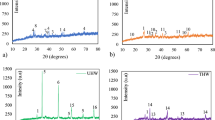
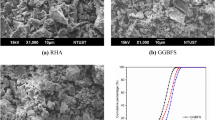
Abstract
This paper proposes an alternative use for waste such as the ash generated by coal-fired power plants and municipal incineration facilities, specifically as a raw material in alkali-activated hybrid cements. The proposal was tested by preparing a series of hybrid cements with blends of fly ash (FA) and clinker (CK) or municipal solid waste incinerator ash (MSWI) and clinker (CK) in varying proportions. Two and 28 day mechanical performance was assessed in these systems and the reaction products generated by alkaline activation were characterised using XRD and SEM/EDX. The FA hybrid cements exhibited excellent 28 day strength at very high replacement ratios (80 % FA and 20 % Portland clinker). While MSWI performance was somewhat more limited, the 28 day material containing 40 % waste reached a strength of 33 MPa, sufficient to qualify for cement category 32.5 as defined in the existing codes and standards.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Habert, G.: Enviromental impact of Portland cement production. In: Pacheco-Torgal, Y., Jalali, S., Labrincha, J., John, V.M. (eds.) Eco-efficient Concrete, pp. 3–25. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge (2013)
Lothenbach, B., Scrivener, K., Hooton, R.D.: Supplementary cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 41(12), 1244–1256 (2011)
Aïtcin, P.C.: Supplementary cementitious materials and blended cements. In: Science and Technology of Concrete Admixtures, pp. 53–76. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge UK (2016)
Tyrer, M.: Municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) concrete. In: Pacheco-Torgal, F., Jalali, S., Labrincha, J., John, V.M. (eds.) Eco-efficient Concrete. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge UK (2013)
Bertolini, L., Carcana, M., Cassago, D., Collepardi, M., Curzio, Q.: MSWI ashes as mineral additions in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 34, 1899–1906 (2004)
EN 197-1: 2000 Cement - Part 1: Composition, specifications and conformity criteria for common cements
Lane, R.O., Best, J.F.: Properties and use of fly ash in Portland cement concrete. Concr. Int. 4(7), 81–92 (1982)
Atis, C.D.: High-Volume fly ash concrete with high-strength and low drying shrinkage. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. ASCE 15(2), 153–156 (2003)
Malhotra, V.M., Zhang, M.-H., Read, P.H., Ryell, J.: Long term mechanical properties and durability characteristics of high strength/high-performance concrete incorporating supplementary cementing materials under outdoor exposure conditions. ACI Mater. J. 97(5), 518–525 (2000)
Malhotra, V.M., Mehta, P.K.: High-Performance, High-Volume Fly Ash Concrete. Supplementary Cementing Materials for Sustainable Development Inc, Ottawa (2005)
Cheeseman, C.R., Makinde, A., Bethenis, S.: Properties of lightweight aggregate produced by rapid sintering of incinerator bottom ash. Res Conserv. Recycl. 43(2), 147–162 (2005)
Ferraris, M., Salvo, M., Ventrella, A., Buzzi, L., Veglia, M.: Use of vitrified MSWI bottom ashes for concrete production. Waste Manag. 29, 1041–1047 (2009)
Ginés, O., Chimenosa, J.M., Vizcarro, A., Formosa, J., Rosell, J.R.: Combined use of MSWI bottom ash and fly ash as aggregate in concrete formulation: environmental and mechanical considerations. J. Hazard. Mater. 169, 643–650 (2009)
Jaturapitakkul, C., Cheerarot, R.: Development of bottom ash as pozzolanic material. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 151, 48–53 (2003)
Juric, B., Hanzic, L., Ilic, R., Samec, N.: Utilization of municipal solid waste botton ash and recycled aggregate in concrete. Waste Manag. 26, 239–259 (2006)
Lin, L.L., Wang, K.S., Tzeng, B.Y., Lin, C.Y.: The reuse of municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash slag as a cement substitute. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 39, 315–324 (2003)
Müller, U., Rübner, K.: The microstructure of concrete made with municipal waste incinerator bottom ash as an aggregate component. Cem. Concr. Res. 36, 1434–1443 (2006)
Pavlík, Z., Jerman, M., Keppert, M., Pavlíková, M., Reiterman, P., Cerny, R.: Use of municipal solid waste incineration waste materials as admixtures in concrete. Convertry University and The University of Wisconsin Milwaukee Centre for By-productos Utilization, Second International Conference on Sustainable Construction Materials and Technologies, 28–30 June, Univesita Politecnica del le Marche, Ancona, Italy (2010)
Pera, J., Coutaz, L., Ambroise, J., Chababbet, M.: Use of incinerator bottom ash in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 27(1), 1–5 (1997)
Wiles, C.C.: Municipal waste combustion ash: state of knowledge. J. Hazard. Mater. 47, 325–344 (1996)
Palomo A., Krivenko P., Garcia-Lodeiro I., Kavalerova E., Malteseva O., Fernandez-Jimenez, A.: A review on alkaline activation: new analytical perspectives, Materiales de Construcción 64, (2014) e022. ISSN-L: 0465–2746. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.3989/mc.2014.00314
Garcia-Lodeiro, I., Fernández-Jiménez, Palomo, A.: Variation in hybrid cements over time. Alkaline activation of fly ash–portland cement blends. Cem. Concr. Res. 52, 112–122 (2013)
Garcia-Lodeiro, I., Maltseva, O., Fernández-Jiménez, Palomo, A.: Hybrid alkaline cements: part I Fundamentals. Roman. J. Mater. 42(4), 330–335 (2012)
Garcia-Lodeiro, I., Fernández-Jiménez, A., Palomo, A.: Hydration kinetics in hybrid binders: early reac–tion stages. Cem. Concr. Compos. 39, 82–92 (2013)
Palomo, A., Grutzeck, M.W., Blanco, M.T.: Alkali-activated fly ashes—A cement for the future. Cem. Concr. Res. 29(8), 1323–1329 (1999)
Shi, C., Fernández Jiménez, A., Palomo, A.: New cements for the 21st Century, the pursuit of an alternative to Portland cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 41, 750–763 (2011)
Glukhovsky, V.: Ancient, modern and future concretes. In: First International. Conference. Alkaline Cements and Concretes, Kiev, Ukraine, 1, pp. 1–8 (1994)
Provis, J., van Deventer, J.S.J. (eds.): Geopolymers: Structure, Processing, Properties and Industrial Aplications. Woodhead Publishing Limited, Cambridge (2009)
Taylor, H.F.W.: Cement Chemistry, 2nd edn. Thomas Telford, London (1997)
Wang, S.D., Scrivener, K.L.: Hydration products of alkali activated slag cement”. Cem. Concr. Res. 25(3), 561–571 (1995)
Puertas, F.: Cementos de escorias activadas alcalinamente: situación actual y perspectivas de futuro. Mater. de Constr. 45(239), 53–92 (1995)
Fernández-Jiménez, A., Palomo, A.: Characterization of fly ashes. Potencial reactivity as alkaline cements. Fuel 82(18), 2259–2265 (2003)
Duxson, P., Lukey, G.C., Van De Venter, J.S.J., Mallicoat, S.W., Kriven, W.M.: Microstructural characterization of metakaolin-based geopolymers. Ceram. Trans. 165, 71–85 (2005)
Garcia-Lodeiro, I., Carelen-Taboada, V., Fernández-Jiménez, A., Palomo, A.: Manufacture of hybrid cements with fly ash and bottom ash from a municipal solid waste incinerator. Constr. Build. Mater. 105, 218–226 (2016)
Qiao, X.C., Tyrer, M., Poon, C.S., Cheeseman, C.R.: Novel cementitious materials produced from incinerator bottom ash‖. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 52, 496–510 (2008)
Jutnes, H., Østnor, T.A: Designing alternative binders utilizing synergic reactions. In: NTCC2014: International Conference on Non-Traditional Cement and Concrete, June 16–19, Brno, Czech Republic (2014)
Fernandez-Jimenez, A., Sobrados, I., Sanz, J, Palomo, A., Hybrid cements with very low OPC content. In: Proceedings of XII International Congress of Chemistry of Cement, 2nd–8th July Madrid, Spain (2011)
Shi, C., Day, R.L.: Pozzolanic reaction in the presence of chemical activators. Part II. Reaction products and mechanism. Cem. Concr. Res. 30, 607–613 (2000)
Donatello, S., Fernandez-Jimenez, A., Palomo, A.: —Very High Volume of fly ash cements Early age hydration study using Na2SO4 as an activator‖. J Am Ceram Soc 96(3), 900–906 (2013)
Skapa R., Optimum sulphate content of portland cement, Ph.D Thesis, Aberdeen UK (2009)
Zhu, F., Takaota, M., Oshitaa, K., Kitajima, Y., Inada, Y., Mosrisawa, S., Tsunoa, H.: Chlorides behavior in raw fly ash washing experiments. J. Hazard. Mater. 178, 547–552 (2010)
Roy, A., Eaton, H.C., Cartledge, F.K., Tittlebaum, M.E.: Solidification/stabilization of heavy metal sludge by a Portland cement/fly ash binding mixture hazard. Waste Hazard Mater. 8, 33 (1992)
Mací, A., Goñi, S., Guerrero, A., Fernández, E.: Immobilization/solidification of hazardous toxic waste in cement matrices, Materiales de Construccion 49 [254] abril/mayo/junio (1999)
Conner, J.R.: Chemical Fixation and Solidification of Hazardous Wastes. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York (1990)
U.S.E.P.A Method 1311—Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure, Code of Federal Regulations, 40 CFR part 261, Appendix II (July 1991)
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Spanish Ministry of the Economy and Competitiveness under projects BIA2013-43293-R and RTC-2014-2351-5. One of the authors worked under a Post-graduate Studies Council grant co-funded by the Spanish National Research Council and the European Social Fund (ESF) (JAE DOC2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garcia-Lodeiro, I., Taboada, V.C., Fernández-Jiménez, A. et al. Recycling Industrial By-Products in Hybrid Cements: Mechanical and Microstructure Characterization. Waste Biomass Valor 8, 1433–1440 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9679-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9679-x