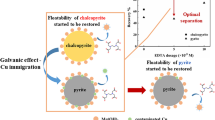
Abstract
The efficient separation of chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) and galena (PbS) is essential for optimal resource utilization. However, finding a selective depressant that is environmentally friendly and cost effective remains a challenge. Through various techniques, such as microflotation tests, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observation, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and Raman spectroscopy measurements, this study explored the use of ferric ions (Fe3+) as a selective depressant for galena. The results of flotation tests revealed the impressive selective inhibition capabilities of Fe3+ when used alone. Surface analysis showed that Fe3+ significantly reduced the adsorption of isopropyl ethyl thionocarbamate (IPETC) on the galena surface while having a minimal impact on chalcopyrite. Further analysis using SEM, XPS, and Raman spectra revealed that Fe3+ can oxidize lead sulfide to form compact lead sulfate nanoparticles on the galena surface, effectively depressing IPETC adsorption and increasing surface hydrophilicity. These findings provide a promising solution for the efficient and environmentally responsible separation of chalcopyrite and galena.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Guo, B. Feng, J.X. Peng, W.P. Zhang, and X.W. Zhu, Depressant behavior of tragacanth gum and its role in the flotation separation of chalcopyrite from talc, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 8(2019), No. 1, p. 697.
Q. Zhang, S.M. Wen, Q.C. Feng, and H. Wang, Enhanced sulfidization of azurite surfaces by ammonium phosphate and its effect on flotation, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 29(2022), No. 6, p. 1150.
J.S. Yu, R.Q. Liu, L. Wang, W. Sun, H. Peng, and Y.H. Hu, Selective depression mechanism of ferric chromium lignin sulfonate for chalcopyrite-galena flotation separation, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 25(2018), No. 5, p. 489.
X.M. Qiu, H.Y. Yang, G.B. Chen, S.P. Zhong, C.K. Cai, and B.B. Lan, Inhibited mechanism of carboxymethyl cellulose as a galena depressant in chalcopyrite and galena separation flotation, Miner. Eng., 150(2020), art. No. 106273.
A.A. Nikolaev and B.E. Goryachev, Thermodynamic and flotation analysis of influence exerted by chromate ions on separation of galena and chaclopyrite in alkaline media, J. Min. Sci., 43(2007), No. 6, p. 670.
X. Chen, G.H. Gu, and Z.X. Chen, Seaweed glue as a novel polymer depressant for the selective separation of chalcopyrite and galena, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 26(2019), No. 12, p. 1495.
Q. Liu and Y.H. Zhang, Effect of calcium ions and citric acid on the flotation separation of chalcopyrite from galena using dextrin, Miner. Eng., 13(2000), No. 13, p. 1405.
Z.J. Piao, D.Z. Wei, Z.L. Liu, W.G. Liu, S.L. Gao, and M.Y. Li, Selective depression of galena and chalcopyrite by O,O-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl) dithiophosphate, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 23(2013), No. 10, p. 3063.
J.M. Li, K.W. Song, D.W. Liu, et al., Hydrolyzation and adsorption behaviors of SPH and SCT used as combined depressants in the selective flotation of galena from sphalerite, J. Mol. Liq., 231(2017), p. 485.
R.Z. Liu, W.Q. Qin, F. Jiao, et al., Flotation separation of chalcopyrite from galena by sodium humate and ammonium persulfate, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 26(2016), No. 1, p. 265.
P. Huang, L. Wang, and Q. Liu, Depressant function of high molecular weight polyacrylamide in the xanthate flotation of chalcopyrite and galena, Int. J. Miner. Process., 128(2014), p. 6.
P. Huang, M.L. Cao, and Q. Liu, Selective depression of sphalerite by chitosan in differential PbZn flotation, Int. J. Miner. Process., 122(2013), p. 29.
P. Huang, M.L. Cao, and Q. Liu, Adsorption of chitosan on chalcopyrite and galena from aqueous suspensions, Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects, 409(2012), p. 167.
A. López-Valdivieso, L.A. Lozano-Ledesma, A. Robledo-Cabrera, and O.A. Orozco-Navarro, Cboboxymethylcellulose (CMC) as PbS depressant in the processing of Pb-Cu bulk concentrates. Adsorption and floatability studies, Miner. Eng., 112(2017), p. 77.
Z.G. Yin, W. Sun, Y.H. Hu, et al., Synthesis of acetic acid-[(hydrazinylthioxomethyl)thio]-sodium and its application on the flotation separation of molybdenite from galena, J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 52(2017), p. 82.
X.R. Zhang, Z.B. Qian, G.B. Zheng, Y.G. Zhu, and W.G. Wu, The design of a macromolecular depressant for galena based on DFT studies and its application, Miner. Eng., 112(2017), p. 50.
J.H. Chen, X.H. Long, L.H. Lan, and Q. He, Thermodynamics and density functional theory study of potassium dichromate interaction with galena, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 21(2014), No. 10, p. 947.
R.P. Liao, S.M. Wen, Q.C. Feng, J.S. Deng, and H. Lai, Activation mechanism of ammonium oxalate with pyrite in the lime system and its response to flotation separation of pyrite from arsenopyrite, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 30(2023), No. 2, p. 271.
G. Hong, J. Choi, Y. Han, et al., Relationship between surface characteristics and floatability in representative sulfide minerals: Role of surface oxidation, Mater. Trans., 58(2017), No. 7, p. 1069.
B. Feng, X.K. Jiao, H.H. Wang, J.X. Peng, and G. Yang, Improving the separation of chalcopyrite and galena by surface oxidation using hydroxyethyl cellulose as depressant, Miner. Eng., 160(2021), art. No. 106657.
D.W. Wang, F. Jiao, W.Q. Qin, and X.J. Wang, Effect of surface oxidation on the flotation separation of chalcopyrite and galena using sodium humate as depressant, Sep. Sci. Technol., 53(2018), No. 6, p. 961.
S.A. Khoso, Y.H. Hu, F. Lü, Y. Gao, R.Q. Liu, and W. Sun, Xanthate interaction and flotation separation of H2O2-treated chalcopyrite and pyrite, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 29(2019), No. 12, p. 2604.
F. Jiang, L.M. Zhang, T. Yue, et al., Defect-boosted molybdenite-based co-catalytic Fenton reaction, Inorg. Chem. Front., 8(2021), No. 14, p. 3440.
A.P. Chandra, L. Puskar, D.J. Simpson, and A.R. Gerson, Copper and xanthate adsorption onto pyrite surfaces: Implications for mineral separation through flotation, Int. J. Miner. Process., 114–117(2012), p. 16.
Y.L. Botero, A. Canales-Mahuzier, R. Serna-Guerrero, A. López-Valdivieso, M. Benzaazoua, and L.A. Cisternas, Physical-chemical study of IPETC and PAX collector’s adsorption on covellite surface, Appl. Surf. Sci., 602(2022), art. No. 154232.
P. Forson, W. Skinner, and R. Asamoah, Decoupling pyrite and arsenopyrite in flotation using thionocarbamate collector, Powder Technol., 385(2021), p. 12.
Y.H. Zhang, Z. Cao, Y.D. Cao, and C.Y. Sun, FTIR studies of xanthate adsorption on chalcopyrite, pentlandite and pyrite surfaces, J. Mol. Struct., 1048(2013), p. 434.
K. Laajalehto, J. Leppinen, I. Kartio, and T. Laiho, XPS and FTIR study of the influence of electrode potential on activation of pyrite by copper or lead, Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects, 154(1999), No. 1–2, p. 193.
B.C. Wu, G.H. Gu, S. Deng, D.H. Liu, and X.X. Xiong, Efficient natural pyrrhotite activating persulfate for the degradation of O-isopropyl-N-ethyl thionocarbamate: Iron recycle mechanism and degradation pathway, Chemosphere, 224(2019), p. 120.
H. Wang, J.C. Wang, Q.P. Zou, W.Q. Liu, C.Q. Wang, and W.Q. Huang, Surface treatment using potassium ferrate for separation of polycarbonate and polystyrene waste plastics by froth flotation, Appl. Surf. Sci., 448(2018), p. 219.
W.Q. Qin, X.J. Wang, L.Y. Ma, et al., Electrochemical characteristics and collectorless flotation behavior of galena: With and without the presence of pyrite, Miner. Eng., 74(2015), p. 99.
G. De Giudici, A. Rossi, L. Fanfani, and P. Lattanzi, Mechanisms of galena dissolution in oxygen-saturated solutions: Evaluation of pH effect on apparent activation energies and mineral-water interface, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 69(2005), No. 9, p. 2321.
Y.L. Mikhlin, A.A. Karacharov, and M.N. Likhatski, Effect of adsorption of butyl xanthate on galena, PbS, and HOPG surfaces as studied by atomic force microscopy and spectroscopy and XPS, Int. J. Miner. Process., 144(2015), p. 81.
X. Ma, Y. Hu, H. Zhong, S. Wang, G.Y. Liu, and G. Zhao, A novel surfactant S-benzoyl-N,N-diethyldithiocarbamate synthesis and its flotation performance to galena, Appl. Surf. Sci., 365(2016), p. 342.
H.Y. Xie, Y.L. Jin, P. Zhang, et al., Surface modification mechanism of galena with H2SO4 and its effect on flotation separation performance, Appl. Surf. Sci., 579(2022), art. No. 152129.
M.F. Liu, C.Y. Zhang, B. Hu, et al., Enhancing flotation separation of chalcopyrite and galena by the surface synergism between sodium sulfite and sodium lignosulfonate, Appl. Surf. Sci., 507(2020), art. No. 145042.
G.K. Parker, R. Woods, and G.A. Hope, Raman investigation of chalcopyrite oxidation, Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects, 318(2008), No. 1–3, p. 160.
B. Li, L. Huang, M.Z. Zhong, Z.M. Wei, and J.B. Li, Electrical and magnetic properties of FeS2 and CuFeS2 nanoplates, RSC Adv., 5(2015), No. 111, p. 91103.
M.D. Lane, Mid-infrared emission spectroscopy of sulfate and sulfate-bearing minerals, Am. Mineral., 92(2007), No. 1, p. 1.
M. Monneron-Gyurits, E. Joussein, A. Courtin-Nomade, et al., A fast one-pot synthesize of crystalline anglesite by hydrothermal synthesis for environmental assessment on pure phase, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int., 29(2022), No. 12, p. 17373.
B. Han, A.J. Xie, Q.B. Yu, F.Z. Huang, Y.H. Shen, and L. Zhu, Synthesis of PbSO4 crystals by hydrogel template on postprocessing strategy for secondary pollution, Appl. Surf. Sci., 261(2012), p. 623.
G. Falgayrac, S. Sobanska, J. Laureyns, and C. Brémard, Heterogeneous chemistry between PbSO4 and calcite micro-particles using Raman microimaging, Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc., 64(2006), No. 5, p. 1095.
L. Yu, Q.J. Liu, S.M. Li, J.S. Deng, B. Luo, and H. Lai, Depression mechanism involving Fe3+ during arsenopyrite flotation, Sep. Purif. Technol., 222(2019), p. 109.
P.X. Li, G. Zhang, W.J. Zhao, G. Han, and Q.C. Feng, Interaction mechanism of Fe3+ with smithsonite surfaces and its response to flotation performance, Sep. Purif. Technol., 291(2022), art. No. 121001.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 52204298 and 52004335), the National Key R&D Program of China (Nos. 2022YFC2904502 and 2022YFC2904501), the Major Science and Technology Projects in Yunnan Province (No. 202202AB080012), and the Science Research Initiation Fund of Central South University (No. 202044019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Zhang, L., Jiang, F. et al. Ferric ion-triggered surface oxidation of galena for efficient chalcopyrite-galena separation. Int J Miner Metall Mater 31, 261–267 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-023-2674-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-023-2674-x