Abstract
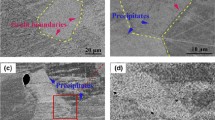
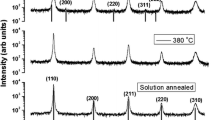
Precipitates play an important role in determining the mechanical and magnetic properties of silicon steel. This paper aims to investigate the growth kinetics of precipitates in commercial silicon steel by analyzing its magnetic properties during isothermal annealing at 200°C. The growth of precipitates was studied by optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and magnetic measurements. In combination with the coercive field and initial susceptibility, this technique offers the advantage of being non-destructive and providing quantitative information about the number, mean radius of precipitates, and fraction of transformation. An observed decrease in the number of precipitated particles indicates that the transformation starts from particles of appreciable initial size.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Yu, Y.L. Kang, Z.Z. Zhao, and H. Sun, Morphology and precipitation kinetics of MnS in low-carbon steel during thin slab continuous casting process, J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 13(2006), No. 5, p. 30.
L. Xiang, E.B. Yue, D.D. Fan, S.T. Qiu, and P. Zhao, Calculation of AIN and MnS precipitation in non-oriented electrical steel produced by CSP process, J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 15(2008), No. 5, p. 88.
Y.L. Chen, Y. Wang, and A.M. Zhao, Precipitation of AlN and MnS in low carbon aluminium-killed steel, J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 19(2012), No. 4, p. 51.
J.H. Liu, H.J. Wu, Y.P. Bao, and M. Wang, Inclusion variations and calcium treatment optimization in pipeline steel production, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 18(2011), No. 5, p. 527.
C.S. Kim, C.J. Lissenden, I.K. Park, and K.S. Ryu, Dynamic coercivity of advanced ferritic steel during long-term isothermal ageing, Mater. Trans., 50(2009), No. 11, p. 2691.
D.C. Jiles, The influence of size and morphology of eutectoid carbides on the magnetic properties of carbon steels, J. Appl. Phys., 63(1988), No. 8, p. 2980.
C.S. Kim, Characterization of reversible permeability in advanced USC steel during thermal aging, Phys. Status Solidi A, 207(2010), No. 1, p. 97.
A. Martínez-de-Guerenu, F. Arizti, and I. Gutiérrez, Recovery during annealing in a cold rolled low carbon steel: Part II. Modelling the kinetics, Acta Mater., 52(2004), No. 12, p. 3665.
F.J.G. Landgraf, J.R.F. da Silveira, and D. Rodrigues Jr., Determining the effect of grain size and maximum induction upon coercive field of electrical steels, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 323(2011), No. 18–19, p. 2335.
F. Heider, A. Zitzelsberger, and K. Fabian, Magnetic susceptibility and remanent coercive force in grown magnetite crystals from 0.1 μm to 6 mm, Phys. Earth Planet. Int., 93(1996), No. 3–4, p. 239.
Y. Sidor and F. Kovac, Microstructural aspects of grain growth kinetics in non-oriented electrical steels, Mater. Charact., 55(2005), No. 1, p. 1.
C.W. Chen, Magnetism and Metallurgy of Soft Magnetic Materials, Dover Publications, Dover, 2011, p. 132.
L. Vanherpe, N. Moelans, B. Blanpain, and S. Vandewalle, Pinning effect of spheroid second-phase particles on grain growth studied by three-dimensional phase-field simulations, Comput. Mater. Sci., 49(2010), No. 2, p. 340.
H.R. Hilzinger, Computer simulation of magnetic domain wall pinning, Phys. Status Solidi A, 38(1976), No. 2, p. 487.
H.R. Hilzinger and H. Kronmüller, Statistical theory of the pinning of Bloch walls by randomly distributed defects, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2(1976), No. 1–3, p. 11.
J.W. Christian, The Theory of Transformations in Metals and Alloys (Part I + II), Pergamon Press, Oxford, 2002, p. 746.
W. F. Brown Jr., The effect of dislocations on magnetization near saturation, Phys. Rev., 60(1941), No. 2, p. 139.
J. Guo, H.W. Qu, L.G. Liu, Y.L. Sun, Y. Zhang, and Q.X. Yang, Study on stable and meta-stable carbides in a high speed steel for rollers during tempering processes, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 20(2013), No. 2, p. 146.
K. Jenkins and M. Lindenmo, Precipitates in electrical steels, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 320(2008), No. 20, p. 2423.
E. Arzt, Size effects in materials due to microstructural and dimensional constraints: a comparative review, Acta Mater., 46(1998), No. 16, p. 5611.
A. Hubert and R. Schäfer, Magnetic Domains: the Analysis of Magnetic Microstructures, Springer, 1998, p. 205.
K.M. Podurets and S.S. Shilstein, Measurement of the domain wall thickness in silicon iron using the adiabatic spin-flip effect on neutron refraction, Phys. B, 297(2001), No. 1–4, p. 263.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Yf., Yu, H., Sun, J. et al. Study on precipitation and transition mechanisms from the magnetic properties of silicon steel during annealing. Int J Miner Metall Mater 21, 379–387 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-014-0919-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-014-0919-4