Abstract
Levulinic acid (LA) was discovered in 1875 by heating candy with concentrated acid. Since then, it has been generated in a variety of ways from commercial sugars and their products in-cluding glucose, fructose, cellulose, 5-(hydroxymethyl)furfural (5-HMF), maleic anhydride and furfuryl alcohol. However, the concern of food security has led to search for sustainable feedstock for the production of LA such as biomass. Although the use of biomass as substrate for LA synthesis offer various advantages, however, the shift to a bioeconomy remains difficult due to the several contributing variables that must be addressed, as detailed in this review. Various catalysts, including homogeneous, heterogeneous, and ionic liquids, have been employed in the development of an ecologically acceptable and lucrative method for producing LA from biomass. This study examines the literature on LA production from 1875 to 2021, what has been accomplished, and what ongoing obstacles exist.
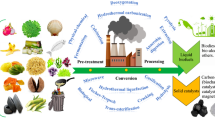
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yan, K., Jarvis, C., Gu, J., Yan, Y.: Production and catalytic transformation of levulinic acid: A platform for speciality chemicals and fuels. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 51, 986–997 (2015)
Kurian, J.K., Nair, G.R., Hussain, A., Raghavan, G.V.: Feedstocks, logistics and pre-treatment processes for sustainable lignocellulosic biorefineries: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 25, 205–219 (2013)
Lomba, L., Giner, B., Bandrés, I., Lafuente, C., Pino, M.R.: Physicochemical properties of green solvents derived from biomass. Green Chem. 13(8), 2062–2070 (2011)
Ariba, H., Wang, Y., Devouge-Boyer, C., Stateva, R.P., Leveneur, S.: Physicochemical properties for the reaction systems: Levulinic acid, its esters, and γ-valerolactone. J. Chem. Eng. Data 65(6), 3008–3020 (2020)
Mthembu, L.D., Lokhat, D., Deenadayalu, N.: Catalytic condensation of depithed sugarcane bagasse derived levulinic acid into diphenolic acid. BioResources 16(2), 2235–2248 (2021)
Delgado, J., Salcedo, W.N.V., Bronzetti, G., Moreno, V.C., Mignot, M., Legros, J., Held, C., Grénman, H., Leveneur, S.: Kinetic model assessment for the synthesis of γ-valerolactone from n-butyl levulinate and levulinic acid hydrogenation over the synergy effect of dual catalysts Ru/C and Amberlite IR-120. Chem. Eng. J. 430, 133053 (2022)
Wang, Y., Cipolletta, M., Vernières-Hassimi, L., Casson-Moreno, V., Leveneur, S.: Application of the concept of linear free energy relationships to the hydrogenation of levulinic acid and its corresponding esters. Chem. Eng. J. 374, 822–831 (2019)
Piskun, A., Van de Bovenkamp, H., Rasrendra, C., Winkelman, J., Heeres, H.: Kinetic modeling of levulinic acid hydrogenation to γ-valerolactone in water using a carbon supported Ru catalyst. Appl. Catal. A 525, 158–167 (2016)
Mthembu, L., Lokhat, D., Deenadayalu, N.: Esterification of levulinic acid to ethyl levulinate: optimization of process conditions using commercial levulinic acid and extension to the use of levulinic acid derived from depithed sugarcane bagasse. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01632-5
Russo, V., Tesser, R., Rossano, C., Cogliano, T., Vitiello, R., Leveneur, S., Di Serio, M.: Kinetic study of Amberlite IR120 catalyzed acid esterification of levulinic acid with ethanol: From batch to continuous operation. Chem. Eng. J. 401, 126126 (2020)
Démolis, A., Essayem, N., Rataboul, F.: Synthesis and applications of alkyl levulinates. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2(6), 1338–1352 (2014)
da Costa Lopes, A.M., João, K.G., Morais, A.R.C., Bogel-Łukasik, E., Bogel-Łukasik, R.: Ionic liquids as a tool for lignocellulosic biomass fractionation. Sustain. Chem. Processes 1(1), 1–31 (2013)
Rackemann, D.W., Doherty, W.O.: The conversion of lignocellulosics to levulinic acid. Biofuels, Bioprod. Biorefin. 5(2), 198–214 (2011)
Di Bucchianico, D.D.M., Wang, Y., Buvat, J.-C., Pan, Y., Moreno, V.C., Leveneur, S.: Production of levulinic acid and alkyl levulinates: A process insight. Green Chem. 24(2), 614–646 (2022)
Antonetti, C., Licursi, D., Fulignati, S., Valentini, G., Raspolli Galletti, A.M.: New frontiers in the catalytic synthesis of levulinic acid: From sugars to raw and waste biomass as starting feedstock. Catalysts 6(12), 196 (2016)
https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20210129005254/en/Global-Levulinic-Acid-Industry-2020-to-2027---Market-Trends-and-Drivers---ResearchAndMarkets.com (accessed 15 July 2021).
https://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/3877144/levulinic-acid-market-by-application (accessed 15 July 2021, 2021).
https://www.marketdataforecast.com/market-reports/levulinic-acid-market
Signoretto, M., Taghavi, S., Ghedini, E., Menegazzo, F.: Catalytic production of levulinic acid (LA) from actual biomass. Molecules 24(15), 2760 (2019)
Cha, J., Hanna, M.: Levulinic acid production based on extrusion and pressurized batch reaction. Ind. Crops Prod. 16(2), 109–118 (2002)
Ji, H., Dong, C., Yang, G., Pang, Z.: Production of levulinic acid from lignocellulosic biomass with a recyclable aromatic acid and its kinetic study. BioResources 14(1), 725–736 (2019)
Lopes, E.S., Rivera, E.C., de Jesus Gariboti, J.C., Feistel, L.H.Z., Dutra, J.V., Maciel Filho, R., Tovar, L.P.: Kinetic insights into the lignocellulosic biomass-based levulinic acid production by a mechanistic model. Cellulose 27(10), 5641–5663 (2020)
Meinita, M.D.N., Amron, A., Trianto, A., Harwanto, D., Caesarendra, W., Jeong, G.-T., Choi, J.-S.: Levulinic acid production from macroalgae: Production and promising potential in industry. Sustainability 13(24), 13919 (2021)
Rihko-Struckmann, L.K., Oluyinka, O., Sahni, A., McBride, K., Fachet, M., Ludwig, K., Sundmacher, K.: Transformation of remnant algal biomass to 5-HMF and levulinic acid: Influence of a biphasic solvent system. RSC Adv. 10(42), 24753–24763 (2020)
Suib, S.L.: New and future developments in catalysis: Catalytic biomass conversion. Newnes (2013)
Seretis, A., Diamantopoulou, P., Thanou, I., Tzevelekidis, P., Fakas, C., Lilas, P., Papadogianakis, G.: Recent advances in ruthenium-catalyzed hydrogenation reactions of renewable biomass-derived levulinic acid in aqueous media. Front. Chem. 8, 221 (2020)
https://www.statista.com/statistics/249604/sugar-cane-production-worldwide/ (accessed 10 February 2019).
Van der Poel, P.: Sugar technology: Beet and cane sugar manufacture/PW van der Poel, H. Schiweck, T. Schwartz. Verlag Dr. Albert Vartens KG, Berlin (1998)
van der Poel, P.W.: Zuckertechnologie: Rüben-und Rohrzuckergewinnung. Bartens (2000)
Chandel, A.K., Antunes, F.A., Anjos, V., Bell, M.J., Rodrigues, L.N., Polikarpov, I., de Azevedo, E.R., Bernardinelli, O.D., Rosa, C.A., Pagnocca, F.C.: Multi-scale structural and chemical analysis of sugarcane bagasse in the process of sequential acid–base pretreatment and ethanol production by Scheffersomyces shehatae and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol. Biofuels 7(1), 1–17 (2014)
Himmel, M.E., Ding, S.-Y., Johnson, D.K., Adney, W.S., Nimlos, M.R., Brady, J.W., Foust, T.D.: Biomass recalcitrance: Engineering plants and enzymes for biofuels production. Science 315(5813), 804–807 (2007)
Abdulkhani, A., Marvast, E.H., Ashori, A., Karimi, A.N.: Effects of dissolution of some lignocellulosic materials with ionic liquids as green solvents on mechanical and physical properties of composite films. Carbohyd. Polym. 95(1), 57–63 (2013)
Adav, S.S., Sze, S.K.: Trichoderma secretome: An overview. Biotechnol. Biol. Trichoderma (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-59576-8.00008-4
Walford, S. Sugarcane bagasse: how easy is it to measure its constituents? In Proceedings of the Annual Congress-South African Sugar Technologists’ Association, no. 81: South African Sugar Technologists’ Association, pp. 266–273 (2008).
Saha, B.C.: Hemicellulose bioconversion. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 30(5), 279–291 (2003)
Ebringerová, A.: Structural diversity and application potential of hemicelluloses. Macromol Symposia 232(1), 1–12 (2005)
Schmidt, L.M., Mthembu, L.D., Reddy, P., Deenadayalu, N., Kaltschmitt, M., Smirnova, I.: Levulinic acid production integrated into a sugarcane bagasse based biorefinery using thermal-enzymatic pretreatment. Ind. Crops Prod. 99, 172–178 (2017)
Ya’aini, N., Amin, N.A.S., Asmadi, M.: Optimization of levulinic acid from lignocellulosic biomass using a new hybrid catalyst. Bioresour. Technol. 116, 58–65 (2012)
Zhang, Y., Naebe, M.: Lignin: A review on structure, properties, and applications as a light-colored UV absorber. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 9(4), 1427–1442 (2021)
Galletti, A.M.R., Antonetti, C., De Luise, V., Licursi, D., Nassi, N.: Levulinic acid production from waste biomass. BioResources 7(2), 1824–1835 (2012)
Ramli, N.A.S., Amin, N.A.S.: Optimization of biomass conversion to levulinic acid in acidic ionic liquid and upgrading of levulinic acid to ethyl levulinate. BioEnergy Research 10(1), 50–63 (2017)
Mthembu, L.D., Lokhat, D., Gupta, R., Deenadayalu, N.: Optimization of levulinic acid production from depithed sugarcane bagasse in 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium hydrogen sulfate [EMim][HSO4]. Waste Biomass Valorization 12(6), 3179–3191 (2021)
Lopes, E.S., Dominices, K., Lopes, M., Tovar, L., MacielFilho, R.: A green chemical production: obtaining levulinic acid from pretreated sugarcane bagasse. Chem. Eng. Trans. 57, 145–150 (2017)
Muranaka, Y., Suzuki, T., Sawanishi, H., Hasegawa, I., Mae, K.: Effective production of levulinic acid from biomass through pretreatment using phosphoric acid, hydrochloric acid, or ionic liquid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 53(29), 11611–11621 (2014)
Su, J., Shen, F., Qiu, M., Qi, X.: High-yield production of levulinic acid from pretreated cow dung in dilute acid aqueous solution. Molecules 22(2), 285 (2017)
Gupta, R., Khasa, Y.P., Kuhad, R.C.: Evaluation of pretreatment methods in improving the enzymatic saccharification of cellulosic materials. Carbohyd. Polym. 84(3), 1103–1109 (2011)
Liu, C., Lu, X., Yu, Z., Xiong, J., Bai, H., Zhang, R.: Production of levulinic acid from cellulose and cellulosic biomass in different catalytic systems. Catalysts 10(9), 1006 (2020)
Gupta, R., Sharma, K.K., Kuhad, R.C.: Separate hydrolysis and fermentation (SHF) of Prosopis juliflora, a woody substrate, for the production of cellulosic ethanol by Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pichia stipitis-NCIM 3498. Biores. Technol. 100(3), 1214–1220 (2009)
Manzoor, A., Khokhar, Z.-U., Athar Hussain, U., Ahmad, S.A.: Dilute sulfuric acid: A cheap acid for optimization of bagasse pretreatment. Cellulose 10, 100 (2012)
Jędrzejczyk, M., Soszka, E., Czapnik, M., Ruppert, A.M., Grams, J. Physical and chemical pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. In Second and Third Generation of Feedstocks. Elsevier, pp. 143–196 (2019).
Chen, W.-H., Tsai, C.-C., Lin, C.-F., Tsai, P.-Y., Hwang, W.-S.: Pilot-scale study on the acid-catalyzed steam explosion of rice straw using a continuous pretreatment system. Biores. Technol. 128, 297–304 (2013)
Banerjee, S., Sen, R., Morone, A., Chakrabarti, T., Pandey, R., Mudliar, S.: Improved wet air oxidation pretreatment for enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis of rice husk for bioethanol production. Dyn Biochem Process Biotechnol Mol Biol 6(2), 43–45 (2012)
Murnen, H.K., Balan, V., Chundawat, S.P., Bals, B., Sousa, Ld.C., Dale, B.E.: Optimization of ammonia fiber expansion (AFEX) pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis of Miscanthus × giganteus to fermentable sugars. Biotechnol. Progress 23(4), 846–850 (2007)
Hendriks, A., Zeeman, G.: Pretreatments to enhance the digestibility of lignocellulosic biomass. Biores. Technol. 100(1), 10–18 (2009)
Carvalheiro, F., Duarte, L.C., Gírio, F.M. Hemicellulose biorefineries: A review on biomass pretreatments. Journal of Scientific & Industrial Research, pp. 849–864 (2008).
Zhao, Y., Wang, Y., Zhu, J., Ragauskas, A., Deng, Y.: Enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis of spruce by alkaline pretreatment at low temperature. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 99(6), 1320–1328 (2008)
Zhao, X., Cheng, K., Liu, D.: Organosolv pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for enzymatic hydrolysis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 82(5), 815–827 (2009)
Vasco-Correa, J., Ge, X., Li, Y. Biological pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. In Biomass fractionation technologies for a lignocellulosic feedstock based biorefinery. Elsevier, pp. 561–585 (2016).
Wan, C., Li, Y.: Fungal pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Biotechnol. Adv. 30(6), 1447–1457 (2012)
Merklein, K., Fong, S., Deng, Y. Biomass utilization. In Biotechnology for biofuel production and optimization. Elsevier, pp. 291–324 (2016).
Pratama, A.P., Rahayu, D.U.C., Krisnandi, Y.K.: Levulinic acid production from delignified rice husk waste over manganese catalysts: Heterogeneous versus homogeneous. Catalysts 10(3), 327 (2020)
Yan, L., Yang, N., Pang, H., Liao, B.: Production of levulinic acid from bagasse and paddy straw by liquefaction in the presence of hydrochloride acid. Clean-Soil Air Water 36(2), 158–163 (2008)
Yang, Z., Kang, H., Guo, Y., Zhuang, G., Bai, Z., Zhang, H., Feng, C., Dong, Y.: Dilute-acid conversion of cotton straw to sugars and levulinic acid via 2-stage hydrolysis. Ind. Crops Prod. 46, 205–209 (2013)
Girisuta, B., Janssen, L., Heeres, H.: Kinetic study on the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of cellulose to levulinic acid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 46(6), 1696–1708 (2007)
Efremov, A., Pervyshina, G., Kuznetsov, B.: Thermocatalytic transformations of wood and cellulose in the presence of HCl, HBr, and H 2 SO 4. Chem. Nat. Compd. 33(1), 84–88 (1997)
Rackemann, D.W., Bartley, J.P., Doherty, W.O.: Methanesulfonic acid-catalyzed conversion of glucose and xylose mixtures to levulinic acid and furfural. Ind. Crops Prod. 52, 46–57 (2014)
Rackemann, D.W.: Production of levulinic acid and other chemicals from sugarcane fibre. Queensland University of Technology (2014)
Morone, A., Apte, M., Pandey, R.: Levulinic acid production from renewable waste resources: Bottlenecks, potential remedies, advancements and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 51, 548–565 (2015)
Kang, S., Fu, J., Zhang, G.: From lignocellulosic biomass to levulinic acid: A review on acid-catalyzed hydrolysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 94, 340–362 (2018)
Weingarten, R., Conner, W.C., Huber, G.W.: Production of levulinic acid from cellulose by hydrothermal decomposition combined with aqueous phase dehydration with a solid acid catalyst. Energy Environ. Sci. 5(6), 7559–7574 (2012)
Hara, M.: Biodiesel production by amorphous carbon bearing SO 3 H, COOH and phenolic OH groups, a solid Brønsted acid catalyst. Top. Catal. 53(11–12), 805–810 (2010)
Upare, P.P., Yoon, J.-W., Kim, M.Y., Kang, H.-Y., Hwang, D.W., Hwang, Y.K., Kung, H.H., Chang, J.-S.: Chemical conversion of biomass-derived hexose sugars to levulinic acid over sulfonic acid-functionalized graphene oxide catalysts. Green Chem. 15(10), 2935–2943 (2013)
Ya’aini, N., Amin, N.A.S., Endud, S.: Characterization and performance of hybrid catalysts for levulinic acid production from glucose. Micropor Mesopor Mater 171, 14–23 (2013)
Efremov, A., Pervyshina, G., Kuznetsov, B.: Production of levulinic acid from wood raw material in the presence of sulfuric acid and its salts. Chem. Nat. Compd. 34(2), 182–185 (1998)
Seri, K.-I., Sakaki, T., Shibata, M., Inoue, Y., Ishida, H.: Lanthanum (III)-catalyzed degradation of cellulose at 250 C. Biores. Technol. 81(3), 257–260 (2002)
Qi, X., Smith, R.L., Fang, Z. Production of versatile platform chemical 5-hydroxymethylfurfural from biomass in ionic liquids. In Production of Biofuels and Chemicals with Ionic Liquids. Springer, pp. 223–254 (2014).
Zuo, Y., Zhang, Y., Fu, Y.: Catalytic conversion of cellulose into levulinic acid by a sulfonated chloromethyl polystyrene solid acid catalyst. ChemCatChem 6(3), 753–757 (2014)
Lin, H., Strull, J., Liu, Y., Karmiol, Z., Plank, K., Miller, G., Guo, Z., Yang, L.: High yield production of levulinic acid by catalytic partial oxidation of cellulose in aqueous media. Energy Environ. Sci. 5(12), 9773–9777 (2012)
Joshi, S.S., Zodge, A.D., Pandare, K.V., Kulkarni, B.D.: Efficient conversion of cellulose to levulinic acid by hydrothermal treatment using zirconium dioxide as a recyclable solid acid catalyst. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 53(49), 18796–18805 (2014)
Choudhary, V., Mushrif, S.H., Ho, C., Anderko, A., Nikolakis, V., Marinkovic, N.S., Frenkel, A.I., Sandler, S.I., Vlachos, D.G.: Insights into the interplay of Lewis and Brønsted acid catalysts in glucose and fructose conversion to 5-(hydroxymethyl) furfural and levulinic acid in aqueous media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135(10), 3997–4006 (2013)
Yang, F., Fu, J., Mo, J., Lu, X.: Synergy of Lewis and Brønsted acids on catalytic hydrothermal decomposition of hexose to levulinic acid. Energy Fuels 27(11), 6973–6978 (2013)
Fu, J., Yang, F., Mo, J., Zhuang, J., Lu, X.: Catalytic decomposition of glucose to levulinic acid by synergy of organic Lewis acid and Brønsted acid in water. BioResources 10(1), 1346–1356 (2015)
Shen, Y., Sun, J.-K., Yi, Y.-X., Wang, B., Xu, F., Sun, R.-C.: One-pot synthesis of levulinic acid from cellulose in ionic liquids. Biores. Technol. 192, 812–816 (2015)
Hallet, J. https://www3.imperial.ac.uk/people/j.halett
Cole, A.C., Jensen, J.L., Ntai, I., Tran, K.L.T., Weaver, K.J., Forbes, D.C., Davis, J.H.: Novel Brønsted acidic ionic liquids and their use as dual solvent−catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124(21), 5962–5963 (2002)
Marsh, K.N., Boxall, J.A., Lichtenthaler, R.: Room temperature ionic liquids and their mixtures—A review. Fluid Phase Equilib. 219(1), 93–98 (2004)
Jarosik, A., Krajewski, S.R., Lewandowski, A., Radzimski, P.: Conductivity of ionic liquids in mixtures. J. Mol. Liq. 123(1), 43–50 (2006)
Bubalo, M.C., Radošević, K., Redovniković, I.R., Slivac, I., Srček, V.G.: Toxicity mechanisms of ionic liquids. Arh. Hig. Rada Toksikol. 68(3), 171–179 (2017)
Bubalo, M.C., Radošević, K., Redovniković, I.R., Halambek, J., Srček, V.G.: A brief overview of the potential environmental hazards of ionic liquids. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 99, 1–12 (2014)
Egorova, K.S., Ananikov, V.P.: Toxicity of ionic liquids: eco (cyto) activity as complicated, but unavoidable parameter for task-specific optimization. Chemsuschem 7(2), 336–360 (2014)
Kudłak, B., Owczarek, K., Namieśnik, J.: Selected issues related to the toxicity of ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 22(16), 11975–11992 (2015)
Egorova, K.S., Gordeev, E.G., Ananikov, V.P.: Biological activity of ionic liquids and their application in pharmaceutics and medicine. Chem. Rev. 117(10), 7132–7189 (2017)
Ren, H., Zhou, Y., Liu, L.: Selective conversion of cellulose to levulinic acid via microwave-assisted synthesis in ionic liquids. Biores. Technol. 129, 616–619 (2013)
Alipour, S., Omidvarborna, H.: Enzymatic and catalytic hybrid method for levulinic acid synthesis from biomass sugars. J. Clean. Prod. 143, 490–496 (2017)
Ramli, N.A.S., Amin, N.A.S.: A new functionalized ionic liquid for efficient glucose conversion to 5-hydroxymethyl furfural and levulinic acid. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 407, 113–121 (2015)
Li, K., Bai, L., Amaniampong, P.N., Jia, X., Lee, J.M., Yang, Y.: One-pot transformation of cellobiose to formic acid and levulinic acid over ionic-liquid-based polyoxometalate hybrids. Chemsuschem 7(9), 2670–2677 (2014)
Sun, Z., Cheng, M., Li, H., Shi, T., Yuan, M., Wang, X., Jiang, Z.: One-pot depolymerization of cellulose into glucose and levulinic acid by heteropolyacid ionic liquid catalysis. RSC Adv. 2(24), 9058–9065 (2012)
Mthembu, L.D. Production of levulinic acid from sugarcane bagasse (2016).
Ramli, N.A.S., Amin, N.A.S.: Catalytic hydrolysis of cellulose and oil palm biomass in ionic liquid to reducing sugar for levulinic acid production. Fuel Process. Technol. 128, 490–498 (2014)
Fu, J., Sheng, D., Lu, X.: Hydrogenation of levulinic acid over nickel catalysts supported on aluminum oxide to prepare γ-valerolactone. Catalysts 6(1), 6 (2016)
Mukherjee, A., Dumont, M.-J., Raghavan, V.: Sustainable production of hydroxymethylfurfural and levulinic acid: Challenges and opportunities. Biomass Bioenerg. 72, 143–183 (2015)
Tong, X., Li, Y.: Efficient and selective dehydration of fructose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural catalyzed by brønsted-acidic ionic liquids. Chemsuschem 3(3), 350–355 (2010)
Qu, Y., Huang, C., Zhang, J., Chen, B.: Efficient dehydration of fructose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural catalyzed by a recyclable sulfonated organic heteropolyacid salt. Biores. Technol. 106, 170–172 (2012)
Shimizu, K.-I., Uozumi, R., Satsuma, A.: Enhanced production of hydroxymethylfurfural from fructose with solid acid catalysts by simple water removal methods. Catal. Commun. 10(14), 1849–1853 (2009)
Di Bucchianico, D.D.M., Buvat, J.-C., Mignot, M., Moreno, V.C., Leveneur, S.: Role of solvent the production of butyl levulinate from fructose. Fuel 318, 123703 (2022)
Alonso, D.M., Gallo, J.M.R., Mellmer, M.A., Wettstein, S.G., Dumesic, J.A.: Direct conversion of cellulose to levulinic acid and gamma-valerolactone using solid acid catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 3(4), 927–931 (2013)
Timokhin, B.V., Baransky, V.A., Eliseeva, G.D.: Levulinic acid in organic synthesis. Russ. Chem. Rev. 68(1), 73–84 (1999)
Wettstein, S.G., Alonso, D.M., Chong, Y., Dumesic, J.A.: Production of levulinic acid and gamma-valerolactone (GVL) from cellulose using GVL as a solvent in biphasic systems. Energy Environ. Sci. 5(8), 8199–8203 (2012)
Liu, F., Sivoththaman, S., Tan, Z. Solvent extraction of 5-HMF from simulated hydrothermal conversion product. Sustain. Environ. Res. 24 (2) (2014).
Chheda, J.N., Román-Leshkov, Y., Dumesic, J.A.: Production of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and furfural by dehydration of biomass-derived mono-and poly-saccharides. Green Chem. 9(4), 342–350 (2007)
Gürbüz, E.I., Wettstein, S.G., Dumesic, J.A.: Conversion of hemicellulose to furfural and levulinic acid using biphasic reactors with alkylphenol solvents. Chemsuschem 5(2), 383–387 (2012)
Bicker, M., Hirth, J., Vogel, H.: Dehydration of fructose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in sub-and supercritical acetone. Green Chem. 5(2), 280–284 (2003)
Sangarunlert, W., Piumsomboon, P., Ngamprasertsith, S.: Furfural production by acid hydrolysis and supercritical carbon dioxide extraction from rice husk. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 24(6), 936–941 (2007)
Fu, J., Xu, X., Lu, X., Lu, X.: Hydrothermal decomposition of carbohydrates to levulinic acid with catalysis by ionic liquids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 55(42), 11044–11051 (2016)
Pileidis, F.D., Titirici, M.-M.: Levulinic acid biorefineries: New challenges for efficient utilization of biomass. Chemsuschem (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/chin.201621274
Chaudhari, C., Shiraishi, M., Nishida, Y., Sato, K., Nagaoka, K.: One-pot synthesis of pyrrolidones from levulinic acid and amines/nitroarenes/nitriles over the Ir-PVP catalyst. Green Chem. 22(22), 7760–7764 (2020)
Liu, H.-F., Zeng, F.-X., Deng, L., Liao, B., Pang, H., Guo, Q.-X.: Brønsted acidic ionic liquids catalyze the high-yield production of diphenolic acid/esters from renewable levulinic acid. Green Chem. 15(1), 81–84 (2013)
Guo, Y., Li, K., Clark, J.H.: The synthesis of diphenolic acid using the periodic mesoporous H 3 PW 12 O 40-silica composite catalysed reaction of levulinic acid. Green Chem. 9(8), 839–841 (2007)
Shen, Y., Sun, J., Wang, B., Xu, F., Sun, R.: Catalytic synthesis of diphenolic acid from levulinic acid over bronsted acidic ionic liquids. BioResources 9(2), 3264–3275 (2014)
Li, W., Xie, J.-H., Lin, H., Zhou, Q.-L.: Highly efficient hydrogenation of biomass-derived levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone catalyzed by iridium pincer complexes. Green Chem. 14(9), 2388–2390 (2012)
Ortiz-Cervantes, C., García, J.J.: Hydrogenation of levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone using ruthenium nanoparticles. Inorg. Chim. Acta 397, 124–128 (2013)
Rodiansono, R., Astuti, M.D., Ghofur, A., Sembiring, K.C.: Catalytic hydrogenation of levulinic acid in water into g-valerolactone over bulk structure of inexpensive intermetallic Ni-Sn alloy catalysts. Bull. Chem. React. Eng. Catal. 10(2), 192 (2015)
Pileidis, F.D., Tabassum, M., Coutts, S., Titirici, M.-M.: Esterification of levulinic acid into ethyl levulinate catalysed by sulfonated hydrothermal carbons. Chin. J. Catal. 35(6), 929–936 (2014)
Saravanamurugan, S., Riisager, A.: Solid acid catalysed formation of ethyl levulinate and ethyl glucopyranoside from mono-and disaccharides. Catal. Commun. 17, 71–75 (2012)
Yan, K., Wu, G., Wen, J., Chen, A.: One-step synthesis of mesoporous H4SiW12O40-SiO2 catalysts for the production of methyl and ethyl levulinate biodiesel. Catal. Commun. 34, 58–63 (2013)
Chen, J., Zhao, G., Chen, L.: Efficient production of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and alkyl levulinate from biomass carbohydrate using ionic liquid-based polyoxometalate salts. RSC Adv. 4(8), 4194–4202 (2014)
Weina, Z., Chang, C., Chen, M., Fengguang, D.: Kinetics of glucose ethanolysis catalyzed by extremely low sulfuric acid in ethanol medium. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 22(2), 238–242 (2014)
Zhao, S., Xu, G., Chang, J., Chang, C., Bai, J., Fang, S., Liu, Z.: Direct production of ethyl levulinate from carbohydrates catalyzed by H-ZSM-5 supported phosphotungstic acid. BioResources 10(2), 2223–2234 (2015)
Fernandes, D., Rocha, A., Mai, E., Mota, C.J., Da Silva, V.T.: Levulinic acid esterification with ethanol to ethyl levulinate production over solid acid catalysts. Appl. Catal. A 425, 199–204 (2012)
Li, Z., Wnetrzak, R., Kwapinski, W., Leahy, J.J.: Synthesis and characterization of sulfated TiO2 nanorods and ZrO2/TiO2 nanocomposites for the esterification of biobased organic acid. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 4(9), 4499–4505 (2012)
Nandiwale, K.Y., Sonar, S.K., Niphadkar, P.S., Joshi, P.N., Deshpande, S.S., Patil, V.S., Bokade, V.V.: Catalytic upgrading of renewable levulinic acid to ethyl levulinate biodiesel using dodecatungstophosphoric acid supported on desilicated H-ZSM-5 as catalyst. Appl. Catal. A 460, 90–98 (2013)
Cirujano, F., Corma, A., Xamena, FXi.: Conversion of levulinic acid into chemicals: Synthesis of biomass derived levulinate esters over Zr-containing MOFs. Chem. Eng. Sci. 124, 52–60 (2015)
Hayes, D.J., Fitzpatrick, S., Hayes, M.H., Ross, J.R.: The biofine process–production of levulinic acid, furfural, and formic acid from lignocellulosic feedstocks. Biorefineries-Industrial Processes Product 1, 139–164 (2006)
Haverty, D., Dussan, K., Piterina, A.V., Girisuta, B., Hayes, D., Leahy, J., Hayes, M. Levulinic acid production from lignocellulose biomass: Comparison of the DIBANET proposed design with the Biofine process for the acid hydrolysis route to Levulinic Acid. https://dibanet.geonardo.com/library/networking_day_2012/presentations/dibanet_donncha_haverty_levulinic_acid_production.pdf (accessed 20 January 2019).
Hayes, D. Report on Optimal Use of DIBANET Feedstocks and Technologies. EU’s Seventh Framework Programme (2013).
Girisuta, B., Danon, B., Manurung, R., Janssen, L., Heeres, H.: Experimental and kinetic modelling studies on the acid-catalysed hydrolysis of the water hyacinth plant to levulinic acid. Biores. Technol. 99(17), 8367–8375 (2008)
Kang, S., Yu, J.: Effect of methanol on formation of levulinates from cellulosic biomass. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 54(46), 11552–11559 (2015)
Angellinnov, F., Yusuf, H., Rahayu, D., Krisnandi, Y.: Conversion of rice husks cellulose to levulinic acid on hierarchical Mn3O4/ZSM-5 catalyst from natural aluminosilicate. AIP Conf. Proc. 2243(1), 020001 (2020)
Bevilaqua, D.B., Rambo, M.K., Rizzetti, T.M., Cardoso, A.L., Martins, A.F.: Cleaner production: Levulinic acid from rice husks. J. Clean. Prod. 47, 96–101 (2013)
Kang, M., Kim, S.W., Kim, J.-W., Kim, T.H., Kim, J.S.: Optimization of levulinic acid production from Gelidium amansii. Renewable Energy 54, 173–179 (2013)
Galletti, A.M.R., Antonetti, C., Ribechini, E., Colombini, M.P., Di Nasso, NNo., Bonari, E.: From giant reed to levulinic acid and gamma-valerolactone: A high yield catalytic route to valeric biofuels. Appl. Energy 102, 157–162 (2013)
Chen, H., Yu, B., Jin, S.: Production of levulinic acid from steam exploded rice straw via solid superacid, S2O82-/ZrO2–SiO2–Sm2O3. Biores. Technol. 102(3), 3568–3570 (2011)
Cunshan, Z., Xiaojie, Y., Haile, M., Ronghai, H., Vittayapadung, S.: Optimization on the conversion of bamboo shoot shell to levulinic acid with environmentally benign acidic ionic liquid and response surface analysis. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 21(5), 544–550 (2013)
Khan, A.S., Man, Z., Bustam, M.A., Nasrullah, A., Ullah, Z., Sarwono, A., Shah, F.U., Muhammad, N.: Efficient conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to levulinic acid using acidic ionic liquids. Carbohyd. Polym. 181, 208–214 (2018)
Mascal, M., Nikitin, E.B.: Dramatic advancements in the saccharide to 5-(chloromethyl) furfural conversion reaction. Chemsuschem 2(9), 859–861 (2009)
Zhi, Z., Li, N., Qiao, Y., Zheng, X., Wang, H., Lu, X.: Kinetic study of levulinic acid production from corn stalk at relatively high temperature using FeCl3 as catalyst: A simplified model evaluated. Ind. Crops Prod. 76, 672–680 (2015)
Hartono, C.D., Marlie, K.J., Putro, J.N., Soetardjo, F.E., Ju, Y.H., Sirodj, D.A.N., Ismadji, S.: Levulinic acid from corncob by subcritical water process. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 7(4), 401–409 (2016)
Fang, Q., Hanna, M.A.: Experimental studies for levulinic acid production from whole kernel grain sorghum. Biores. Technol. 81(3), 187–192 (2002)
Chang, C., Xiaojian, M., Peilin, C.: Kinetic studies on wheat straw hydrolysis to levulinic acid. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 17(5), 835–839 (2009)
Carlson, L.J. United States patent. In Office USPaT. United states of America: Rayonier Incorporated, 1962.
Tyrlik, S.K., Szerszen, D., Kurzak, B., Bal, K. Concentrated water solution of salts as solvents for reactions of carbohydrates. Part 1: reactions of glucose promoted by concentrated solutions of alkaline and alkaline earth metal salts. Starch-Staerke (Germany) (1995).
Girisuta, B., Janssen, L., Heeres, H.: Green chemicals: A kinetic study on the conversion of glucose to levulinic acid. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 84(5), 339–349 (2006)
Heeres, H., Handana, R., Chunai, D., Rasrendra, C.B., Girisuta, B., Heeres, H.J.: Combined dehydration/(transfer)-hydrogenation of C6-sugars (D-glucose and D-fructose) to γ-valerolactone using ruthenium catalysts. Green Chem. 11(8), 1247–1255 (2009)
Farone, W.A., Cuzens, J.E. United States of America (2000).
B. Girisuta, Levulinic acid from lignocellulosic biomass. University Library Groningen [Host], (2007).
Shen, J., Wyman, C.E.: Hydrochloric acid-catalyzed levulinic acid formation from cellulose: Data and kinetic model to maximize yields. AIChE J. 58(1), 236–246 (2012)
Suacharoen, S., Tungasmita, D.N.: Hydrothermolysis of carbohydrates to levulinic acid using metal supported on porous aluminosilicate. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 88(8), 1538–1544 (2013)
Lourvanij, K.: Partial dehydration of glucose to oxygenated hydrocarbons in molecular-sieving catalysts. Oregon State University (1995)
Ding, D., Wang, J., Xi, J., Liu, X., Lu, G., Wang, Y.: High-yield production of levulinic acid from cellulose and its upgrading to γ-valerolactone. Green Chem. 16(8), 3846–3853 (2014)
Yang, H., Wang, L., Jia, L., Qiu, C., Pang, Q., Pan, X.: Selective decomposition of cellulose into glucose and levulinic acid over Fe-resin catalyst in NaCl solution under hydrothermal conditions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 53(15), 6562–6568 (2014)
Amarasekara, A.S., Wiredu, B.: Acidic ionic liquid catalyzed one-pot conversion of cellulose to ethyl levulinate and levulinic acid in ethanol-water solvent system. BioEnergy Res. 7(4), 1237–1243 (2014)
Funding
This study was supported by the L’Oréal-UNESCO Women in Science Sub-Saharan Africa Regional Fellowship, Durban University of Technology to Lethiwe D. Mthembu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mthembu, L.D., Gupta, R. & Deenadayalu, N. Advances in Biomass-Based Levulinic Acid Production. Waste Biomass Valor 14, 1–22 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-022-01948-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-022-01948-x