Abstract
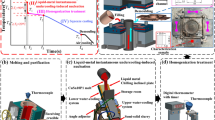
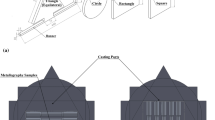
Based on horizontal continuous casting with a heating-cooling combined mold (HCCM) technology, this article investigated the effects of processing parameters on the liquid-solid interface (LSI) position and the influence of LSI position on the surface quality, microstructure, texture, and mechanical properties of a BFe10-1-1 tube (ϕ50 mm × 5 mm). HCCM efficiently improves the temperature gradient in front of the LSI. Through controlling the LSI position, the radial columnar-grained microstructure that is commonly generated by cooling mold casting can be eliminated, and the axial columnar-grained microstructure can be obtained. Under the condition of 1250°C melting and holding temperature, 1200–1250°C mold heating temperature, 50–80 mm/min mean drawing speed, and 500–700 L/h cooling water flow rate, the LSI position is located at the middle of the transition zone or near the entrance of the cooling section, and the as-cast tube not only has a strong axial columnar-grained microstructure \((\{ hkl\} < 6\bar 21 > , \{ hkl\} < 2\bar 21 > )\) due to strong axial heating conduction during solidification but also has smooth internal and external surfaces without cracks, scratches, and other macroscopic defects due to short solidified shell length and short contact length between the tube and the mold at high temperature. The elongation and tensile strength of the tube are 46.0%–47.2% and 210–221 MPa, respectively, which can be directly used for the subsequent cold-large-strain processing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.J. Glover, Copper-nickel alloy for the construction of ship and boat hulls, Br. Corros. J., 17(1982), No. 4, p. 155.
Z.M. Yan, X.T. Li, and K. Qi, Study on horizontal electromagnetic continuous casting of CuNi10Fe1Mn alloy hollow billets, Mater. Des., 30(2009), No. 6, p. 2072.
C.L. Gan, X.F. Liu, H.Y. Huang, and J.X. Xie, Fabrication process, microstructure and mechanical properties of BFe10-1-1 alloy tubes by continuous unidirectional solidification, Acta Metall Sin., 46(2010), No. 12, p. 1549.
J.X. Xie, H.F. Lou, Z.D. Wang, P.X. Hu, H. Zhang, Y.Z. Dong, J.L. Kang, G..W. Miao, X.Z. Fu, M. Yan, B.H. Guan, and X.L. Jiang, Compact Process for Fabrication of Copper and Copper Alloy Precision Tube, Chinese Patent, Appl. ZL200710065281.9, 2009.
A. Ohno, G. Motoyasu, and H. Kawai, Strengthening and bending deformability of Al-4.5 mass% Mg alloy billets produced by heated mold continuous casting method (OCC), Light Met., 40(1990), No. 11, p. 817.
J.X. Xie, J. Mei, X.H. Liu, and X.F. Liu, A Kind of Process and Equipment for Fabricating Cupronickel Pipes with Heating-Cooling Combined Mold Casting, Chinese Patent, Appl. ZL201010501407.4, 2012.
J. Mei, X.H. Liu, and J.X. Xie, Microstructure and mechanical properties of BFe10 cupronickel alloy tubes fabricated by a horizontal continuous casting with heatingcooling combined mold technology, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 19(2012), No. 4, p. 339.
J. Mei, X.H. Liu, and J.X. Xie, Solidification temperature field simulation of BFe10 cupronickel tube during heatingcooling combined mold continuous casting, Chin. J. Nonferrous Met., 22(2012), No. 5, p. 1430.
T.L. Li, Y.F. Gao, H. Bei, and E.P. George, Indentation Schmid factor and orientation dependence of nanoindentation pop-in behavior of NiAl single crystals, J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 59(2011), No. 6, p. 1147.
K.H. Kim and Y.M. Koo, Glide strains dependency on Schmid’s factor of secondary slip systems in copper single crystals, Mater. Lett., 57(2002), No. 1, p. 6.
S. Godet, L. Jiang, A.A. Luo, and J.J. Jonas, Use of Schmid factors to select extension twin variants in extruded magnesium alloy tubes, Scripta Mater., 55(2006), No. 11, p. 1055.
K.W. Gao, M.Y. Liu, F.L. Zou, X.L. Pang, and J.X. Xie, Characterization of microstructure evolution after severe plastic deformation of pure copper with continuous columnar crystals, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 527(2010), No. 18–19, p. 4750.
H.D. Fu, Z.H. Zhang, Q. Yang, and J.X. Xie, Strainsoftening behavior of an Fe-6.5wt%Si alloy during warm deformation and its applications, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 528(2011), No. 3, p. 1391.
Y. Wang, H.Y. Huang, and J.X. Xie, Texture evolution and flow stress of columnar-grained polycrystalline copper during intense plastic deformation process at room temperature, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 530(2011), p. 418.
J. Mei, X.H. Liu, and J.X. Xie, Evolution of microstructure, texture and mechanical properties of BFe10-1-1 tube with microstructure along axial orientation during cold-rolling, Chin. J. Nonferrous Met., 22(2012), No. 9, p. 2529.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mei, J., Liu, Xh., Jiang, Yb. et al. Liquid-solid interface control of BFe10-1-1 cupronickel alloy tubes during HCCM horizontal continuous casting and its effect on the microstructure and properties. Int J Miner Metall Mater 20, 748–758 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-013-0793-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-013-0793-5