Abstract
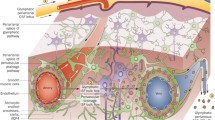
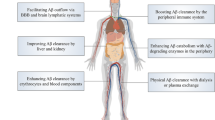
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disease. Pathological proteins of AD mainly contain amyloid-beta (Aβ) and tau. Their deposition will lead to neuron damage by a series of pathways, and then induce memory and cognitive impairment. Thus, it is pivotal to understand the clearance pathways of Aβ and tau in order to delay or even halt AD. Aβ clearance mechanisms include ubiquitin–proteasome system, autophagy-lysosome, proteases, microglial phagocytosis, and transport from the brain to the blood via the blood-brain barrier (BBB), arachnoid villi and blood-CSF barrier, which can be named blood circulatory clearance. Recently, lymphatic clearance has been demonstrated to play a key role in transport of Aβ into cervical lymph nodes. The discovery of meningeal lymphatic vessels is another direct evidence for lymphatic clearance in the brain. Furthermore, periphery clearance also contributes to Aβ clearance. Tau clearance is almost the same as Aβ clearance. In this review, we will mainly introduce the clearance mechanisms of Aβ and tau proteins, and summarize corresponding targeted drug therapies for AD.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD :
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- Aβ :
-
Beta-amyloid
- ALS :
-
Autophagy-lysosome system
- AQP4 :
-
Aquaporin 4
- ABCC1 :
-
ATP-binding cassette C1
- BBB :
-
Blood-brain barrier
- BCSFB :
-
Blood-brain barrier
- CSF :
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
- DHA :
-
Docosahexaenoic acid
- EPA :
-
Eicosapentaenoic acid
- GULT1 :
-
Glucose transporter 1
- IDE :
-
Insulin-degrading enzyme
- ISF :
-
Interstitial fluid
- LRP1 :
-
Lipoprotein receptor protein-1
- MMPs :
-
Matrix metalloproteinases
- NEP :
-
Neprilysin
- PICALM :
-
Phosphatidylinositol-binding clathrin assembly protein
- P-gp :
-
P-glycoprotein
- RAGE :
-
Receptor for advanced glycation end products
- RBC :
-
Red blood cell
- UPS :
-
Ubiquitin–proteasome system
References
Abbott NJ (2004) Evidence for bulk flow of brain interstitial fluid: significance for physiology and pathology. Neurochemistry International 45:545–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2003.11.006
Alzheimer's A (2015) 2015 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures Alzheimer's & dementia : the journal of the Alzheimer's Association 11:332–384
Arbel-Ornath M et al (2013) Interstitial fluid drainage is impaired in ischemic stroke and Alzheimer's disease mouse models. Acta Neuropathologica 126:353–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1145-2
Baranello RJ, Bharani K, Padmaraju V, Chopra N, Lahiri D, Greig N, Pappolla M, Sambamurti K (2015) Amyloid-beta protein clearance and degradation (ABCD) pathways and their role in Alzheimer's disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 12:32–46
Barnes NM, Cheng CH, Costall B, Naylor RJ, Williams TJ, Wischik CM (1991) Angiotensin converting enzyme density is increased in temporal cortex from patients with Alzheimer's disease European journal of pharmacology 200:289–292
Bolos M, Llorens-Martin M, Jurado-Arjona J, Hernandez F, Rabano A, Avila J (2015) Direct evidence of internalization of tau by microglia in vitro and in vivo. J Alzheimer's disease : JAD 50:77–87. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-150704
Bradbury MW, Westrop RJ (1983) Factors influencing exit of substances from cerebrospinal fluid into deep cervical lymph of the rabbit. J Physiology 339:519–534
Caccamo A, Majumder S, Richardson A, Strong R, Oddo S (2010) Molecular interplay between mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), amyloid-beta, and tau: effects on cognitive impairments the journal of biological chemistry 285:13107–13120. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.100420
Carare RO, Teeling JL, Hawkes CA, Puntener U, Weller RO, Nicoll JA, Perry VH (2013) Immune complex formation impairs the elimination of solutes from the brain: implications for immunotherapy in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathologica Communications 1:48. https://doi.org/10.1186/2051-5960-1-48
Chen Q, Chen YQ, Ye HY, Yu JQ, Shi QQ, Huang Y (2015) [The mechanism of tenuigenin for eliminating waste product accumulation in cerebral neurons of Alzheimer's disease rats via ubiquitin-proteasome pathway] Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi jiehe zazhi = Chinese journal of integrated traditional and western medicine / Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he xue hui. Zhongguo Zhong yi yan jiu yuan zhu ban 35:327–332
Chen X, Petranovic D (2015) Amyloid-beta peptide-induced cytotoxicity and mitochondrial dysfunction in yeast FEMS yeast research 15 doi:https://doi.org/10.1093/femsyr/fov061, Amyloid-β peptide-induced cytotoxicity and mitochondrial dysfunction in yeast, 15
Chesser AS, Ganeshan V, Yang J, Johnson GV (2016) Epigallocatechin-3-gallate enhances clearance of phosphorylated tau in primary neurons nutritional neuroscience 19:21–31. https://doi.org/10.1179/1476830515y.0000000038
Chesser AS, Pritchard SM, Johnson GV (2013) Tau clearance mechanisms and their possible role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease. Frontiers Neurology 4:122. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2013.00122
Chiu C, Miller MC, Monahan R, Osgood DP, Stopa EG, Silverberg GD (2015) P-glycoprotein expression and amyloid accumulation in human aging and Alzheimer's disease: preliminary observations. Neurobiology Aging 36:2475–2482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.05.020
Christianson HC, Belting M (2014) Heparan sulfate proteoglycan as a cell-surface endocytosis receptor. Matrix Biology : J Int Soc Matrix Biology 35:51–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2013.10.004
Chu TT et al (2014) Clearance of the intracellular high level of the tau protein directed by an artificial synthetic hydrolase molecular. Bio Systems 10:3081–3085. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4mb00508b
Congdon EE et al. (2012) Methylthioninium chloride (methylene blue) induces autophagy and attenuates tauopathy in vitro and in vivo autophagy 8:609–622. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.19048
Cserr HF, Harling-Berg CJ, Knopf PM (1992) Drainage of brain extracellular fluid into blood and deep cervical lymph and its immunological significance. Brain Pathology (Zurich, Switzerland) 2:269–276
Deane R et al. (2003) RAGE mediates amyloid-beta peptide transport across the blood-brain barrier and accumulation in brain. Nature Medicine 9:907–913. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm890
DeMattos RB, Bales KR, Cummins DJ, Dodart JC, Paul SM, Holtzman DM (2001) Peripheral anti-A beta antibody alters CNS and plasma A beta clearance and decreases brain A beta burden in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 98:8850–8855. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.151261398
Demattos RB et al. (2012) A plaque-specific antibody clears existing beta-amyloid plaques in Alzheimer's disease mice. Neuron 76:908–920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2012.10.029
Doi Y, Takeuchi H, Mizoguchi H, Fukumoto K, Horiuchi H, Jin S, Kawanokuchi J, Parajuli B, Sonobe Y, Mizuno T, Suzumura A (2014) Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor attenuates oligomeric amyloid beta neurotoxicity by activation of neprilysin. PloS One 9:e103458. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0103458
Du J, Liang Y, Xu F, Sun B, Wang Z (2013) Trehalose rescues Alzheimer's disease phenotypes in APP/PS1 transgenic mice the journal of pharmacy and pharmacology 65:1753–1756. https://doi.org/10.1111/jphp.12108
Dugger BN et al. (2016) The presence of select tau Speciesin human peripheral tissues and their relation to Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease : JAD 51:345–356. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-150859
El-Shimy IA, Heikal OA, Hamdi N (2015) Minocycline attenuates Abeta oligomers-induced pro-inflammatory phenotype in primary microglia while enhancing Abeta fibrils phagocytosis. Neuroscience Letters 609:36–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2015.10.024
Erickson MA, Banks WA (2013) Blood-brain barrier dysfunction as a cause and consequence of Alzheimer's disease. J Cerebral Blood Flow Metabolism : Official J Int Soc Cerebral Blood Flow Metabolism 33:1500–1513. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2013.135
Escribano L et al. (2010) Rosiglitazone rescues memory impairment in Alzheimer's transgenic mice: mechanisms involving a reduced amyloid and tau pathology Neuropsychopharmacology : official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology 35:1593–1604. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2010.32
Fan W, Long Y, Lai Y, Wang X, Chen G, Zhu B (2016) NPAS4 facilitates the Autophagic clearance of endogenous tau in rat cortical neurons journal of molecular neuroscience : MN 58:401–410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0692-5
Ferreira A, Bigio EH (2011) Calpain-mediated tau cleavage: a mechanism leading to neurodegeneration shared by multiple tauopathies. Molecular Medicine (Cambridge, Mass) 17:676–685. https://doi.org/10.2119/molmed.2010.00220
Fujiwara H et al. (2014) Nobiletin, a flavone from Citrus depressa, induces gene expression and increases the protein level and activity of neprilysin in SK-N-SH cells Canadian journal of physiology and pharmacology 92:351–355. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjpp-2013-0440
Fujiyoshi M et al. (2011) Amyloid-beta peptide(1-40) elimination from cerebrospinal fluid involves low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 at the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier journal of neurochemistry 118:407–415. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07311.x
Ghiso J et al. (2004) Systemic catabolism of Alzheimer's Abeta40 and Abeta42 the journal of biological chemistry 279:45897–45908 https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M407668200
Glebov K, Walter J (2012) Statins in unconventional secretion of insulin-degrading enzyme and degradation of the amyloid-beta peptide. Neuro-Degenerative Diseases 10:309–312. https://doi.org/10.1159/000332595
Gonzalez-Marrero I et al (2015) Choroid plexus dysfunction impairs beta-amyloid clearance in a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Frontiers Cellular Neuroscience 9:17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2015.00017
Grimm MO et al. (2016) Eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid increase the degradation of amyloid-beta by affecting insulin-degrading enzyme biochemistry and cell biology = Biochimie et biologie cellulaire:534-542 doi:https://doi.org/10.1139/bcb-2015-0149
Guenette SY (2003) Astrocytes: a cellular player in Abeta clearance and degradation. Trends Mol Med 9:279–280
Guo HD et al. (2016a) Electroacupuncture improves memory and protects neurons by regulation of the autophagy pathway in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease. Acupuncture in medicine : journal of the British medical acupuncture society 34:449–456. https://doi.org/10.1136/acupmed-2015-010894
Guo YX, He LY, Zhang M, Wang F, Liu F, Peng WX (2016b) 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D regulates expression of LRP1 and RAGE in vitro and in vivo, enhancing Abeta brain-to-blood efflux and peripheral uptake transport neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.01.041
Halle M et al. (2015) Methods to monitor monocytes-mediated amyloid-beta uptake and phagocytosis in the context of adjuvanted immunotherapies journal of immunological methods 424:64–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2015.05.002
Hartz AM, Zhong Y, Wolf A, LeVine H, 3rd, Miller DS, Bauer B (2016) Abeta40 reduces P-glycoprotein at the blood-brain barrier through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway the journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 36:1930–1941. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0350-15.2016
Hashimoto M, Hossain S, Katakura M, Al Mamun A, Shido O (2015) The binding of Abeta1-42 to lipid rafts of RBC is enhanced by dietary docosahexaenoic acid in rats: implicates to Alzheimer's disease Biochimica et biophysica acta 1848:1402–1409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.03.008
Hawkes CA, Gentleman SM, Nicoll JA, Carare RO (2015) Prenatal high-fat diet alters the cerebrovasculature and clearance of beta-amyloid in adult offspring. J Pathology 235:619–631. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.4468
Hawkes CA, Hartig W, Kacza J, Schliebs R, Weller RO, Nicoll JA, Carare RO (2011) Perivascular drainage of solutes is impaired in the ageing mouse brain and in the presence of cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Acta Neuropathologica 121:431–443. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-011-0801-7
Hawkes CA, Jayakody N, Johnston DA, Bechmann I, Carare RO (2014) Failure of perivascular drainage of beta-amyloid in cerebral amyloid angiopathy brain pathology (Zurich, Switzerland) 24:396-403 doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/bpa.12159
Hawkes CA, Sullivan PM, Hands S, Weller RO, Nicoll JA, Carare RO (2012) Disruption of arterial perivascular drainage of amyloid-beta from the brains of mice expressing the human APOE epsilon4 allele. PloS One 7:e41636. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0041636
He Y, Zhao H, Su G (2014) Ginsenoside Rg1 decreases neurofibrillary tangles accumulation in retina by regulating activities of neprilysin and PKA in retinal cells of AD mice model journal of molecular neuroscience: MN 52:101–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0173-7
Hemming ML, Selkoe DJ (2005) Amyloid beta-protein is degraded by cellular angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and elevated by an ACE inhibitor. J Biological Chemistry 280:37644–37650. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M508460200
Henderson SJ et al. (2014) Sustained peripheral depletion of amyloid-beta with a novel form of neprilysin does not affect central levels of amyloid-beta brain. A journal of neurology 137:553–564. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awt308
Herring A et al (2016) Late running is not too late against. Alzheimer's Pathology Neurobiology Disease 94:44–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2016.06.003
Hope AD, de Silva R, Fischer DF, Hol EM, van Leeuwen FW, Lees AJ (2003) Alzheimer's associated variant ubiquitin causes inhibition of the 26S proteasome and chaperone expression. Journal of Neurochemistry 86:394–404
Hori Y et al. (2015) A Food and Drug Administration-approved asthma therapeutic agent impacts amyloid beta in the brain in a transgenic model of Alzheimer disease the journal of biological chemistry 290:1966–1978. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.586602
Iliff JJ, Chen MJ, Plog BA, Zeppenfeld DM, Soltero M (2014) Impairment of glymphatic pathway function promotes tau pathology after traumatic brain injury 34:16180–16193. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.3020-14.2014
Iliff JJ, Lee H, Yu M, Feng T, Logan J, Nedergaard M, Benveniste H (2013a) Brain-wide pathway for waste clearance captured by contrast-enhanced MRI. J Clinical Investigation 123:1299–1309. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci67677
Iliff JJ, Nedergaard M (2013) Is there a cerebral lymphatic system? Stroke 44:S93–S95. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.678698
Iliff JJ et al. (2012) A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid beta science translational medicine 4:147ra111. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3003748
Iliff JJ et al. (2013b) Cerebral arterial pulsation drives paravascular CSF-interstitial fluid exchange in the murine brain the journal of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 33:18190-18199. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1592-13.2013
Jariel-Encontre I, Bossis G, Piechaczyk M (2008) Ubiquitin-independent degradation of proteins by the proteasome. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1786:153–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2008.05.004
Jay T, Lamb B, Landreth G (2015) Peripheral macrophages not ADept at amyloid clearance. J Experimental Medicine 212:1758. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.21211insight5
Jiang T et al. (2014a) Upregulation of TREM2 ameliorates neuropathology and rescues spatial cognitive impairment in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease Neuropsychopharmacology: official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology 39:2949–2962. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.164
Jiang T, Yu JT, Hu N, Tan MS, Zhu XC, Tan L (2014b) CD33 in Alzheimer's disease molecular neurobiology 49:529–535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8536-1
Jiang T, Yu JT, Zhu XC, Tan L (2013) TREM2 in Alzheimer's disease molecular neurobiology 48:180–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8424-8
Jiang T et al. (2014c) Temsirolimus promotes autophagic clearance of amyloid-beta and provides protective effects in cellular and animal models of Alzheimer's disease. Pharmacological Research 81:54–63 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2014.02.008
Jiang T et al (2014d) Temsirolimus attenuates tauopathy in vitro and in vivo by targeting tau hyperphosphorylation and autophagic clearance. Neuropharmacology 85:121–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.05.032
Jin WS et al (2017) Peritoneal dialysis reduces amyloid-beta plasma levels in humans and attenuates Alzheimer-associated phenotypes in an APP/PS1 mouse model. Acta Neuropathologica 134:207–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-017-1721-y
Johnston M, Zakharov A, Papaiconomou C, Salmasi G, Armstrong D (2004) Evidence of connections between cerebrospinal fluid and nasal lymphatic vessels in humans, non-human primates and other mammalian species cerebrospinal fluid research 1:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-8454-1-2
Kang EB, Cho JY (2015) Effect of treadmill exercise on PI3K/AKT/mTOR, autophagy, and tau hyperphosphorylation in the cerebral cortex of NSE/htau23 transgenic mice journal of exercise nutrition & biochemistry 19:199–209. https://doi.org/10.5717/jenb.2015.15090806
Kenessey A, Nacharaju P, Ko LW, Yen SH (1997) Degradation of tau by lysosomal enzyme cathepsin D: implication for Alzheimer neurofibrillary degeneration. J Neurochemistry 69:2026–2038
Kitazawa M, Hsu HW, Medeiros R (2016) Copper exposure perturbs brain inflammatory responses and impairs clearance of amyloid-beta toxicological sciences: an official journal of the Society of Toxicology. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfw081
Kochkina EG, Plesneva SA, Vasilev DS, Zhuravin IA, Turner AJ, Nalivaeva NN (2015) Effects of ageing and experimental diabetes on insulin-degrading enzyme expression in male rat tissues. Biogerontology 16:473–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-015-9569-9
Kruger U, Wang Y, Kumar S, Mandelkow EM (2012) Autophagic degradation of tau in primary neurons and its enhancement by trehalose. Neurobiology Aging 33:2291–2305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.11.009
Ledesma MD, Da Silva JS, Crassaerts K, Delacourte A, De Strooper B, Dotti CG (2000) Brain plasmin enhances APP alpha-cleavage and Abeta degradation and is reduced in Alzheimer's disease brains. EMBO Reports 1:530–535. https://doi.org/10.1093/embo-reports/kvd107
Lee CY, Landreth GE (2010) The role of microglia in amyloid clearance from the AD brain. J Neural Transmission 117:949–960. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-010-0433-4
Lei Z, Brizzee C, Johnson GV (2015) BAG3 facilitates the clearance of endogenous tau in primary neurons neurobiology of aging 36:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.08.012
Li Y, Tan MS, Jiang T, Tan L (2014) Microglia in Alzheimer's disease. BioMed Res Int 2014:437483–437487. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/437483
Liu YH et al. (2015) Clearance of amyloid-beta in Alzheimer's disease: shifting the action site from center to periphery. Molecular Neurobiology 51:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8694-9
Lorenzo MN, Khan RY, Wang Y, Tai SC, Chan GC, Cheung AH, Marsden PA (2001) Human endothelin converting enzyme-2 (ECE2): characterization of mRNA species and chromosomal localization. Biochim Biophys Acta 1522:46–52
Louveau A et al. (2015) Structural and functional features of central nervous system lymphatic vessels. Nature 523:337–341. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14432
Luo W, Liu W, Hu X, Hanna M, Caravaca A, Paul SM (2015) Microglial internalization and degradation of pathological tau is enhanced by an anti-tau monoclonal antibody. Scientific Reports 5:11161. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11161
Madani R et al. (2006) Lack of neprilysin suffices to generate murine amyloid-like deposits in the brain and behavioral deficit in vivo. Journal of Neuroscience Research 84:1871–1878. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.21074
Magnaudeix A et al. (2013) PP2A blockade inhibits autophagy and causes intraneuronal accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins. Neurobiology of Aging 34:770–7900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.06.026
Maki T et al. (2014) Phosphodiesterase III inhibitor promotes drainage of cerebrovascular beta-amyloid. Annals of clinical and translational neurology 1:519–533. https://doi.org/10.1002/acn3.79
Mandrekar-Colucci S, Karlo JC, Landreth GE (2012) Mechanisms underlying the rapid peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma-mediated amyloid clearance and reversal of cognitive deficits in a murine model of Alzheimer's disease. J Neuroscience : official J Society Neuroscience 32:10117–10128. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5268-11.2012
Mann A et al. (2017) Chronic deep brain stimulation in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model enhances memory and reduces pathological hallmarks brain stimulation. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2017.11.012
Mawuenyega KG, Sigurdson W, Ovod V, Munsell L, Kasten T, Morris JC, Yarasheski KE, Bateman RJ (2010) Decreased clearance of CNS beta-amyloid in Alzheimer's disease. Science 330:1774. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1197623
Mendelsohn AR, Larrick JW (2013) Sleep facilitates clearance of metabolites from the brain: glymphatic function in aging and neurodegenerative diseases. Rejuvenation Res 16:518–523. https://doi.org/10.1089/rej.2013.1530
Merino JJ, Muneton-Gomez V, Alvarez MI, Toledano-Diaz A (2016) Effects of CX3CR1 and Fractalkine Chemokines in Amyloid Beta clearance and p-Tau accumulation in Alzheimer,s disease (AD) rodent models: is fractalkine a systemic biomarker for AD? Curr Alzheimer Res 13:403–412
Miners JS, Barua N, Kehoe PG, Gill S, Love S (2011) Abeta-degrading enzymes: potential for treatment of Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathology Experimental Neurology 70:944–959. https://doi.org/10.1097/NEN.0b013e3182345e46
Mohamed LA, Qosa H, Kaddoumi A (2015) Age-related decline in brain and hepatic clearance of amyloid-beta is rectified by the cholinesterase inhibitors donepezil and rivastigmine in rats. ACS Chemical Neuroscience 6:725–736. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00040
Moore KM et al. (2016) A spectrum of exercise training reduces soluble Abeta in a dose-dependent manner in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiology of Disease 85:218–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2015.11.004
Morris AW et al. (2016) Vascular basement membranes as pathways for the passage of fluid into and out of the brain Acta neuropathologica. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-016-1555-z
Myeku N, Clelland CL, Emrani S, Kukushkin NV, Yu WH, Goldberg AL, Duff KE (2016) Tau-driven 26S proteasome impairment and cognitive dysfunction can be prevented early in disease by activating cAMP-PKA signaling nature medicine 22:46-–53. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4011
Olsson B et al. (2016) CSF and blood biomarkers for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurology https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(16)00070-3
Pappolla M, Sambamurti K, Vidal R, Pacheco-Quinto J, Poeggeler B, Matsubara E (2014) Evidence for lymphatic A beta clearance in Alzheimer's transgenic mice. Journal of Neuroscience 71:215–219 https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.3742-14.2015 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2014.07.012
Pascale CL, Miller MC, Chiu C, Boylan M, Caralopoulos IN, Gonzalez L, Johanson CE, Silverberg GD (2011) Amyloid-beta transporter expression at the blood-CSF barrier is age-dependent. Fluids Barriers CNS 8:21. https://doi.org/10.1186/2045-8118-8-21
Pflanzner T et al. (2011) LRP1 mediates bidirectional transcytosis of amyloid-beta across the blood-brain barrier neurobiology of aging 32:2323.e2321–2311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.05.025
Picken MM (2001) The changing concepts of amyloid archives of pathology & laboratory medicine 125:38–43. https://doi.org/10.1043/0003-9985(2001)125<0038:TCCOA>2.0.CO;2
Planque SA et al. (2015) Specific amyloid beta clearance by a catalytic antibody construct. Journal of Biological Chemistry 290:10229–10241. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.641738
Polito VA et al. (2014) Selective clearance of aberrant tau proteins and rescue of neurotoxicity by transcription factor EB EMBO molecular medicine 6:1142–1160. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201303671
Pollay M (2010) The function and structure of the cerebrospinal fluid outflow system. Cerebrospinal Fluid Res 7:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-8454-7-9
Qosa H, Batarseh YS, Mohyeldin MM, El Sayed KA, Keller JN, Kaddoumi A (2015) Oleocanthal enhances amyloid-beta clearance from the brains of TgSwDI mice and in vitro across a human blood-brain barrier model. ACS Chemical Neuroscience 6:1849–1859. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00190
Reitz C, Mayeux R (2014) Alzheimer disease: epidemiology, diagnostic criteria, risk factors and biomarkers. Biochemical Pharmacology 88:640–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2013.12.024
Ren Z et al. (2013) 'Hit & Run' model of closed-skull traumatic brain injury (TBI) reveals complex patterns of post-traumatic AQP4 dysregulation journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism : official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 33:834–845. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2013.30
Rennels ML, Gregory TF, Blaumanis OR, Fujimoto K, Grady PA (1985) Evidence for a 'paravascular' fluid circulation in the mammalian central nervous system, provided by the rapid distribution of tracer protein throughout the brain from the subarachnoid space. Brain Research 326:47–63
Ribeiro CA, Oliveira SM, Guido LF, Magalhães A, Valencia G, Arsequell G, Saraiva MJ, Cardoso I (2014) Transthyretin stabilization by iododiflunisal promotes amyloid-beta peptide clearance, decreases its deposition, and ameliorates cognitive deficits in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model. J Alzheimer's Disease : JAD 39:357–370. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-131355
Ries M, Loiola R, Shah UN, Gentleman SM, Solito E, Sastre M (2016) The anti-inflammatory Annexin A1 induces the clearance and degradation of the amyloid-beta peptide. J Neuroinflammation 13:234. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-016-0692-6
Roberts KF, Elbert DL, Kasten TP, Patterson BW, Sigurdson WC, Connors RE, Ovod V, Munsell LY, Mawuenyega KG, Miller-Thomas MM, Moran CJ, Cross DT III, Derdeyn CP, Bateman RJ (2014) Amyloid-beta efflux from the central nervous system into the plasma. Ann Neurol 76:837–844. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24270
Rogers J, Li R, Mastroeni D, Grover A, Leonard B, Ahern G, Cao P, Kolody H, Vedders L, Kolb WP, Sabbagh M (2006) Peripheral clearance of amyloid beta peptide by complement C3-dependent adherence to erythrocytes. Neurobiol Aging 27:1733–1739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.09.043
Sakae N, Liu CC, Shinohara M, Frisch-Daiello J, Ma L, Yamazaki Y, Tachibana M, Younkin L, Kurti A, Carrasquillo MM, Zou F, Sevlever D, Bisceglio G, Gan M, Fol R, Knight P, Wang M, Han X, Fryer JD, Fitzgerald ML, Ohyagi Y, Younkin SG, Bu G, Kanekiyo T (2016) ABCA7 deficiency accelerates amyloid-beta generation and Alzheimer's neuronal pathology. J neuroscience : Official J Soc Neuroscience 36:3848–3859. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3757-15.2016
Schwartz AL, Ciechanover A (2009) Targeting proteins for destruction by the ubiquitin system: implications for human pathobiology. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 49:73–96. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.051208.165340
Sehgal N, Gupta A, Valli RK, Joshi SD, Mills JT, Hamel E, Khanna P, Jain SC, Thakur SS, Ravindranath V (2012) Withania somnifera reverses Alzheimer's disease pathology by enhancing low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in liver. Proceedings National Academy Sci United States Am 109:3510–3515. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1112209109
Serot JM, Zmudka J, Jouanny P (2012) A possible role for CSF turnover and choroid plexus in the pathogenesis of late onset Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimer's Disease : JAD 30:17–26. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2012-111964
Shang F, Taylor A (2011) Ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and cellular responses to oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 51:5–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.03.031
Shimada K, Motoi Y, Ishiguro K, Kambe T, Matsumoto SE, Itaya M, Kunichika M, Mori H, Shinohara A, Chiba M, Mizuno Y, Ueno T, Hattori N (2012) Long-term oral lithium treatment attenuates motor disturbance in tauopathy model mice: implications of autophagy promotion. Neurobiol Dis 46:101–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2011.12.050
Shirotani K, Tsubuki S, Iwata N, Takaki Y, Harigaya W, Maruyama K, Kiryu-Seo S, Kiyama H, Iwata H, Tomita T, Iwatsubo T, Saido TC (2001) Neprilysin degrades both amyloid beta peptides 1–40 and 1–42 most rapidly and efficiently among thiorphan- and phosphoramidon-sensitive endopeptidases. J Biological Chemistry 276:21895–21901. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M008511200
Silverberg GD, Mayo M, Saul T, Rubenstein E, McGuire D (2003) Alzheimer's disease, normal-pressure hydrocephalus, and senescent changes in CSF circulatory physiology: a hypothesis. The Lancet Neurology 2:506–511
Simonovitch S et al. (2016) Impaired Autophagy in APOE4 Astrocytes Journal of Alzheimer's disease : JAD. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-151101
Spencer B, Marr RA, Rockenstein E, Crews L, Adame A, Potkar R, Patrick C, Gage FH, Verma IM, Masliah E (2008) Long-term neprilysin gene transfer is associated with reduced levels of intracellular Abeta and behavioral improvement in APP transgenic mice. BMC Neurosci 9:109. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2202-9-109
Spilman P, Podlutskaya N, Hart MJ, Debnath J, Gorostiza O, Bredesen D, Richardson A, Strong R, Galvan V (2010) Inhibition of mTOR by rapamycin abolishes cognitive deficits and reduces amyloid-beta levels in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. PLoS One 5:e9979. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0009979
Stanyon HF, Viles JH (2012) Human serum albumin can regulate amyloid-beta peptide fiber growth in the brain interstitium: implications for Alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem 287:28163–28168. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C112.360800
Suzuki Y, Nakamura Y, Yamada K, Igarashi H, Kasuga K, Yokoyama Y, Ikeuchi T, Nishizawa M, Kwee IL, Nakada T (2015) Reduced CSF water influx in Alzheimer's disease supporting the beta-amyloid clearance hypothesis. PLoS One 10:e0123708. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0123708
Tachibana M, Yamazaki Y, Liu CC, Bu G, Kanekiyo T (2018) Pericyte implantation in the brain enhances cerebral blood flow and reduces amyloid-beta pathology in amyloid model mice. Exp Neurol 300:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.10.023
Tai HC, Serrano-Pozo A, Hashimoto T, Frosch MP, Spires-Jones TL, Hyman BT (2012) The synaptic accumulation of hyperphosphorylated tau oligomers in Alzheimer disease is associated with dysfunction of the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Am J Pathol 181:1426–1435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.06.033
Tan CC, Yu JT, Tan L (2014a) Biomarkers for preclinical Alzheimer's disease Journal of Alzheimer's disease : JAD 42:1051–1069. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-140843, Biomarkers for preclinical Alzheimer's disease
Tan CC, Yu JT, Tan MS, Jiang T, Zhu XC, Tan L (2014b) Autophagy in aging and neurodegenerative diseases: implications for pathogenesis and therapy. Neurobiol Aging 35:941–957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.11.019
Tarasoff-Conway JM, Carare RO, Osorio RS, Glodzik L, Butler T, Fieremans E, Axel L, Rusinek H, Nicholson C, Zlokovic BV, Frangione B, Blennow K, Ménard J, Zetterberg H, Wisniewski T, de Leon MJ (2015) Clearance systems in the brain-implications for Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol 11:457–470. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2015.119
Tian Y, Bustos V, Flajolet M, Greengard P (2011) A small-molecule enhancer of autophagy decreases levels of Abeta and APP-CTF via Atg5-dependent autophagy pathway. FASEB J: Official Publication Federation Am Societies Experimental Biology 25:1934–1942. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.10-175158
Tundo G, Ciaccio C, Sbardella D, Boraso M, Viviani B, Coletta M, Marini S (2012) Somatostatin modulates insulin-degrading-enzyme metabolism: implications for the regulation of microglia activity in AD. PLoS One 7:e34376. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0034376
Ullrich C, Mlekusch R, Kuschnig A, Marksteiner J, Humpel C (2010) Ubiquitin enzymes, ubiquitin and proteasome activity in blood mononuclear cells of MCI, Alzheimer and Parkinson patients. Curr Alzheimer Res 7:549–555
van Assema DM et al (2012) Blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein function in Alzheimer's disease. Brain : a J Neurology 135:181–189. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awr298
van Tijn P, Dennissen FJA, Gentier RJG, Hobo B, Hermes D, Steinbusch HWM, van Leeuwen FW, Fischer DF (2012) Mutant ubiquitin decreases amyloid beta plaque formation in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Neurochem Int 61:739–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2012.07.007
Varnum MM, Kiyota T, Ingraham KL, Ikezu S, Ikezu T (2015) The anti-inflammatory glycoprotein, CD200, restores neurogenesis and enhances amyloid phagocytosis in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 36:2995–3007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.07.027
Vekrellis K, Ye Z, Qiu WQ, Walsh D, Hartley D, Chesneau V, Rosner MR, Selkoe DJ (2000) Neurons regulate extracellular levels of amyloid beta-protein via proteolysis by insulin-degrading enzyme. J Neuroscience: Official J Soc Neuroscience 20:1657–1665
Vilchez D, Saez I, Dillin A (2014) The role of protein clearance mechanisms in organismal ageing and age-related diseases. Nat Commun 5:5659. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6659
Wang S, He F, Wang Y (2015a) Association between polymorphisms of the insulin-degrading enzyme gene and late-onset Alzheimer disease. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 28:94–98. https://doi.org/10.1177/0891988714554707
Wang XX, Tan MS, Yu JT, Tan L (2014) Matrix metalloproteinases and their multiple roles in Alzheimer's disease Biomed Res Int 2014:908636. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/908636, 1, 8
Wang Y, Cella M, Mallinson K, Ulrich JD, Young KL, Robinette ML, Gilfillan S, Krishnan GM, Sudhakar S, Zinselmeyer BH, Holtzman DM, Cirrito JR, Colonna M (2015b) TREM2 lipid sensing sustains the microglial response in an Alzheimer's disease model. Cell 160:1061–1071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.049
Wang Y, Mandelkow E (2012) Degradation of tau protein by autophagy and proteasomal pathways. Biochem Soc Trans 40:644–652. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20120071
Wang Y, Martinez-Vicente M, Krüger U, Kaushik S, Wong E, Mandelkow EM, Cuervo AM, Mandelkow E (2009) Tau fragmentation, aggregation and clearance: the dual role of lysosomal processing. Hum Mol Genet 18:4153–4170. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddp367
Wei W, Bodles-Brakhop AM, Barger SW (2016) A role for P-glycoprotein in clearance of Alzheimer amyloid beta-peptide from the brain current Alzheimer research
Winkler EA, Nishida Y, Sagare AP, Rege SV, Bell RD, Perlmutter D, Sengillo JD, Hillman S, Kong P, Nelson AR, Sullivan JS, Zhao Z, Meiselman HJ, Wenby RB, Soto J, Abel ED, Makshanoff J, Zuniga E, de Vivo DC, Zlokovic BV (2015) GLUT1 reductions exacerbate Alzheimer's disease vasculo-neuronal dysfunction and degeneration. Nat Neurosci 18:521–530. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3966
Wong AD, Ye M, Levy AF, Rothstein JD, Bergles DE, Searson PC (2013) The blood-brain barrier: an engineering perspective. Frontiers Neuroengineering 6:7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneng.2013.00007
Wong E, Cuervo AM (2010) Integration of clearance mechanisms: the proteasome and autophagy. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2:a006734. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a006734
Xiang Y, Bu XL, Liu YH, Zhu C, Shen LL, Jiao SS, Zhu XY, Giunta B, Tan J, Song WH, Zhou HD, Zhou XF, Wang YJ (2015) Physiological amyloid-beta clearance in the periphery and its therapeutic potential for Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 130:487–499. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1477-1
Xiao Q, Yan P, Ma X, Liu H, Perez R, Zhu A, Gonzales E, Burchett JM, Schuler DR, Cirrito JR, Diwan A, Lee JM (2014) Enhancing astrocytic lysosome biogenesis facilitates Abeta clearance and attenuates amyloid plaque pathogenesis. J Neuroscience : Official J Soc Neuroscience 34:9607–9620. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.3788-13.2014
Xie L, Kang H, Xu Q, Chen MJ, Liao Y, Thiyagarajan M, O'Donnell J, Christensen DJ, Nicholson C, Iliff JJ, Takano T, Deane R, Nedergaard M (2013) Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain. Science 342:373–377. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1241224
Xu D, Emoto N, Giaid A, Slaughter C, Kaw S, deWit D, Yanagisawa M (1994) ECE-1: a membrane-bound metalloprotease that catalyzes the proteolytic activation of big endothelin-1. Cell 78:473–485
Xu W, Tan L, Yu JT (2015) The role of PICALM in Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurobiol 52:399–413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8878-3
Yamamoto N, Fujii Y., Kasahara R., Tanida M., Ohora K., Ono Y., Suzuki K., Sobue K. (2016) Simvastatin and atorvastatin facilitates amyloid beta-protein degradation in extracellular spaces by increasing neprilysin secretion from astrocytes through activation of MAPK/Erk1/2 pathways. Glia https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.22974
Yu Y, Ye RD (2015) Microglial A beta receptors in Alzheimer's disease. Cell Mol Neurobiol 35:71–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0101-6
Zhang YD, Zhao JJ (2015) TFEB participates in the A beta-induced pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease by regulating the autophagy-lysosome pathway. DNA Cell Biol 34:661–668. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2014.2738
Zhao QF, Yu JT, Tan MS, Tan L (2015a) ABCA7 in Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurobiol 51:1008–1016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8759-9
Zhao Z, Sagare AP, Ma Q, Halliday MR, Kong P, Kisler K, Winkler EA, Ramanathan A, Kanekiyo T, Bu G, Owens NC, Rege SV, Si G, Ahuja A, Zhu D, Miller CA, Schneider JA, Maeda M, Maeda T, Sugawara T, Ichida JK, Zlokovic BV (2015b) Central role for PICALM in amyloid-beta blood-brain barrier transcytosis and clearance. Nat Neurosci 18:978–987. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4025
Zhu Y, Wang J (2015) Wogonin increases beta-amyloid clearance and inhibits tau phosphorylation via inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin: potential drug to treat Alzheimer's disease. Neurological Sci : Official J Italian Neurological Soc Italian Soc Clinical Neurophysiology 36:1181–1188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-015-2070-z
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National key projects for research and development of MOST (2016YFC1305800), the Shandong Provincial Outstanding Medical Academic Professional Program, Qingdao Key Health Discipline Development Fund, Qingdao Outstanding Health Professional Development Fund, and Shandong Provincial Collaborative Innovation Center for Neurodegenerative Disorders.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xin, SH., Tan, L., Cao, X. et al. Clearance of Amyloid Beta and Tau in Alzheimer’s Disease: from Mechanisms to Therapy. Neurotox Res 34, 733–748 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-018-9895-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-018-9895-1