0