Abstract
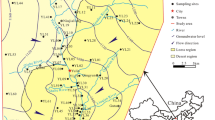
Surface water and groundwater samples were collected in a loss distribution area, northeastern China, to assess groundwater quality and health risks in a typical loess irrigation area and to provide a theoretical basis for the development and utilization of groundwater resources. The following results were obtained. (1) The total non-carcinogenic risk values of 14 surface water samples were all lower than 1, which indicates that these surface water samples will not pose non-carcinogenic risk. Drinking water intake is the main exposure pathway of non-carcinogenic risk. (2) Among the 15 phreatic groundwater wells monitored, the total non-carcinogen levels at 6 points exceeded safe levels for children, which indicates that the local groundwater is harmful to children’s health. The order of contaminants contributing to this risk is NO3-N > Mn > Fe > NH4-N > NO2-N. (3) Among the 29 points of confined groundwater monitoring wells, 2 points showed total non-carcinogenic risk values exceeding safe levels for children, which indicates that the local groundwater is unsafe to children health. The order of contaminants contributing to non-carcinogenic risk is NO3-N > Mn > Fe > NH4-N > NO2-N.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asare-Donkor NK, Boadu TA, Adimado AA (2016) Evaluation of groundwater and surface water quality and human risk assessment for trace metals in human settlements around the Bosomtwe Crater Lake in Ghana. Springer Plus 5:1812
Du SH, Su XS, Zhang WJ (2013) Effective storage rates analysis of groundwater reservoir with surplus local and transferred water used in Shijiazhuang City, China. Water Environ J 27:157–169
El Alfy M, Faraj T (2017) Spatial distribution and health risk assessment for groundwater contamination from intensive pesticide use in arid areas. Environ Geochem Health 39:231–253
Gao ZL, Zhang L, Cheng L, Zhang XP, Cowan T, Cai WJ, Brutsaert W (2015) Groundwater storage trends in the Loess Plateau of China estimated from stream flow records. J Hydrol 530:281–290
Giri S, Singh AK (2015) Human health risk assessment via drinking water pathway due to metal contamination in the groundwater of Subarnarekha River Basin, India. Environ Monit Assess 187:63
Li P, Qian H (2011) Human health risk assessment for chemical pollutants in drinking water source in Shizuishan City, Northwest China. Iran J Environ Health Sci Eng 8:41–48
Li P, Qian H, Wu J (2014a) Accelerate research on land creation. Nature 510(7503):29–31
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2014b) Origin and assessment of groundwater pollution and associated health risk: a case study in an industrial park, northwest China. Environ Geochem Health 36:693–712
Li PY, Li XY, Meng XY, Li MN, Zhang YT (2016a) Appraising groundwater quality and health risks from contamination in a semiarid region of Northwest China. Expo Health 8:361–379
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2016b) Hydrochemical appraisal of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and the major influencing factors: a case study in and around Hua County, China. Arab J Geosci 9:15
Li PY, Tian R, Xue CY, Wu JH (2017) Progress, opportunities, and key fields for groundwater quality research under the impacts of human activities in China with a special focus on western China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 15:13224–13234
Qian JZ, Wang LL, Zhan HB, Chen Z (2011) Urban land-use effects on groundwater phosphate distribution in a shallow aquifer, Nanfei River basin, China. Hydrogeol J 19:1431–1442
Roden NM, Sargent EV, DiFerdinando GT et al (2015) The cumulative risk to human health of pharmaceuticals in New Jersey surface water. Human Ecol Risk Assess 21:280–295
Sharma S, Kaur J, Nagpal AK, Kaur I (2016) Quantitative assessment of possible human health risk associated with consumption of arsenic contaminated groundwater and wheat grains from Ropar Wetland and its environs. Environ Monit Assess 189:2
Su XS, Wang H, Zhang YL (2013) Health risk assessment of nitrate contamination in groundwater: a case study of an agricultural area in northeast China. Water Resour Manag 27:3025–3034
Su XS, Xu W, Du SH (2014) Responses of groundwater vulnerability to artificial recharge under extreme weather conditions in Shijiazhuang City, China. J Water Supply Res Technol 63(3):224–238
Tan HB, Liu ZH, Rao WB, Wei HZ, Zhang YD, Jin B (2017) Stable isotopes of soil water: Implications for soil water and shallow groundwater recharge in hill and gully regions of the Loess Plateau, China. Agr Ecosyst Environ 243:1–9
United States Environmental Protection Agency (1989) Risk assessment guidance for superfund. Vol I. Human health evaluation manual (Part A)
Vannoppen W, Verachtert E, Poesen J (2017) Pipeflow response in loess-derived soils to precipitation and groundwater table fluctuations in a temperate humid climate. Hydrol Process 31:586–596
Wongsanit J, Teartisup P, Kerdsueb P, Thampoophasiam P, Worakhunpiset S (2015) Contamination of nitrate in groundwater and its potential human health: a case study of lower Mae Klong river basin, Thailand. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:11504–11512
Wongsasuluk P, Chotpantarat S, Siriwong W, Robson M (2014) Heavy metal contamination and human health risk assessment in drinking water from shallow groundwater wells in an agricultural area in UbonRatchathani province, Thailand. Environ Geochem Health 36:169–182
Wu JH, Sun ZC (2016) Evaluation of shallow groundwater contamination and associated human health risk in an alluvial plain impacted by agricultural and industrial activities, mid-west China. Expo Health 8:311–329
Wu J, Xue C, Tian R, Wang S (2017) Lake water quality assessment: a case study of Shahu Lake in the semi-arid loess area of northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 76:232
Xiao CL, Liu JF, Liang XJ, Du SH (2016) Hydrogeochemistry characteristics of groundwater and its suitability for water supply and irrigation in Jilin City, China. Arab J Geosci 9:434
Yang YY, Toor GS, Wilson PC, Williams CF (2017) Micropollutants in groundwater from septic systems: transformations, transport mechanisms, and human health risk assessment. Water Res 123:258–267
Yi SW, Lu HY, Stevens T (2012) SAR TT-OSL dating of the loess deposits in Horqindunefield (northeastern China). Q Geochronol 10:56–61
Yi SW, Buylaert JP, Murray AS, Thiel C, Zeng L, Lu HY (2015) High resolution OSL and post-IR IRSL dating of the last interglacial-glacial cycle at the Sanbahuo loess site (northeastern China). Q Geochronol 30:200–206
Yi SW, Buylaert JP, Murray AS, Lu HY, Thiel C, Zeng L (2016) A detailed post-IR IRSL dating study of the Niuyangzigou loess site in northeastern China. Boreas 45:644–657
Yin XX, Chen LW, He JD, Feng XQ, Zeng W (2016) Characteristics of groundwater flow field after land creation engineering in the hilly and gully area of the Loess Plateau. Arab J Geosci 9:646
Zeng L, Lu HY, Yi SW, Stevens T, Xu ZW, Zhuo HX, Yu KF, Zhang HF (2017) Long-term Pleistocene aridification and possible linkage to high-latitude forcing: new evidence from grain size and magnetic susceptibility proxies from loess–paleosol record in northeastern China. CATENA 154:21–32
Zhai YZ, Zhao XB, Teng YG, Li X, Zhang JJ, Wu J, Zuo R (2017) Groundwater nitrate pollution and human health assessment by using HHRA model in an agricultural area, NE China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 137:130–142
Zhang MS, Dong Y, Sun PP (2012) Impact of reservoir impoundment-caused groundwater level changes on regional slope stability: a case study in the Loess Plateau of Western China. Environ Earth Sci 66:1715–1725
Zhang YL, Ma R, Li ZH (2014) Human health risk assessment of groundwater in Hetao Plain (Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China). Environ Monit Assess 186:4669–4684
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41502223, 51379088, 41772239), Jilin Province Science and Technology Development Plan (Grant No. 20170101202JC) and Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 8164066). The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for comments during the review process that greatly improved the quality of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is a part of a Topical Collection in Environmental Earth Sciences on Water resources development and protection in loess areas of the world, edited by Drs. Peiyue Li and Hui Qian.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, S., Liu, Y., Zhang, L. et al. Assessment of non-carcinogenic health risks due to water contamination in a loess distribution area, northeastern China. Environ Earth Sci 76, 761 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7097-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7097-4