Abstract
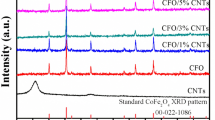
Cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4), with good chemical stability and magnetic loss, can be used to prepare composites with a unique structure and high absorption. In this study, CoFe2O4@mesoporous carbon hollow spheres (MCHS) with a core-shell structure were prepared by introducing CoFe2O4 magnetic particles into hollow mesoporous carbon through a simple in situ method. Then, the microwave absorption performance of the CoFe2O4@MCHS composites was investigated. Magnetic and dielectric losses can be effectively coordinated by constructing the porous structure and adjusting the ratio of MCHS and CoFe2O4. Results show that the impedance matching and absorption properties of the CoFe2O4@MCHS composites can be altered by tweaking the mass ratio of MCHS and CoFe2O4. The minimum reflection loss of the CoFe2O4@MCHS composites reaches -29.7 dB at 5.8 GHz. In addition, the effective absorption bandwidth is 3.7 GHz, with the thickness being 2.5 mm. The boosted microwave absorption can be ascribed to the porous core-shell structure and introduction of magnetic particles. The coordination between the microporous morphology and the core-shell structure is conducive to improving the attenuation coefficient and achieving good impedance matching. The porous core-shell structure provides large solid-void and CoFe2O4−C interfaces to induce interfacial polarization and extend the electromagnetic waves’ multiple scattering and reflection. Furthermore, natural resonance, exchange resonance, and eddy current loss work together for the magnetic loss. This method provides a practical solution to prepare core-shell structure microwave absorbents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z.L. Ma, X.L. Xiang, L. Shao, Y.L. Zhang, and J.W. Gu, Multifunctional wearable silver nanowire decorated leather nanocomposites for joule heating, electromagnetic interference shielding and piezoresistive sensing, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed, 61(2022), No. 15, art. No. e202200705.
J.K. Liu, Z.R. Jia, W.H. Zhou, et al., Self-assembled MoS2/magnetic ferrite CuFe2O4 nanocomposite for high-efficiency microwave absorption, Chem. Eng. J., 429(2022), art. No. 132253.
Y.X. Han, K.P. Ruan, and J.W. Gu, Janus (BNNS/ANF)−(AgNWs/ANF) thermal conductivity composite films with superior electromagnetic interference shielding and Joule heating performances, Nano Res., 15(2022), p. 4747.
K.R. Yang, W.J. Chen, Y.S. Zhao, et al., Enhancing dielectric strength of thermally conductive epoxy composites by preventing interfacial charge accumulation using micron-sized diamond, Compos. Sci. Technol., 221(2022), art. No. 109178.
H. Lv, Z. Yang, B. Liu, et al., A flexible electromagnetic wave-electricity harvester, Nat. Commun., 12(2021), art. No. 834.
L. Chai, Y.Q. Wang, N.F. Zhou, et al., In-situ growth of core-shell ZnFe2O4@porous hollow carbon microspheres as an efficient microwave absorber, J. Colloid. Interface. Sci., 581(2020), p. 475.
S.H. Zhu, C.W. Lou, S.H. Zhang, et al., Clean surface additive manufacturing of aramid paper-based electrically heated devices for medical therapy application, Surf. Interfaces, 29(2022), art. No. 101689.
Z.R. Jia, M.Y. Kong, B.W. Yu, Y et al., Tunable Co/ZnO/C@MWCNTs based on carbon nanotube-coated MOF with excellent microwave absorption properties, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 127(2022), p. 153.
Q.L. Sun, W. Ye, J.H. Cheng, and X.Y. Long, Effects of boron nitride coatings at high temperatures and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of carbon fiber-based magnetic materials, J. Nanomater., 2020(2020), art. No. 3672517.
C. Mu, X. Du, A. Nie, et al., Microwave absorption properties of heterostructure composites of two dimensional layered magnetic materials and graphene nanosheets, Appl. Phys. Lett., 115(2019), No. 4, art. No. 043103.
D.Q. Zhang, Y.X. Jia, J.Y. Cheng, et al., High-performance microwave absorption materials based on MoS2-graphene isomorphic hetero-structures, J. Alloys Compd., 758(2018), p. 62.
C.Q. Song, X.W. Yin, M.K. Han, et al., Three-dimensional reduced graphene oxide foam modified with ZnO nanowires for enhanced microwave absorption properties, Carbon, 116(2017), p. 50.
X.M. Huang, X.H. Liu, Z.R. Jia, et al., Synthesis of 3D cerium oxide/porous carbon for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance, Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater., 4(2021), No. 4, p. 1398.
T.Q. Hou, Z.R. Jia, Y.H. Dong, X.H. Liu, and G.L. Wu, Layered 3D structure derived from MXene/magnetic carbon nanotubes for ultra-broadband electromagnetic wave absorption, Chem. Eng. J., 431(2022), art. No. 133919.
Z. Xiang, Y.M. Song, J. Xiong, et al., Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption of nanoporous Fe3O4@carbon composites derived from metal-organic frameworks, Carbon, 142(2019), p. 20.
H.X. Zhang, B.B. Wang, A.L. Feng, et al., Mesoporous carbon hollow microspheres with tunable pore size and shell thickness as efficient electromagnetic wave absorbers, Composites Part B, 167(2019), p. 690.
Z.J. Li, H. Lin, S.Q. Ding, et al., Synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performances of Fe3O4@C decorated walnut shell-derived porous carbon, Carbon, 167(2020), p. 148.
Y. Qiu, Y. Lin, H.B. Yang, et al., Hollow Ni/C microspheres derived from Ni-metal organic framework for electromagnetic wave absorption, Chem. Eng. J., 383(2020), art. No. 123207.
J.X. Chai, J.Y. Cheng, D.Q. Zhang, et al., Enhancing electromagnetic wave absorption performance of Co3O4 nanoparticles functionalized MoS2 nanosheets, J. Alloys Compd., 829(2020), art. No. 154531.
C.Y. Liu, B.C. Wang, C. Zhang, et al., Simple preparation and excellent microwave attenuation property of Fe3O4- and FeS2-decorated graphene nanosheets by liquid-phase exfoliation, J. Alloys Compd., 810(2019), art. No. 151881.
L.R. Cui, C.H. Tian, L.L. Tang, et al., Space-confined synthesis of core-shell BaTiO3@carbon microspheres as a high-performance binary dielectric system for microwave absorption, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 11(2019), No. 34, p. 31182.
D. Ding, Y. Wang, X.D. Li, et al., Rational design of core-shell Co@C microspheres for high-performance microwave absorption, Carbon, 111(2017), p. 722.
L.F. Sun, Z.R. Jia, S. Xu, et al., Synthesis of NiCo2−0.5xCr2O3@C nanoparticles based on hydroxide with the heterogeneous interface for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties, Compos. Commun., 29(2022), art. No. 100993.
Y.N. Shi, X.H. Gao, and J. Qiu, Synthesis and strengthened microwave absorption properties of three-dimensional porous Fe3O4/graphene composite foam, Ceram. Int., 45(2019), No. 3, p. 3126.
S.H. Zhang, H.B. Dong, R.D. He, et al., Hydro electroactive Cu/Zn coated cotton fiber nonwovens for antibacterial and antiviral applications, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 207(2022), p. 100.
Y.P. Zhao, H. Zhang, X. Yang, et al., In situ construction of hierarchical core-shell Fe3O4@C nanoparticles-helical carbon nanocoil hybrid composites for highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorption, Carbon, 171(2021), p. 395.
Z.H. Du, X.B. Chen, Y.W. Zhang, et al., One-pot hydrothermal preparation of Fe3O4 decorated graphene for microwave absorption, Materials, 13(2020), No. 14, p. 3065.
M. Fu, Q.Z. Jiao, Y. Zhao, and H.S. Li, Vapor diffusion synthesis of CoFe2O4 hollow sphere/graphene composites as absorbing materials, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2(2014), No. 3, p. 735.
J.W. Wang, Z.R. Jia, X.H. Liu, et al., Construction of 1D heterostructure NiCo@C/ZnO nanorod with enhanced microwave absorption, Nano-Micro Lett., 13(2021), No. 1, art. No. 175.
X.D. Zhang, X. Ren, C. Wang, N.K. Chen, and N.N. Song, Synthesis of layered Fe3O4 nanodisk and nanostructure dependent microwave absorption property, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron., 32(2021), No. 4, p. 4404.
X. Cao, Z.R. Jia, D. Hu, and G.L. Wu, Synergistic construction of three-dimensional conductive network and double heterointerface polarization via magnetic FeNi for broadband microwave absorption, Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater., 5(2022), p. 1030.
L.H. Wang, H. Guan, J.Q. Hu, et al., Jute-based porous biomass carbon composited by Fe3O4 nanoparticles as an excellent microwave absorber, J. Alloys Compd., 803(2019), p. 1119.
W.Y. Dai, F. Chen, H. Luo, et al., Synthesis of yolk-shell structured carbonyl iron@void@nitrogen doped carbon for enhanced microwave absorption performance, J. Alloys Compd., 812(2020), art. No. 152083.
F. Zhang, W.D. Zhang, W.F. Zhu, B. Cheng, H. Qiu, and S.H. Qi, Core-shell nanostructured CS/MoS2: A promising material for microwave absorption, Appl. Surf. Sci., 463(2019), p. 182.
G.Z. Wang, Z. Gao, S.W. Tang, et al., Microwave absorption properties of carbon nanocoils coated with highly controlled magnetic materials by atomic layer deposition, ACS Nano, 6(2012), No. 12, p. 11009.
D. Lan, Z.G. Gao, Z.H. Zhao, et al., Double-shell hollow glass microspheres@Co2SiO4 for lightweight and efficient electromagnetic wave absorption, Chem. Eng. J., 408(2021), art. No. 127313.
Y.Q. Wang, H.G. Wang, J.H. Ye, L.Y. Shi, and X. Feng, Magnetic CoFe alloy@C nanocomposites derived from ZnCo-MOF for electromagnetic wave absorption, Chem. Eng. J., 383(2020), art. No. 123096.
Y.Q. Zhang, Y.Y. Liu, L.S. Zhou, et al., The role of Ce doping in enhancing sensing performance of ZnO-based gas sensor by adjusting the proportion of oxygen species, Sens. Actuators B, 273(2018), p. 991.
G.L. Wu, Y.H. Cheng, Z.H. Yang, et al., Design of carbon sphere/magnetic quantum dots with tunable phase compositions and boost dielectric loss behavior, Chem. Eng. J., 333(2018), p. 519.
S.P. Liu, S.H. Zhang, L.G. Yang, et al., Nanofibrous scaffold by cleaner magnetron-sputtering additive manufacturing: A novel biocompatible platform for antibacterial application, J. Clean. Prod., 315(2021), art. No. 128201.
H.Y. Yan, Y.Q. Fu, X.M. Wu, et al., Core-shell structured NaTi2(PO4)3@polyaniline as an efficient electrode material for electrochemical energy storage, Solid State Ionics, 336(2019), p. 95.
S.J. Zhang, Z.R. Jia, B. Cheng, et al., Recent progress of perovskite oxides and their hybrids for electromagnetic wave absorption: A mini-review, Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater., 5(2022), p. 2440.
X. Li, C.Y. Wen, L.T. Yang, et al., MXene/FeCo films with distinct and tunable electromagnetic wave absorption by morphology control and magnetic anisotropy, Carbon, 175(2021), p. 509.
H.B. Dong, S.H. Zhang, L.G. Yang, et al., Cu/Zn galvanic couples composite antibacterial dressings prepared by templateassisted magnetron sputtering, Composites Part B, 224(2021), art. No. 109240.
X.F. Zhou, Z.R. Jia, A.L. Feng, et al., Dependency of tunable electromagnetic wave absorption performance on morphology-controlled 3D porous carbon fabricated by biomass, Compos. Commun., 21(2020), art. No. 100404.
S.P. Liu, Z.Q. Zheng, S. Wang, et al., Polydopamine-coated chitosan/calcium pyrophosphate hybrid microflowers as an effective hemostatic agent, Carbohydr. Polym., 224(2019), art. No. 115175.
X. Zhang, J. Qiao, C. Liu, et al., A MOF-derived ZrO2/C nanocomposite for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption, Inorg. Chem. Front., 7(2020), No. 2, p. 385.
F. Zhang, Z.R. Jia, Z. Wang, et al., Tailoring nanoparticles composites derived from metal-organic framework as electromagnetic wave absorber, Mater. Today Phys., 20(2021), art. No. 100475.
Y. Cheng, J. Cao, Y. Li, et al., The outside-in approach to construct Fe3O4 nanocrystals/mesoporous carbon hollow spheres core-shell hybrids toward microwave absorption, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 6(2018), No. 1, p. 1427.
Y. Liu, Z.R. Jia, Q.Q. Zhan, et al., Magnetic manganese-based composites with multiple loss mechanisms towards broadband absorption, Nano Res., 15(2022), p. 5590.
L.G. Ren, Y.Q. Wang, Z.R. Jia, Q.C. He, and G.L. Wu, Controlling the heterogeneous interfaces of Fe3O4/N-doped porous carbon via facile swelling for enhancing the electromagnetic wave absorption, Compos. Commun., 29(2022), art. No. 101052.
P. Song, Z.L. Ma, H. Qiu, Y.F. Ru, and J.W. Gu, High-efficiency electromagnetic interference shielding of rGO@FeNi/epoxy composites with regular honeycomb structures, Nano-Micro Lett., 14(2022), No. 1, art. No. 51.
P.B. Liu, Y.Q. Zhang, J. Yan, et al., Synthesis of lightweight N-doped graphene foams with open reticular structure for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption, Chem. Eng. J., 368(2019), p. 285.
H.Q. Zhao, Y. Cheng, H.L. Lv, G.B. Ji, and Y.W. Du, A novel hierarchically porous magnetic carbon derived from biomass for strong lightweight microwave absorption, Carbon, 142(2019), p. 245.
X.F. Zhou, Z.R. Jia, A.L. Feng, et al., Synthesis of fish skin-derived 3D carbon foams with broadened bandwidth and excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance, Carbon, 152(2019), p. 827.
L. Chai, Y.Q. Wang, Z.R. Jia, et al., Tunable defects and interfaces of hierarchical dandelion-like NiCo2O4 via Ostwald ripening process for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption, Chem. Eng. J., 429(2022), art. No. 132547.
X.J. Zhu, Y.Y. Dong, F. Pan, et al., Covalent organic framework-derived hollow core-shell Fe/Fe3O4@porous carbon composites with corrosion resistance for lightweight and efficient microwave absorption, Compos. Commun., 25(2021), art. No. 100731.
H.X. Zhang, Z.R. Jia, B.B. Wang, et al., Construction of remarkable electromagnetic wave absorber from heterogeneous structure of Co−CoFe2O4@mesoporous hollow carbon spheres, Chem. Eng. J., 421(2021), art. No. 129960.
L. Kong, S.H. Luo, S.Y. Zhang, et al., Ultralight pyrolytic carbon foam reinforced with amorphous carbon nanotubes for broadband electromagnetic absorption, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 30(2023), No. 3, p. 570.
C.X. Wang, Z.R. Jia, S.Q. He, et al., Metal-organic framework-derived CoSn/NC nanocubes as absorbers for electromagnetic wave attenuation, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 108(2022), p. 236.
X. Feng, P.F. Yin, L.M. Zhang, et al., Innovative preparation of Co@CuFe2O4 composite via ball-milling assisted chemical precipitation and annealing for glorious electromagnetic-wave absorption, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 30(2023), No. 3, p. 559.
X.R. Gao, Z.R. Jia, B.B. Wang, et al., Synthesis of NiCo-LDH/MXene hybrids with abundant heterojunction surfaces as a lightweight electromagnetic wave absorber, Chem. Eng. J., 419(2021), art. No. 130019.
Y.L. Zhang, K.P. Ruan, and J.W. Gu, Flexible sandwich-structured electromagnetic interference shielding nanocomposite films with excellent thermal conductivities, Small, 17(2021), No. 42, art. No. 2101951.
T.Q. Hou, Z.R. Jia, A.L. Feng, et al., Hierarchical composite of biomass derived magnetic carbon framework and phytic acid doped polyanilne with prominent electromagnetic wave absorption capacity, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 68(2021), p. 61.
Y. Zhao, L.L. Hao, X.D. Zhang, et al., A novel strategy in electromagnetic wave absorbing and shielding materials design: Multi-responsive field effect, Small. Sci., 2(2022), No. 2, art. No. 2100077.
T.T. Zheng, Z.R. Jia, Q.Q. Zhan, et al., Self-assembled multi-layered hexagonal-like MWCNTs/MnF2/CoO nanocomposite with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption, Carbon, 186(2022), p. 262.
Z.D. Wang, T. Zhang, J.K. Wang, et al., The investigation of the effect of filler sizes in 3D-BN skeletons on thermal conductivity of epoxy-based composites, Nanomaterials, 12(2022), No. 3, art. No. 446.
G.S. Ma, L. Xia, H. Yang, et al., Multifunctional lithium aluminosilicate/CNT composite for gas filtration and electromagnetic wave absorption, Chem. Eng. J., 418(2021), art. No. 129429.
M. Chang, Z.R. Jia, S.Q. He, et al., Two-dimensional interface engineering of NiS/MoS2/Ti3C2Tx heterostructures for promoting electromagnetic wave absorption capability, Composites Part B, 225(2021), art. No. 109306.
F. Pan, Z.C. Liu, B.W. Deng, et al., Lotus leaf-derived gradient hierarchical porous C/MoS2 morphology genetic composites with wideband and tunable electromagnetic absorption performance, Nano-Micro Lett., 13(2021), No. 1, art. No. 43.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51407134), the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (No. 2021108), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2019YQ24), the Taishan Scholars and Young Experts Program of Shandong Province (No. tsqn202103057), and the Qingchuang Talents Induction Program of Shandong Higher Education Institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
12613_2022_2509_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Efficient microwave absorption achieved through in situ construction of core-shell CoFe2O4@mesoporous carbon hollow spheres
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, L., Wang, Y., Zhang, X. et al. Efficient microwave absorption achieved through in situ construction of core-shell CoFe2O4@mesoporous carbon hollow spheres. Int J Miner Metall Mater 30, 504–514 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-022-2509-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-022-2509-1