Abstract
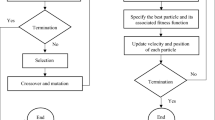
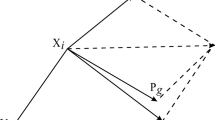
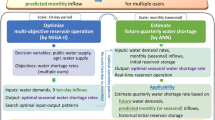
In this paper, a new methodology is developed for optimization of water and waste load allocation in reservoir–river systems considering the existing uncertainties in reservoir inflow, waste loads and water demands. A stochastic dynamic programming (SDP) model is used to optimize reservoir operation considering the inflow uncertainty, and another model called PSO-SA is developed and linked with the SDP model for optimizing water and waste load allocation in downstream river. In the PSO-SA model, a particle swarm optimization technique with a dynamic penalty function for handling the constraints is used to optimize water and waste load allocation policies. Also, a simulated annealing technique is utilized for determining the upper and lower bounds of constraints and objective function considering the existing uncertainties. As the proposed water and waste load allocation model has a considerable run-time, some powerful soft computing techniques, namely, Regression tree Induction (named M5P), fuzzy K-nearest neighbor, Bayesian network, support vector regression and an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system, are trained and validated using the results of the proposed methodology to develop real-time water and waste load allocation rules. To examine the efficiency and applicability of the methodology, it is applied to the Dez reservoir–river system in the south-western part of Iran.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bashi-Azghadi SN, Kerachian R (2010) Locating monitoring wells in groundwater systems using embedded optimization and simulation models. Sci Total Environ 408(10):2189–2198
Bashi–Azghadi SN, Kerachian R, Bazargan–Lari MR, Solouki K (2010) Characterizing an unknown pollution source in groundwater resources systems using PSVM and PNN. Expert Syst Appl 37(10):7154–7161
Cai X, McKinney D, Lasdon LA (2001) Piece-by-piece approach to solving large non linear water resources management models. J Water Resour Plan Manag 127(6):363–368
Chaves P, Chang FJ (2008) Intelligent reservoir operation system based on evolving artificial neural networks. Adv Water Resour 31:926–936
Dai T, Labadie JW (2001) River basin network model for integrated water quantity/quality management. J Water Resour Plan Manag 127(5):295–305
de Azevedo LGT, Gates TK, Fontane DG, Labadie JW, Porto RL (2000) Integration of water quantity and quality in strategic river basin planning. J Water Resour Plan Manag 126(2):85–97
de Moraes MA, Cai X, Ringler C, Albuquerque BE, Vieira da Rocha S, Amorim CA (2010) Joint water quantity-quality management in a biofuel production area—integrated economic-hydrologic modeling analysis. J Water Resour Plan Manag 136(4):502–511
Dezab Consulting Engineers (2001) Restoration of the Karoon-Dez river system, Technical Report
Etemad-Shahidi A, Ghaemi N (2011) Model tree approach for prediction of pile groups scour due to waves. Ocean Eng 38:1522–1527
Etemad–Shahidi A, Mahjoobi J (2009) Comparison between M5 model tree and neural networks for prediction of significant wave height in Lake Superior. Ocean Eng 36:1175–1181
Jiang C, Han H, Liu GR, Liu GP (2008) A nonlinear interval number programming method for uncertain optimization problems. Eur J Oper Res 188:1–13
Karamouz M, Moridi A, Fayyazi HM (2006) Dealing with conflict over water quality and quantity allocation: a case study. Scientia Iranica 15(1):34–49
Karamouz M, Ahmadi A, Moridi A (2009) Probabilistic reservoir operation using Bayesian stochastic model and support vector machine. Adv Water Resour 32:1588–1600
Keller JM, Gray MR, Givens JA Jr (1985) A fuzzy K-nearest neighbor algorithm. IEEE Trans Syste Cybernetics 15(4):580–585
Kerachian R, Karamouz M (2007) A stochastic conflict resolution model for water quality management in reservoir–river systems. Adv Water Resour 30:866–882
Malekmohamadi I, Bazargan–Lari MR, Kerachian R, Nikoo MR, Fallahnia M (2011) Evaluating the efficacy of SVMs, BNs, ANNs and ANFIS in wave height prediction. Ocean Eng 38:487–497
Malekmohammadi B, Kerachian R, Zahraie B (2009) Developing monthly operating rules for a cascade system of reservoirs: application of Bayesian networks. Environ Model Softw 24:1420–1432
Mesbah SM, Kerachian R, Nikoo MR (2009) Developing real time operating rules for trading discharge permits in rivers: application of Bayesian Networks. Environ Model Softw 24:238–246
Mousavi SJ, Ponnambalam K, Karray F (2007) Inferring operating rules for reservoir operations using fuzzy regression and ANFIS. Fuzzy Sets Syst 158:1064–1082
Nikoo MR, Kerachian R, Karimi A, Azadnia AA (2012a) Optimal water and waste-load allocations in rivers using a fuzzy transformation technique: a case study. Environ Monit Assess. doi:10.1007/s10661-012-2726-6
Nikoo MR, Kerachian R, Karimi A (2012b) A nonlinear interval model for water and waste load allocations in river basins. Water Resour Manage 26(10):2911–2926
Paredes–Arquiola J, Andreu–Álvarez J, Martín–Monerris M, Solera A (2010) Water quantity and quality model applied to the Jucar river basin, Spain. J Water Resour Manage ASCE 24:2759–2779
Soltani F, Kerachian R, Shirangi E (2010) Developing operating rules for reservoirs considering the water quality issues: application of ANFIS-based surrogate models. Expert Syst Appl 37:6639–6645
Wang XL, Cheng JH, Yin ZJ, Guo MJ (2011) A new approach of obtaining reservoir operation rules: artificial immune recognition system. Expert Syst Appl 38:11701–11707
Zhang W, Wang Y, Peng H, Li Y, Tang J, Wu KB (2010) A coupled water quantity–quality model for water allocation analysis. Water Resour Manage 24:485–511
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by Islamic Azad University, East-Tehran Brach, Tehran, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikoo, M.R., Kerachian, R., Karimi, A. et al. Optimal water and waste load allocation in reservoir–river systems: a case study. Environ Earth Sci 71, 4127–4142 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2801-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2801-5