Abstract
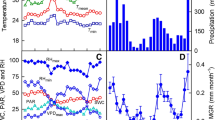
Sap flow (SF)of a willow tree, meteorological variables, soil water content, and water table depth were measured during the growing period from mid-April to October, 2011 in the semi-arid Hailiutu River catchment, Northwest China. The measurements of SF showed diurnal fluctuations in sunny days and seasonal changes from 1.65 l/h in mid-April to 33 l/h in July. At hourly scale, SF is significantly correlated with net radiation, followed by air temperature, relative humidity, and wind speed. At daily scale, air temperature affects the dynamics of SF significantly. Daily SF correlates positively with net radiation and negatively with relative humidity. There is no correlation observed between daily SF and wind speed. The measurements of SF do not indicate water stress although the experimental period is dry. Correlation analysis shows that SF is strongly correlated with soil moisture and water table depth, indicating the willow tree uses both soil water and groundwater for transpiration.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alarcon JJ, Ortuno MF, Nicolas E, Torres R, Torrecillas A (2005) Compensation heat-pulse measurements of sap flow for estimating transpiration in young lemon trees. Biol Plant 49(4):527–532
Bai YG, Song YD, Zhou HF, Zhao RF, Chai ZP (2005) Study on the change of sap flow in the stems of Populus euphratica using thermal pulse measurement. Arid Land Geogr 28(3):373–376
Cao SL (2011) Impact of China’s large-scale ecological restoration program on the environment and society in arid and semiarid areas of China: achievements, problems, synthesis, and applications, critical reviews. Environ Sci Technol 41(4):317–335
Cao SX, Wang GS (2010) Questionable value of planting thirsty trees in dry regions. Nature 465:31
Chu CR, Hsieh CI, Wu SY, Phillips NG (2009) Transient response of sap flow to wind speed. J Exp Bot 60(1):249–255
Ding RS, Kang SZ, Li FS, Zhang YQ, Tong L, Sun QT (2010) Evaluating eddy covariance method by large-scale weighing lysimeter in a maize field of northwest China. Agric Water Manag 98(1):87–95
Du ZC, Yang ZG, Cui XY (2001) A comparative study on leaf area index of five plant communities in typical steppe region of Inner Mongolia. Chin J Grassland 23(5):13–18
Granier A (1985) A new method of sap flow measurement in tree stems. Annales Des Sciences Forestieres 42:193–200
Green SR, Mcnaughton KG, Clothier BE (1989) Observations of night-time water use in kiwifruit vines and apple trees. Agric For Meteorol 48:251–261
Green SR, Clothier BE, Jardine B (2003) Theory and practical application of heat pulse to measure sap flow. Agron J 95:1371–1379
Guan DX, Zhang XJ, Yuan FH, Chen NN, Wang AZ, Wu JB, Jin CJ (2011) The relation between sap flow of intercropped young poplar trees (Populus × euramericana cv. N3016) and environmental factors in a semiarid region of northeastern China. Hydrol Process. doi:10.1002/hyp.8250
Hall RL, Allen SJ, Rosier PTW, Hopkings R (1998) Transpiration from coppiced poplar and willow measured using sap flow methods. Agric For Meteorol 90:275–290
Huang L, Zhang ZS, Li XP (2010) Sap flow of Artemisia ordosica and the influence of environmental factors in a revegetated desert area: Tengger Desert, China. Hydrol Process 24:1248–1253
Jackson BJ, Jobbagy EG, Avissar R, Roy SB, Barrett DJ, Cook CW, Farley KA, Le Maitre DC, McCarl BA, Murray BC (2005) Trading water for carbon with biological carbon sequestration. Science 310:1944–1947
Jonard F, Andre F, Ponette Q, Vincke C, Jonard M (2011) Sap flux density and stomatal conductance of European beech and common oak trees in pure and mixed stands during the summer drought of 2003. J Hydrol 409:271–381
Kjelgaard JF, Stockle CO, Black RA, Campbell GS (1997) Measuring sap flow with the heat balance approach using constant and variable heat inputs. Agric For Meteorol 74(1–2):27–40
Kume T, Otsuki K, Du S, Yamanaka N, Wang YL, Liu GB (2011) Spatial variation in sap flow velocity in semiarid region trees: its impact on stand-scale transpiration estimates. Hydrol Process. doi:10.1002/hyp.8205
Kunert N, Schwendenmann L, Holscher D (2010) Seasonal dynamics of tree sap flux and water use in nine species in Panamanian forest plantations. Agric For Meteorol 150:411–419
Lamb D, Erskine PD, Parrotta JA (2005) Restoration of degraded tropical forest landscapes. Science 310:1628–1632
Liu B, Zhao WZ, Jin B (2011) The response of sap flow in desert shrubs to environmental variables in an arid region of China. Ecohydrology 4:448–457
Loik ME, Breshears DD, Lauenroth WK, Belnap J (2004) A multi-scale perspective of water pulses in dryland ecosystems: climatology and ecohydrology of the western USA. Oecologia 141(2):269–281
Ma JX, Chen YN, Li WH, Huang X, Zhu CG, Ma XD (2012) Sap flow characteristics of four typical species in desert shelter forest and their responses to environmental factors. Environ Earth Sci 68(1):151–160
Malek E, Bingham G (1993) Comparison of the Bowen ratio-energy balance and the water balance methods for the measurement of evapotranspiration. J Hydrol 146:209–220
Mollema PN, Antonellini M, Gabbianelli G, Galloni E (2013) Water budget management of a coastal pine forest in a Mediterranean catchment (Marina Romea, Ravenna, Italy). Environ Earth Sci 68(6):1707–1721
O’Brien JJ, Oberbauer SF, Clark DB (2004) Whole tree xylem sap flow responses to multiple environmental variables in a wet tropical forest. Plant, Cell Environ 27:551–567
Oguntunde PG (2005) Whole-plant water use and canopy conductance of cassava under limited available soil water and varying evaporative demand. Plant Soil 278:371–383
Pereira AR, Green SR, Nova NAV (2007) Sap flow, leaf area, net radiation and the Priestley-Taylor formula for irrigated orchards ad isolated trees. Agric Water Manag 16:48–52
Qu YP, Kang SZ, Li FS, Zhang JH, Xia GM, Li WC (2007) Xylem sap flows of irrigated Tamarix eloongata Ledeb and the influence of environmental factors in the desert region of Northwest China. Hydrol Process 21:1363–1369
Saugier B, Granier A, Pontailler JY, Dufrene E, Baldocchi DD (1997) Transpiration of a boreal pine forest measured by branch bag, sap flow and micrometeorological methods. Tree Physiol 17(8–9):511–519
Si JH, Feng Q, Zhang XY (2004) Application of heat-pulse technique to determine the stem sap flow of Populus euphratica. J Glaciol Geocryol 26(4):503–508
Sun G, Zhou G, Zhang Z, Wei X, McNulty SG, Vose JM (2006) Potential water yield reduction due to forestation across China. J Hydrol 328:548–558
Sun G, Noormets A, Chen J, McNulty SG (2008) Evapotranspiration estimates from eddy covariance towers and hydrologic modeling in managed forests in Northern Wisconsin, USA. Agric For Meteorl 148:257–267
Wullschleger SD, Meinzer FC, Vertessy RA (1998) A review of whole-plant water use studies in trees. Tree Physiol 18:499–512
Xia GM, Kang SZ, Li FS, Zhang JH, Zhou QY (2008) Diurnal and seasonal variations of sap flow of Caragana korshinskii in the arid desert region of north-west China. Hydrol Process 22:1197–1205
Yang Z, Zhou YX, Wenninger J, Uhlenbrook S (2012) The causes of flow regime shifts in the semi-arid Hailiutu River. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 16:87–103
Yue GY, Zhao HL, Zhang TH, Zhao XY, Niu L, Drake S (2008) Evaluation of water use of Caragana microphylla with the stem heat-balance method in Horqin Sandy Land, Inner Mongolia, China. Agric For Meteorol 148:1668–1678
Zeggaf AT, Takuechi S, Dehghanisanij Anyoji H, Aaron TY (2008) A Bowen ratio technique for partitioning energy fluxes between maize transpiration and soil surface evaporation. Agron J 100(4):988–996
Zhang XY, Gong JD, Zhou MX (2004) Study on volume and velocity of stem sap flow of Haloxylon ammodendron by heat pulse technique. Acta Botanica Boreal Occident Sinica 24(12):2250–2254
Zhang BZ, Kang SZ, Zhang L, Du TS, Li SE, Yang XY (2007) Estimation of seasonal crop water consumption in vineyard using Bowen ratio-energy balance method. Hydrol Process 21(26):3635–3641
Zhao WZ, Liu B (2010) The response of sap flow in shrubs to rainfall pulses in the desert region of China. Agric For Meteorol 150:1297–1306
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Asia Facility for China project “Partnership for education and research in water and ecosystem interactions”, the Groundwater Circulation and Rational Development in the Ordos Plateau project (1212010634204), Groundwater monitoring in the Ordos Basin, the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (4103752), Shaanxi Science and Technology Research and Development Program (2011KJXX56) and Honor Power Foundation. We would like to thank the three anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments and suggestions that greatly improved the earlier version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, L., Zhou, Y., Huang, J. et al. Dynamics of willow tree (Salix matsudana) water use and its response to environmental factors in the semi-arid Hailiutu River catchment, Northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 71, 4997–5006 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2891-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2891-0