Abstract
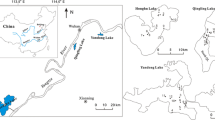
Lake Dongping is a typical warm temperate floodplain lake located in the lower reaches of the Yellow River, North China. As part of the waterway for the South-to-North Water Diversion Project of China, the water quality and trophic status of Lake Dongping are crucial for the successful operation of this project. In order to better understand the controlling factors of water quality and trophic status of Lake Dongping and to provide data for studying ecological baseline of lake restoration, the distribution and the controlling factors of subfossil chironomids were studied here. Our results show that a total of 41 taxa of subfossil chironomids are present in Lake Dongping. The dominant taxa consist of Stempellinella–Zavrelia (30.88%), Propsilocerus akamusi-type (26.79%), Paratanytarsus (13.15%), Cricotopus sylvestris-type (9.12%), and Hydrobaenus conformis-type (6.67%). Among them, the nutrient-tolerant taxa of Stempellinella–Zavrelia and eutrophic taxa of Propsilocerus akamusi-type are widely present in the lake, indicating that Lake Dongping is in a transition from mesotrophication to eutrophication. Redundancy analysis reveals that total phosphorus, water depth, and sulfate (SO4 2−) concentrations are dominant factors controlling the spatial distribution of subfossil chironomids, which explain 12, 9, and 8.5% of the variance, respectively. Therefore, in order to secure the water quality for the South-to-North Water Diversion Project, it is crucial to regulate the input of nutrient and sulfate to Lake Dongping.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barley EM, Walker IR, Kurek J, Cwynar LC, Mathewes RW, Gajewski K, Finney BP (2006) A northwest North American training set: distribution of freshwater midges in relation to air temperature and lake depth. Journal of Paleolimnoly 36:295–314
Brodersen KP, Odgaard BV, Vestergaard O, Anderson NJ (2001) Chironomid stratigraphy in the shallow and eutrophic Lake Sobygaard, Denmark: chironomid-macrophyte co-occurrence. Freshw Biol 46(2):253–267
Brodersen KP, Quinlan R (2006) Midges as palaeoindicators of lake productivity, eutrophication and hypolimnetic oxygen. Quat Sci Rev 25(15):1995–2012
Brooks SJ (2003) Chironomid analysis to interpret and quantify Holocene climate change. In: Mackay AW, Battarbee RW, Birks HJB, Oldfield F (eds) Global change in the Holocene. Arnold, London, pp 328–341
Brooks SJ, Birks HJB (2000) Chironomid-inferred Late-glacial air temperatures at Whitrig Bog, southeast Scotland. J Quat Sci 15:759–764
Brooks SJ, Langdon PG, Heiri O (2007) The identification and use of Palaearctic Chironomidae larvae in palaeoecology. In: QRA technical guide no. 10 quaternary research association, London
Cao YM, Zhang EL, Chen X, John Anderson N, Shen J (2012) Spatial distribution of subfossil chironomidae in surface sediments of a large, shallow and hypertrophic lake (Taihu, SE China). Hydrobiologia 691:59–70
Chaib N, Bouhala Z, Fouzari L, Marziali L, Samraoui B, Rossaro B (2013) Environmental factors affecting the distribution of Chironomid larvae of the Seybouse wadi, North-Eastern Algeria. Journal of Limnoly 72(2):203–214
Chen SY, Liu SS, Yang LW, Chen YY (2014a) Structure characteristics of sediment diatom communities and their relationships with water environment in Lake Dongping, North of China. Journal of Jiangsu Normal University (Natural Science Edition) 32(2):1–6 (in Chinese)
Chen YY, Chen SY, Ma CM, Yu SY, Zhang ZK, Yang LW, Yao M (2014b) Palynological evidence of natural and anthropogenic impacts on aquatic environmental changes over the past 150 years in Dongping Lake, North China. Quatern Int 349:2–9
Chen YY, Chen SY, Yu SY, Zhang ZK, Yang LW, Yao M (2014c) Distribution and speciation of phosphorus in sediments of Lake Dongping. North of China. Environmental Earth Sciences 72(8):3173–3182
Compiling Team for Annals of Dongping County Shandong Province (2006) Annals of Dongping County (1986–2003). Zhonghua Book Company, Beijing (in Chinese)
Davidson TA, Sayer CD, Langdon PG, Burgess A, Jackson M (2010) Inferring past zooplanktivorous fish and macrophyte density in a shallow lake: application of a new regression tree model. Freshw Biol 55:584–599
Engels S, Cwynar LC (2011) Changes in fossil chironomid remains along a depth gradient: evidence for common faunal thresholds within lakes. Hydrobiologia 665:15–38
He DJ, Xing YH, Jiang RX, Cheng L (2010) Distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus in water and eutrophication assessment of Lake Dongping. Environ Sci Technol 33(8):45–61 (in Chinese)
Heiri O (2004) Within-lake variablility of subfossil chironomid assemblages in shallow Norwegian lakes. J Paleolimnol 32:67–84
Henrikson L, Olofsson JB, Oscarson HG (1982) The impact of acidification on Chironomidae (Diptera) as indicated by subfossil stratification. Hydrobiologia 86:223–229
Hill MO (1973) Diversity and evenness: a unifying notation and its consequences. Ecology 54:427–432
Hou HP, Ge YX, Pan N (2013) Water quality assessment and water pollution prevention countermeasures of Lake Dongping. Yellow River 35(12):43–46 (in Chinese)
Korhola A, Olander H, Blom T (2000) Cladocera and chironomid assemblages as quantitative indicators of water depth in subarctic Fennoscandian lakes. J Paleolimnol 24:43–54
Langdon PG, Ruiz Z, Brodersen KP, Foster IDL (2006) Assessing lake eutrophication using chironomids: understanding the nature of community response in different lake types. Freshw Biol 51:562–577
Langdon PG, Ruiz Z, Wynne S, Sayer CD, Davidson TA (2010) Ecological influences on larval chironomid communities in shallow lakes: implications for palaeolimnological interpretations. Freshw Biol 55:531–545
Liu HC (2012) The research of water environmnent condition and the influencing factor of Lake Dongping. Shandong University, China (in Chinese)
Lu M, Liu JZ, Chen YJ (2012) Analysis on the influencing factors and comprehensive management of environmental problems in Lake Dongping. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences 40(9):5490–5492 (in Chinese)
Lv YF (2013) Studies on distribution of nutrients and their release from sediment in Lake Dongping. Shandong Jianzhu University, China (in Chinese)
Margalef R (1958) Information theory in ecology. General Systems 3:36–71
Mei RB, Wang Y, Wang XQ, Qin S (2014) Reason analysis and prevention measure of pollution in Dawen River Basin. Environment and Development 26(1):125–127 (in Chinese)
Pielou EC (1975) Ecological diversity. John Wiley Sons, New York, p 165
Pinder LCV, Morley DJ (1995) Chironomidae as indicators of water quality-with a comparison of the chironomid faunas of a series of contrasting Cumbrian tarns. In: Harrington R, Stork NE (eds) Insects in a changing environment. Academic Press, London, pp 272–290
Rieradevall M, Brooks SJ (2001) An identification guide to subfossil Tanypodinae larvae (Insecta: Diptera: Chironomidae) based on cephalic setation. J Paleolimnol 25:81–99
Saether OA (1979) Chironomid communities as water quality indicators. Ecography 2:65–74
Shannon CE, Weaver W (1963) The mathematical theory of communication. University Illinois Press, Urbana, p 117
Shu FY, Kong L, Wang SD, Zi FF (2013) Chironomid larva community and indication to eutrophication progress in Lake Nansi, Shandong, China. Chin J Appl Environ Biol 19(1):141–146 (in Chinese)
Walker IR, MacDonald GM (1995) Distributions of Chironomidae (Insecta: Diptera) and other freshwater midges with respect to treeline, Northwest Territories, Canada. Arct Alp Res 27:258–263
Wang S, Dou H (1998) Lakes in China. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Wen YM, Wei XG, Shu TF, Zhou JF, Yu GH, Li F, Huang YY (2007) Forms and balance of nitrogen and phosphorus in cage culture waters in Guangdong Province, China. Chin Geogra Sci 17(4):370–375
Wiederholm T (1980) Use of benthos in lake monitoring. J Water Pollut Control Fed 52(3):537–547
Wiederholm T (1983) Chironomidae of the Holarctic region: keys and diagnoses. Part 1-Larvae. Entomol Scand Suppl 19:1–457
Wu ZB (2003) Environment monitoring. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Wu FC, Wan GJ, Huang RG, Cai YR (1998) Environmental impact of sulfate concentration increasing of lakes. Acta Sci Circumst 18(1):28–33 (in Chinese)
Yu FF (2013) Effect of external sulfate on nutrients and heavy metals in the sediments of Lake Moshui in Wuhan. Huazhong Agriculture University, Wuhan (in Chinese)
Zhang HJ (1987) Process of lakes along the lower Yellow River in ancient time. J Yellow River 5:67–69 (in Chinese)
Zhang EL, Liu EF, Jones R, Langdon P, Yang XD, Shen J (2010) A 150-year record of recent changes in human activity and eutrophication of Lake Wushan from the middle reach of the Yangtze River, China. J Limnol 69(2):235–241
Zhang M, Cai QH, Tang T, Wang XZ, Yang SY, Kong LH (2011) Macrobenthos community structure and its spatial distribution in Erhai watershed lakes. Chin J Ecol 30(8):1696–1702 (in Chinese)
Zhang EL, Zheng BY, Cao YM, Gao G, Shen J (2012) Influence of environmental parameters on the distribution of subfossil chironomids in surface sediments of Bosten lake (Xinjiang, China). J Limnol 71(2):291–298
Zhong F, Liu BY, He F, Liang W, Cheng SP, Zuo JC, Wu ZB (2007) Effect of aquatic ecological restoration on zoobenthos community of Lotus Lake. Chin J Appl Environ Biol 13(1):55–60 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41672345 and 41401563), a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education. We are grateful to Profs. Xiangdong Yang, Yanhong Wu, and Dr. Rong Wang for their assistance in the conduct of field sampling. Our thanks are also expressed to Dr. Yanmin Cao and Zhanfang Hou for their constructive suggestions, and to Dr. Jinjia Wu for his assistance with the diagrams. The authors also would like to thank the anonymous reviewer’s aid in the development and improvement of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Chen, S., Zhang, J. et al. Environmental factors controlling the spatial distribution of subfossil Chironomidae in surface sediments of Lake Dongping, a warm temperate lake in North China. Environ Earth Sci 76, 524 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6858-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6858-4