Abstract
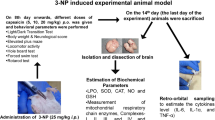
Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (C I/R) accelerates neuronal injury through the overproduction of reactive oxygen species due to mitochondrial dysfunction. Hesperidin has cerebroprotective effects due to its antioxidant and anti-apoptotic nature against oxidative damage caused by C I/R. The blood-brain barrier also limits the hesperidin passage into the cerebral region due to its poor bioavailability. Current research included analysis of binding energy, hesperidin inhibitory constant on inflammatory cytokines (TNF α, IL 6) and apoptotic protein (caspase 3), hesperidin nanoparticles prepared, and investigation of their defense against C I/R rats. Binding energy and IC50 of hesperidin on pathological proteins using AutoDoc. 1.5.6 and PyRx in silico tools were compared with thalidomide. The fabrication method was engaged in the preparing of nano-hesperidin, characterized by SEM assessment. Bilateral common carotid artery occlusion technique has been used in experimental rats to cause C I/R. Nano-hesperidin cerebroprotective activity was assessed by differing infarction magnitude, oxidative stress parameters, TNF α and IL 6, and hippocampal histopathology with rats treated with unformulated hesperidin. Hesperidin found stronger binding strength and IC50 was relative to thalidomide on TNF α, IL 6, and caspase 3. Nano-hesperidin with a size of 100–500 nm was shown in a uniform nano-size and spherical form. Nano-hesperidin-treated rats showed significantly increased glutathione (p < 0.00***), catalase (p < 0.01**), and total protein (p < 0.001***), and decreased cerebral infarction size, TNF α (p < 0.01**), IL 6 (p < 0.01**), and malondialdehyde (p < 0.05*), compared with hesperidin-treated ischemic rats. Therefore, hesperidin nanoparticles may confer protection to the neurons against ischemic injury compared with hesperidin treatment.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali SH, Sulaiman GM, Al-Halbosiy MM, Jabir MS, Hameed AH (2019) Fabrication of hesperidin nanoparticles loaded by poly lactic co-glycolic acid for improved therapeutic efficiency and cytotoxicity. Artif Cell Nanomed Biotechnol 47(1):378–394
Aydogmus E, Gul S, Bahadir B (2019) Neuroprotective effects of hesperidin on cerebral vasospasm after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats: biochemical, pathologic, and histomorphometric analysis. World Neurosurg 122:e1332–e1337
Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Tsuji M (1996) Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke 17(3):472–476
Cao W, Carney JM, Duchon A, Floyd RA, Chevion M (1988) Oxygen free radical involvement in ischemia and reperfusion injury to brain. Neurosci Lett 88(2):233–238
Castigli E, Arcuri C, Giovagnoli L (2000) Interleukin-1β induces apoptosis in GL15 glioblastoma derived human cell line. Am J Phys Cell Phys 279(6):C2043–C2049
Chamorro A, Dirnagl U, Urra X, Planas AM (2016) Neuroprotection in acute stroke: targeting excitotoxicity, oxidative and nitrosative stress, and inflammation. Lancet Neurol 15(8):869–881
Chandrashekhar VM, Ranpariya VL, Ganapaty S, Parashar A, Muchandi AA (2010) Neuroprotective activity of Matricaria recutita Linn against global model of ischemia in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 127(3):645–651
Cho J (2006) Antioxidant and neuroprotective effects of hesperidin and its aglycone hesperetin. Arch Pharm Res 29(8):699–706
Coyle P, Panzenbeck MJ (1990) Collateral development after carotid artery occlusion in Fischer 344 rats. Stroke 21(2):316–321
Dokoumetzidis A, Macheras PA (2006) Century of dissolution research: from Noyes and Whitney to the biopharmaceutics classification system. Int J Pharm 32(1–2):1–1
Doyle KP, Simon RP, Stenzel-Poore MP (2008) Mechanisms of ischemic brain damage. Neuropharmacology 55(3):310–318
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82(1):70–77
Garg A, Garg S, Zaneveld LJ, Singla AK (2001) Chemistry and pharmacology of the citrus bioflavonoid hesperidin. Phytother Res 15(8):655–669
Greenwald RA (2018) Handbook methods for oxygen radical research. Boca Raton
Gupta R, Ghosh S (2017) Putative roles of mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel, Bcl-2 family proteins and c-Jun N-terminal kinases in ischemic stroke associated apoptosis. Biochim Open 4:47–55
Hanada S, Fujioka K, Inoue Y, Kanaya F, Manome Y, Yamamoto K (2014) Cell based in vitro blood–brain barrier model can rapidly evaluate nanoparticles’ brain permeability in association with particle size and surface modification. Int J Mol Sci 15(2):1812–1825
Hartings JA, Tortella FC, Rolli ML (2006) AC electrocorticographic correlates of peri infarct depolarizations during transient focal ischemia and reperfusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26(5):696–707
Justin Thenmozhi A, William Raja TR, Manivasagam T, Janakiraman U, Essa MM (2017) Hesperidin ameliorates cognitive dysfunction, oxidative stress and apoptosis against aluminium chloride induced rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nutr Neurosci 20(6):360–368
Kakkar V, Muppu SK, Chopra K, Kaur IP (2013) Curcumin loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: an efficient formulation approach for cerebral ischemic reperfusion injury in rats. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 85(3):339–345
Kakran M, Sahoo GN, Li L (2015) Fabrication of nanoparticles of silymarin, hesperetin and glibenclamide by evaporative precipitation of nanosuspension for fast dissolution. Pharm Anal Acta 6(1):2
Kesisoglou F, Panmai S, Wu Y (2007) Nanosizing oral formulation development and biopharmaceutical evaluation. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59(7):631–644
Khoshnam SE, Winlow W, Farzaneh M (2017a) The interplay of MicroRNAs in the inflammatory mechanisms following ischemic stroke. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 76(7):548–561
Khoshnam SE, Winlow W, Farbood Y, Moghaddam HF, Farzaneh M (2017b) Emerging roles of microRNAs in ischemic stroke: as possible therapeutic agents. J Stroke 19(2):166–187
Khoshnam SE, Winlow W, Farzaneh M, Farbood Y, Moghaddam HF (2017c) Pathogenic mechanisms following ischemic stroke. Neurol Sci 38(7):1167–1186
Li C, Zug C, Qu H, Schluesener H, Zhang Z (2015) Hesperidin ameliorates behavioral impairments and neuropathology of transgenic APP/PS1 mice. Behav Brain Res 281:32–42
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Maekawa S, Sato K, Fujita K, Daigaku R, Tawarayama H, Murayama N, Moritoh S, Yabana T, Shiga Y, Omodaka K, Maruyama K (2017) The neuroprotective effect of hesperidin in NMDA-induced retinal injury acts by suppressing oxidative stress and excessive calpain activation. Sci Rep 7(1):6885
Mahato SB, Kundu AP (1994) 13C NMR spectra of pentacyclic triterpenoids a compilation and some salient features. Phytochemistry 37(6):1517–1575
Majumdar S, Srirangam R (2009) Solubility, stability, physicochemical characteristics and in vitro ocular tissue permeability of hesperidin: a natural bioflavonoid. Pharm Res 26(5):1217–1225
Moghaddam AH, Zare M (2018) Neuroprotective effect of hesperetin and nano hesperetin on recognition memory impairment and the elevated oxygen stress in rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Pharmacother 97:1096–1101
Monforte MT, Trovato A, Kirjavainen S, Forestieri AM, Galati EM, Lo RC (1995) Biological effects of hesperidin, a Citrus flavonoid.(note II): hypolipidemic activity on experimental hypercholesterolemia in rat. Farmaco 50(9):595–599
Morimoto T, Globus MY, Busto R, Martinez E, Ginsberg MD (1996) Simultaneous measurement of salicylate hydroxylation and glutamate release in the penumbral cortex following transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16(1):92–99
Nagy Z, Nardai S (2017) Cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury: from bench space to bedside. Brain Res Bull 134:30–37
Nakashima M, Niwa M, Iwai T, Uematsu T (1999) Involvement of free radicals in cerebral vascular reperfusion injury evaluated in a transient focal cerebral ischemia model of rat. Free Radic Biol Med 26(5–6):722–729
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95(2):351–358
Quartu M, Serra MP, Boi M, Pillolla G, Melis T, Poddighe L, Del Fiacco M, Falconieri D, Carta G, Murru E, Cordeddu L (2012) Effect of acute administration of Pistacia lentiscus L. essential oil on rat cerebral cortex following transient bilateral common carotid artery occlusion. Lipids Health Dis 11(1):8
Raza SS, Khan MM, Ahmad A, Ashafaq M, Khuwaja G, Tabassum R, Javed H, Siddiqui MS, Safhi MM, Islam F (2011) Hesperidin ameliorates functional and histological outcome and reduces neuroinflammation in experimental stroke. Brain Res 1420:93–105
Saraiva C, Praça C, Ferreira R, Santos T, Ferreira L, Bernardino L (2016) Nanoparticle mediated brain drug delivery: overcoming blood–brain barrier to treat neurodegenerative diseases. J Control Release 235:34–47
Saver JL, Goyal M, Bonafe A, Diener HC, Levy EI, Pereira VM, Albers GW, Cognard C, Cohen DJ, Hacke W, Jansen O (2015) Stent-retriever thrombectomy after intravenous t-PA vs. t-PA alone in stroke. N Engl J Med 372(24):2285–2295
Spuch C, Saida O, Navarro C (2012) Advances in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders employing nanoparticles. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul 6(1):2–18
Sun AY, Chen YM (1998) Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative disorders. J Biomed Sci 5(6):401–414
Sun W, Depping R, Jelkmann W (2014) Interleukin-1β promotes hypoxia-induced apoptosis of glioblastoma cells by inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor-1 mediated adrenomedullin production. Cell Death Dis 5(1):1020
Tamilselvam K, Braidy N, Manivasagam T, Essa MM, Prasad NR, Karthikeyan S, Thenmozhi AJ, Selvaraju S, Guillemin GJ (2013) Neuroprotective effects of hesperidin, a plant flavanone, on rotenone-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in a cellular model for Parkinson’s disease. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2013:11
Thenmozhi AJ, Raja TR, Janakiraman U, Manivasagam T (2015) Neuroprotective effect of hesperidin on aluminium chloride induced Alzheimer’s disease in Wistar rats. Neuro Chem Res 40(4):767–776
Trott O, Olson AJ (2010) AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem 31(2):455–461
Tsuchiya M, Sako K, Yura S, Yonemasu Y (1993) Local cerebral glucose utilisation following acute and chronic bilateral carotid artery ligation in Wistar rats: relation to changes in local cerebral blood flow. Exp Brain Res 95(1):1–7
Viglino P, Scarpa M, Rotilio G, Rigo A (1988) A kinetic study of the reactions between H2O2 and Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase; evidence for an electrostatic control of the reaction rate. Biochtm Biophys Acta 952:77–82
Yang JL, Mukda S, Chen SD (2018) Diverse roles of mitochondria in ischemic stroke. Redox Biol 16:263–275
Yanpallewar SU, Hota D, Rai S, Kumar M, Acharya SB (2004) Nimodipine attenuates biochemical, behavioral and histopathological alterations induced by acute transient and long-term bilateral common carotid occlusion in rats. Pharmacol Res 49(2):143–150
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to the DST Purse, Andhra University, Andhra, Pradesh, India, for SEM analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Experimental protocols were carried out with the approval of the Proposal Number of the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee: IAEC/CESCOP/AUG-18-05.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Praveen Kumar, P., Sunil kumar, K.T., Kavya Nainita, M. et al. Cerebroprotective Potential of Hesperidin Nanoparticles Against Bilateral Common Carotid Artery Occlusion Reperfusion Injury in Rats and In silico Approaches. Neurotox Res 37, 264–274 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00098-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00098-8