Abstract
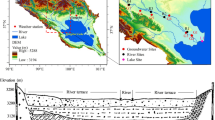
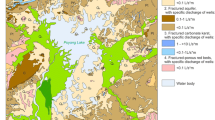
To improve water management, the relation and the hydrochemical evolution of surface water and groundwater were studied in the Songnen Plain. The surface water and groundwater samples were evaluated for stable isotopes and hydrochemistry analyses. The stable isotopic compositions (δ 18O, δ D) indicate the groundwater recharges from the precipitation. However, the connectivity between surface water and groundwater is weak, because of the clay layer and the interrupted aquifer. The water evolution is from Ca–Mg–HCO3 to Na–HCO3 by the evaporation, water–rock interaction, and ion exchange processes. The water evaporation and leaching of saline–alkaline soil are the main reasons for water salinity. Further, the leaching of salts in the soil during recharging from backwater and irrigation water intensifies the salinization. The relationship between and evolution of surface water and groundwater provide important guidance for water management not only in the arid and semi-arid area, but also in the soda saline–alkali soil regions of the world.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson EI (2005) Modeling groundwater–surface water interactions using the Dupuit approximation. Adv Water Resour 28(4):315–327
Ayenew T, Kebede S, Alemyahu T (2008) Environmental isotopes and hydrochemical study applied to surface water and groundwater interaction in the Awash River basin. Hydrol Process 22(10):1548–1563
Banks EW, Simmons CT, Love AJ, Shand P (2011) Assessing spatial and temporal connectivity between surface water and groundwater in a regional catchment: implications for regional scale water quantity and quality. J Hydrol 404:30–49. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.04.017
Baskaran S, Ransley T, Brodie RS, Baker P (2009) Investigating groundwater–river interactions using environmental tracers. J Geol Soc Aust 56(1):13–19
Bruce JP (2011) Protecting groundwater: the invisible and vital resource. Backgrounder, no 136. C.D. Howe Institute, Toronto
Chen Z, Wei W, Liu J, Wang Y, Chen J (2010) Identifying the recharge sources and age of groundwater in the Songnen Plain (Northeast China) using environmental isotopes. Hydrogeol J 19(1):163–176. doi:10.1007/s10040-010-0650-9
Edmunds W (2003) Groundwater evolution in the Continental Intercalaire aquifer of southern Algeria and Tunisia: trace element and isotopic indicators. Appl Geochem 18(6):805–822. doi:10.1016/s0883-2927(02)00189-0
Edmunds WM, Bath AH, Miles DL (1982) Hydrochemical evolution of the East Midlands Triassic sandstone aquifer, England. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 46(11):2069–2081
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 170(3962):1088–1090
Heilongjiang land reclamation bureau (ed) (2009) Statistical yearbook of Heilongjiang reclamation area. China Statistics Press, Beijing
Li B, Zhou C (2001) Sandy desertification in west of Northeast China plain in the past 10 years (in Chinese). Acta Geographica Sinica 56(3):307–315
Liu J, Song X, Yuan G, Sun X, Liu X, Wang S (2010) Characteristics of δ18O in precipitation over eastern monsoon China and the water vapor sources. Chin Sci Bull 55(2):200–211
Liu S, Kang Y, Wan S, Wang Z, Liang Z, Sun X (2011) Water and salt regulation and its effects on Leymus chinensis growth under drip irrigation in saline–sodic soils of the Songnen Plain. Agr Water Manag 98(9):1469–1476. doi:10.1016/j.agwat.2011.04.016
Sophocleous M (2002) Interactions between groundwater and surface water: the state of the science. Hydrogeol J 10(1):52–67
Wang H, Wan Z, Yu S, Luo X, sun G (2004) Catastrophic eco-environmental change in the Songnen plain, northeastern China since 1900s. Chin Geogr Sci 14(2):179–185
Wang L, Seki K, Miyazaki T, Ishihama Y (2009) The causes of soil alkalinization in the Songnen Plain of Northeast China. Paddy Water Environ 7(3):259–270. doi:10.1007/s10333-009-0166-x
Winter TC, Harvey JW, Franke OL, Alley WM (1998) Ground water and surface water: a single resource. Diane Pub Co, Denver
Woessner WW (2000) Stream and fluvial plain ground water interactions: rescaling hydrogeologic thought. Groundw 38(3):423–429
Xiao C, Liang X, Zhang F, Feng B, Xie S (2009) Groundwater numerical simulation of multi-aquifers in Songnen plain. In: Zhang CK, Tang HW (eds) Advances in Water Resources and Hydraulic Engineering, pp 214–218
Yuan L (2006) Hydrochemistry of the groundwater in Songnen plain (in Chinese). Geol Resour 15 (2):122–125,132
Zhang DF, Wang SJ (2001) The process and driving forces of eco-geo-environmental evolution of the Songnen Plain in northeast China since the Quaternary. Environ Geol 40(11–12):1362–1366
Zhang J, Zhang P, Chi Y (1991) The situation and countermeasures of groundwater resource in Songnen plain (in Chinese). Heilongjiang Sci Technol Water Conserv 4:1–5
Zhang GX, Deng W, Yang YS, Salama RB (2007) Evolution study of a regional groundwater system using hydrochemistry and stable isotopes in Songnen Plain, Northeast China. Hydrol Process 21(8):1055–1065
Zhang B, Song X, Zhang Y, Han D, Tang C, Yu Y, Ma Y (2012) Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality assessment of surface water and groundwater in Songnen plain, Northeast China. Water Res 46(8):2737–2748. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2012.02.033
Zhang B, Song X, Zhang Y, Han D, Tang C, Yang L, Wang Z, Liu T (2014) A study of the interrelation between surface water and groundwater using isotopes and chlorofluorocarbons in Sanjiang plain, Northeast China. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3279-5
Zhao H, Zhang Z, Chen Y (2010) Lowering of groundwater level and its negative environment effects in the Songnen Plain (in Chinese). J Arid Land Resour Environ 24(1):126–130
Zhu B, Yang X (2007) The ion chemistry of surface and ground waters in the Taklimakan Desert of Tarim Basin, western China. Chin Sci Bull 52(12):2123–2129. doi:10.1007/s11434-007-0298-6
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Main Direction Program of Knowledge Innovation of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. KZCX2-YW-Q06-1), the Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40830636), the Innovation Team Training Plan of the Tianjin Education Committee (TD12-5037) and the Doctoral Found of Tianjin Normal University (52XB1401). We sincerely thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for comments that greatly improved this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, B., Song, X., Zhang, Y. et al. The relationship between and evolution of surface water and groundwater in Songnen Plain, Northeast China. Environ Earth Sci 73, 8333–8343 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3995-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3995-x