Abstract
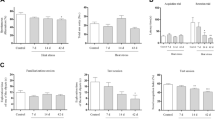
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a primary neurodegenerative disorder associated with progressive memory impairment. Recent studies suggest that hypothermia may contribute to the development and exacerbation of AD. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of chronic hypothermia on spatial learning and memory performance as well as brain immunohistochemical (IHC) and molecular changes. Four groups of male rats were placed in cold water (3.5 ± 0.5 °C) once a day for 1, 3, 6, and 14 days, four other groups were placed in warm water (32 °C) as the control groups to eliminate the effect of swimming stress, and one more group which comprised intact animals that were kept in a normothermic situation and had no swimming stress. Twenty-four hours after the last intervention, spatial learning and memory were assessed, using the modified Morris water maze. After the behavioral test, the rats’ brains were removed for IHC and Western blotting. The results showed that memory retrieval is impaired after 14 days of cold water-induced hypothermia (CWH) (P < 0.05). IHC showed the formation of beta-amyloid plaques after a 14-day CWH. The molecular changes demonstrated that a 14-day CWH induces tau hyperphosphorylation, apoptosis, and reduces COX-II expression. Therefore, chronic CWH, independent of forced swimming stress, impairs learning and memory through molecular mechanisms similar to those of AD. In conclusion, CWH may serve as an important model to assess the role of hypothermia in AD pathogenesis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadian-Attari MM, Ahmadiani A, Kamalinejad M, Dargahi L, Mosaddegh M (2014) Chronic Cold-Water-Induced Hypothermia impairs memory retrieval and Nepeta menthoides as a traditional “Hot” herb reverses the impairment. Iran J Pharm Res 13:185–193
Aid S, Langenbach R, Bosetti F (2008) Neuroinflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide is exacerbated in mice genetically deficient in cyclooxygenase-2. J Neuroinflamm 5:17. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-5-17
Aid S, Silva AC, Candelario-Jalil E, Choi SH, Rosenberg GA, Bosetti F (2010) Cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 differentially modulate lipopolysaccharide-induced blood-brain barrier disruption through matrix metalloproteinase activity. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:370e380. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2009.223
Alzheimer’s Association (2012) Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. pp 5 and 10. http://www.alz.org/downloads/facts_figures_2012.pdf, Accessed 8 Apr 2013
Augustinack JC, Schneider A, Mandelkow EM, Hyman BT (2002) Specific tau phosphorylation sites correlate with severity of neuronal cytopathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 103:26–35
Austin BP, Nair VA, Meier TB, Xu G, Rowley HA, Carlsson CM, Johnson SC, Prabhakaran V (2011) Effects of hypoperfusion in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 26:S123–S133. doi:10.3233/JAD-2011-0010
Avicenna (970–1051 AD) (2010) The Canon (Canon of Medicine), Persian translation of the critical arabic text, 9th edn. vol 3, Soroush Press, Tehran, pp 118–119
Blais V, Turrin NP, Rivest S (2005) Cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) inhibition increases the inflammatory response in the brain during systemic immune stimuli. J Neurochem 95:1563e1574
Carey HV, Andrews MT, Martin SL (2003) Mammalian hibernation: cellular and molecular responses to depressed metabolism and low temperature. Physiol Rev 83:1153–1181
Casadesus G, Arendash G, Laferla F, McDonald M (2010) Animal models of Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Alzheimers Dis. doi:10.4061/2010/606357
Chen L, Wei J, Lei Z, Zhang L, Liu Y, Sun F (2005) Induction of Bcl-2 and Bax was related to hyperphosphorylation of tau and neuronal death induced by okadaic acid in rat brain. Anat Rec A 287:1236–1245
Cheng SX, Zhang S, Sun HT, Tu Y (2013) Effects of mild hypothermia treatment on rat hippocampal β-amyloid expression following traumatic brain injury. Ther Hypothermia Temp Manag 3:132–139
Choi SH, Aid S, Choi U, Bosetti F (2010) Cyclooxygenases-1 and -2 differentially modulate leukocyte recruitment into the inflamed brain. Pharmacogenom J 10:448–457. doi:10.1038/tpj.2009.68
Cowley TR, Fahey B, O’Mara SM (2008) COX-2, but not COX-1, activity is necessary for the induction of perforant path long-term potentiation and spatial learning in vivo. Eur J Neurosci 27:2999–3008. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06251.x
Daulatzai MA (2010) Conversion of elderly to Alzheimer’s dementia: role of confluence of hypothermia and senescent stigmata—the plausible pathway. J Alzheimers Dis 21:1039–1063
Daulatzai MA (2013) Neurotoxic saboteurs: straws that break the hippo’s (hippocampus) back drive cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotox Res 24:407–459
De Groote L, Linthorst ACE (2007) Exposure to novelty and forced swimming evoke stressor-dependent changes in extracellular GABA in the rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 148:794–805
Dong Y, Wu X, Xu Z, Zhang Y, Xie Z (2012) Anesthetic isoflurane increases phosphorylated tau levels mediated by caspase activation and Aβ generation. PLoS One 7:e39386. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039386
Drugan RC, Eren S, Hazi A, Silva J, Christianson JP, Kent S (2005) Impact of water temperature and stressor controllability on swim stress-induced changes in body temperature, serum corticosterone, and immobility in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 82:397–403
Eberspacher E, Werner C, Engelhard K, Pape M, Gelb A, Hutzler P, Henke J, Kochs E (2003) The effect of hypothermia on the expression of the apoptosis-regulating protein Bax after incomplete cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in rats. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 15:200–208
Feng Q, Cheng B, Yang R, Sun F, Zhu C (2005) Dynamic changes of phosphorylated tau in mouse hippocampus after cold water stress. Neurosci Lett 388:13–16
Frick KM, Stillner ET, Berger-Sweeney J (2000) Mice are not little rats: species differences in a one-day water maze task. Neuroreport 11:3461–3465
Götz J, Ittner LM (2008) Animal models of Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:532–544. doi:10.1038/nrn2420
Hardy J, Allsop D (1991) Amyloid deposition as the central event in the aetiology of Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci 12:383–388
Hewett SJ, Bell SC, Hewett JA (2006) Contributions of cyclooxygenase-2 to neuroplasticity and neuropathology of the central nervous system. Pharmacol Ther 112:335e357
Holtzman A, Simon EW (2000) Body temperature as a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. Med Hypotheses 55:440–444
Hoozemans J, van Haastert ES, Veerhuis R, Arendt T, Scheper W, Eikelenboom P, Rozemuller A (2005) Maximal COX-2 and ppRb expression in neurons occurs during early Braak stages prior to the maximal activation of astrocytes and microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflamm 2:27
Idan-Feldman A, Ostritsky R, Gozes I (2012) Tau and caspase 3 as targets for neuroprotection. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2012:493670. doi:10.1155/2012/493670
Kobayashi K, Nakanoa H, Hayashib M, Shimazakia M, Fukutanic Y, Sasakic K, Sugimoria K, Koshino Y (2003) Association of phosphorylation site of tau protein with neuronal apoptosis in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci 208:17–24
Korsmeyer SJ (1999) Bcl-2 gene family and the regulation of programmed cell death. Cancer Res 59:S1693–S1700
Lenhardt R (2010) The effect of anesthesia on body temperature control. Front Biosci 2:1145–1154
Li Z, Sheng M (2012) Caspases in synaptic plasticity. Mol Brain 5:15. doi:10.1186/1756-6606-5-15
Lu SH, Lessure AR, Dai YT (2010) A systematic review of body temperature variations in older people. J Clin Nurs 19:4–16. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2702.2009.02945.x
Ma H, Sinha B, Pandya RS, Lin N, Popp AJ, Li J, Yao J, Wang X (2012) Therapeutic hypothermia as a neuroprotective strategy in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury and traumatic brain injury. Curr Mol Med 12:1282–1296
Misonou H, Morishima-Kawashima M, Ihara Y (2000) Oxidative stress induces intracellular accumulation of amyloid beta-protein (Abeta) in human neuroblastoma cells. Biochemistry 39:6951–6959
Moreira PI (2012) Alzheimer’s disease and diabetes: an integrative view of the role of mitochondria, oxidative stress, and insulin. J Alzheimers Dis 30:S199–S215. doi:10.3233/JAD-2011-111127
Moser E, Mathiesen I, Andersen P (1993) Association between brain temperature and dentate field potentials in exploring and swimming rats. Science 259:1324–1326
Neil HA, Dawson JA, Baker JE (1986) Risk of hypothermia in elderly patients with diabetes. Br Med J 293:416–418
Okawa Y, Ishiguro K, Fujita SC (2003) Stress-induced hyperphosphorylation of tau in the mouse brain. FEBS Lett 535:183–189
Oltvai Z, Milliman C, Korsmeyer SJ (1993) Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conversed homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell 74:609–619
Planel E, Miyasaka T, Launey T, Chui DH, Tanemura K, Sato S, Murayama O, Ishiguro K, Tatebayashi Y, Takashima A (2004) Alterations in glucose metabolism induce hypothermia leading to tau hyperphosphorylation through differential inhibition of kinase and phosphatase activities: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 24:2401–2411
Planel E, Richter KE, Nolan CE, Finley JE, Liu L, Wen Y, Krishnamurthy P, Herman M, Wang L, Schachter JB, Nelson RB, Lau LF, Duff KE (2007) Anesthesia leads to tau hyperphosphorylation through inhibition of phosphatase activity by hypothermia. J Neurosci 27(12):3090–3097
Rhazes (865–925 AD) (1990) Al-Hawi (The continence), persian translation of the critical arabic text, vol 1. Alhavi Pharmaceutical Company, Tehran, pp 101–109
Robins Wahlin TB, Byrne GJ (2011) Personality changes in Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 26:1019–1029. doi:10.1002/gps.2655
Scott AR, Bennett T, Macdonald IA (1987) Diabetes mellitus and thermoregulation. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 65:1365–1376
Senechal Y, Kelly PH, Dev KK (2008) Amyloid precursor protein knockout mice show age-dependent deficits in passive avoidance learning. Behav Brain Res 186:126–132
Serrano-Pozo A, Frosch MP, Masliah E, Hyman BT (2011) Neuropathological alterations in Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 1:a006189. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a006189
Shimohama S (2000) Apoptosis in Alzheimer’s disease—an update. Apoptosis 5:9–16
Stefanovic B, Bosetti F, Silva AC (2006) Modulatory role of cyclooxygenase-2 in cerebrovascular coupling. Neuroimage 32:23e32
Taltavull JF, Chefera VI, Shippenberga TS, Kiyatkinb EA (2003) Severe brain hypothermia as a factor underlying behavioral immobility during cold-water forced swim. Brain Res 975:244–247
Tan W, Cao X, Wang J, Lv H, Wu B, Ma H (2010) Tau hyperphosphorylation is associated with memory impairment after exposure to 1.5% isoflurane without temperature maintenance in rats. Eur J Anaesthesiol 27:835–841. doi:10.1097/EJA.0b013e32833a6561
Teather LA, Packard MG, Bazan NG (2002) Post-training cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibition impairs memory consolidation. Learn Mem 9:41–47
Thinakaran G, Koo EH (2008) Amyloid precursor protein trafficking, processing, and function. J Biol Chem 283:29615–29619. doi:10.1074/jbc.R800019200
Tuo J, Tuaillon N, Shen D, Chan CC (2004) Endotoxin-induced uveitis in cyclooxygenase- 2-deficient mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:2306e2313
Wang H, Zhao H, Ye Y, Xiong N, Huang J, Yao D, Shen Y, Zhao X (2010) Focal cerebral ischemia induces Alzheimer’s disease-like pathological change in rats. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci 30:29–36. doi:10.1007/s11596-010-0106-4
Whittington RA, Papon MA, Chouinard F, Planel E (2010) Hypothermia and Alzheimer’s disease neuropathogenic pathways. Curr Alzheimer Res 7:717–725
Yamagata K, Andreasson KI, Kaufmann WE, Barnes CA, Worley PF (1993) Expression of a mitogen-inducible cyclooxygenase in brain neurons: regulation by synaptic activity and glucocorticoids. Neuron 11:371–386
Yermakova AV, O’Banion MK (2001) Downregulation of neuronal cyclooxygenase-2 expression in end stage Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 22:823–836
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr Sogand Noroozizadeh and Pushpa Gandi for their contributions. This article is based on a part of a PhD thesis number 120, School of Traditional Medicine, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadian-Attari, M.M., Dargahi, L., Mosaddegh, M. et al. Impairment of Rat Spatial Learning and Memory in a New Model of Cold Water-Induced Chronic Hypothermia: Implication for Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurotox Res 28, 95–107 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-015-9525-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-015-9525-0