Abstract
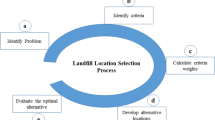
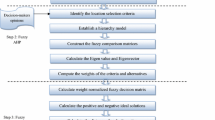
Landfill site selection is a multi-attribute decision problem, through which factors like available land area, soil conditions, climatological conditions, and economic considerations are investigated in detail. Frequently, it is a challenge to come up with “the one” solution while tackling such complex systems. Therefore, use of tools such as fuzzy analytic hierarchy process (fuzzy AHP) and fuzzy technique for order preference by similarity to ideal solution (fuzzy TOPSIS) should be preferred in order to emphasize pros and cons for each of the studied options. In this study, three possible landfill sites for the city of Istanbul are evaluated through expert opinion and by facilitating fuzzy AHP and fuzzy TOPSIS. Initially, the landfill site selection problem is presented in the framework of a model and then the model is mathematically solved by calculating the individual criterion weights. In conclusion, considering the rapid rate of urbanization for the city of Istanbul, the possible landfill sites convey similar overall results, but differ in specific criteria.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinci G, Guven ED, Gok G (2012) Evaluation of waste management options and resource conservation potentials according to the waste characteristics and household income: a case study in Aegean Region, Turkey. Resour Conserv Recycl 58:114–124
Al-Jarrah O, Abu-Qdais H (2006) Municipal solid waste landfill siting using intelligent system. Waste Manag 26:299–306
Al-Yaqout AF, Koushki PA, Hamoda MF (2002) Public opinion and siting solid waste landfills in Kuwait. Resour Conserv Recycl 35:215–227
Barlaz M, Kaplan P, Ranjithan S, Rynk R (2003) Evaluating environmental impacts of solid waste management alternatives. BioCycle 44:52–56
Beskese A, Kahraman C, Irani Z (2004) Quantification of flexibility in advanced manufacturing systems using fuzzy concept. Int J Prod Econ 89:45–56
Bozbura FT, Beskese A, Kahraman C (2007) Prioritization of human capital measurement indicators using fuzzy AHP. Expert Syst Appl 32(4):1100–1112
Chen CT (2000) Extensions of the TOPSIS for group decision-making under fuzzy environment. Fuzzy Set Syst 114:1–9
Chen CT, Lin CT, Sue-Fn H (2006) A fuzzy approach for supplier evaluation and selection in supply chain management. Int J Prod Econ 102:289–301
Dai C, Li YP, Huang GH (2011) A two-stage support-vector-regression optimization model for municipal solid waste management—a case study of Beijing, China. J Environ Manag 92(12):3023–3037
Donevska KR, Gorsevski PV, Jovanovski M, Pesevski I (2012) Regional non-hazardous landfill site selection by integrating fuzzy logic, AHP and geographic information systems. Environ Earth Sci 67:121–131
Ertuğrul İ, Karakaşoğlu N (2008) Comparison of fuzzy AHP and fuzzy TOPSIS methods for facility location selection. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 39(7):783–795
Gbanie SP, Tengbe PB, Momohb JS, Medo J, Tamba V, Kabbac S (2013) Modelling landfill location using geographic information systems (GIS) and multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA): case study Bo, Southern Sierra Leone. Appl. Geogr 36:3–12
Gorsevski PV, Donevska KR, Mitrovski CD, Frizado JP (2012) Integrating multi-criteria evaluation techniques with geographic information systems for landfill site selection: a case study using ordered weighted average. Waste Manag 32:287–296
Huang S, Li X, Wang Y (2012) A new model of geo-environmental impact assessment of mining: a multiple-criteria assessment method integrating fuzzy-AHP with fuzzy synthetic ranking. Environ Earth Sci 66:275–284
Hunce SY, Akgul D, Demir G, Mertoglu B (2012) Solidification/stabilization of landfill leachate concentrate using different aggregate materials Waste Manag 32:1394–1400
Hwang CL, Yoon K (1981) Multiple attribute decision making methods and applications. Springer, New York
Kahraman C, Cebi S (2009) A new multi-attribute decision making method: hierarchical fuzzy axiomatic design. Expert Syst Appl 36(3):4848–4861
Kanat G (2010) Municipal solid waste management in Istanbul. Waste Manag 30:1737–1745
Lohri CR, Camenzind EJ, Zurbrügg C (2014) Financial sustainability in municipal solid waste management—costs and revenues in Bahir Dar, Ethiopia. Waste Manag 34(2):542–552
Moh YC, Abd Manaf L (2014) Overview of household solid waste recycling policy status and challenges in Malaysia. Resour Conserv Recycl 82:50–61
Opricovic S, Tzeng GH (2004) Compromise solution by MCDM methods: a comparative analysis of VIKOR and TOPSIS. Eur J Oper Res 156(2):445–455
Ozcakar N, Demir HH (2011) İmalat sektöründe bulanık TOPSIS yöntemiyle tedarikçi seçimi. İstanbul Üniversitesi İşletme Fakültesi Yönetim Dergisi 22(69):25–44
Saaty TL (1980) The analytic hierarchy process: planning, priority setting, resource allocation. McGraw-Hill, New York
Shahabi S, Keihanfard S, Bin Ahmad B, Amiri MJT (2013) Evaluating Boolean, AHP and WLC methods for the selection of waste landfill sites using GIS and satellite images. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2816-y
Shaw K, Shankar R, Yadav SS, Thakur LS (2012) Supplier selection using fuzzy AHP and fuzzy multi-objective linear programming for developing low carbon supply chain. Expert Syst Appl 39(9):8182–8192
Sener B, Suzen ML, Doyuran V (2006) Landfill site selection by using geographic information systems. Environ Geol 49:376–388
Spires EE (1991) Using the analytic hierarchy process to analyze multi-attribute decisions. Multivar Behav Res 26:345–361
TUIK (2012) Turkish Statistical Institute, Official newsletter, No. 16
Yoon KP, Hwang CL (1995) Multiple attribute decision making: an introduction. Sage University Paper series on quantitative applications in the social sciences, Thousand Oaks, CA
Zhang Y, Huang GH, He L (2014) A multi-echelon supply chain model for municipal solid waste management system. Waste Manag 34(2):553–561
Zadeh L (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8:338–353
Zamorano M, Molero E, Hurtado A, Grindlay A, Ramos A (2008) Evaluation of a municipal landfill site in Southern Spain with GIS-aided methodology. J Hazard Mater 160:473–481
Zimmermann HJ (1994) Fuzzy set theory and its applications. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beskese, A., Demir, H.H., Ozcan, H.K. et al. Landfill site selection using fuzzy AHP and fuzzy TOPSIS: a case study for Istanbul. Environ Earth Sci 73, 3513–3521 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3635-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3635-5