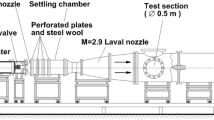
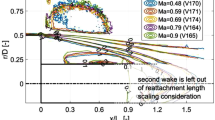
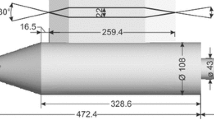
Abstract
The influence on the turbulent wake of a generic space launcher model due to the presence of an under-expanded jet is investigated experimentally. Wake flow phenomena represent a significant source of uncertainties in the design of a space launcher. Especially critical are dynamic loads on the structure. The wake flow is investigated at supersonic (\(M=2.9\)) and hypersonic (\(M=5.9\)) flow regimes. The jet flow is simulated using air and helium as working gas. Due to the lower molar mass of helium, higher jet velocities are realized, and therefore, velocity ratios similar to space launchers can be simulated. The degree of under-expansion of the jet is moderate for the supersonic case (\(p_\mathrm{e}/p_\infty \approx 5\)) and high for the hypersonic case (\(p_\mathrm{e}/p_\infty \approx 90\)). The flow topology is described by Schlieren visualization and mean-pressure measurements. Unsteady pressure measurements are performed to describe the dynamic wake flow. The influences of the under-expanded jet and different jet velocities are reported. On the base fluctuations at a Strouhal number, around \(\mathrm{St}_D \approx 0.25\) dominate for supersonic free-stream flows. With air jet, a fluctuation-level increase on the base is observed for Strouhal numbers above \(\mathrm{St}_D \approx 0.75\) in hypersonic flow regime. With helium jet, distinct peaks at higher frequencies are found. This is attributed to the interactions of wake flow and jet.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Delery, J., Sirieix, M.: Base flows behind missiles. In: AGARD LS-98, 6-1. T.P. no. 1979-14E (1979)
Shvets, A.: Base pressure fluctuations. Fluid Dyn. 14(3), 394–401 (1979)
Eldred, K.: Base pressure fluctuations. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 33(1), 59–63 (1961)
Herrin, J.L., Dutton, J.C.: The turbulence structure of a reattaching axisymmetric compressible free shear layer. Phys. Fluids 9 (1997)
Mabey, D.: Some measurements of base pressure fluctuations at subsonic and supersonic speeds. In: Aeronautical Research Council, ARC-CP-1204. Also Royal Aircraft Establishment, RAE-TR-70148 (1972)
Janssen, J., Dutton, J.: Time-series analysis of supersonic base-pressure fluctuations. AIAA J. 42, 605–613 (2004)
Herrin, J.L., Dutton, J.C.: Supersonic base flow experiments in the near wake of a cylindrical after body. AIAA J. 2(1) (1994)
Xiao, Z., Fu, S.: Studies of the unsteady supersonic base flows around three after bodies. Acta Mech. Sin. 25(4) (2009)
Simon, F., Deck, S., Guillen, P., Sagaut, P.: Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes/large-eddy simulation of supersonic base flow. AIAA J. 44, 2578–2586 (2006)
Kawai, S., Fujii, K.: Computational study of supersonic base flow using hybrid turbulence methodology. AIAA J. 43(6), 1265–1275 (2005)
Deprés, D., Reijasse, P., Dussauge, J.: Analysis of unsteadiness in afterbody transonic flows. AIAA J. 42(12), 2541–2550 (2004)
Sahu, J., Heavey, K.R.: Numerical investigation of supersonic base flow with base bleed. In: Army Research Laboratory, ARL-TR-955 (1995)
Bergman, D.: Effects of engine exhaust flow on boattail drag. J. Aircr. 8(6), 434–438 (1971)
Kumar, R., Viswanah, P.R.: Mean and fluctuating pressure in boat-tail separated flows at transonic speeds. J. Spacecr. Rockets 39(3) (2002)
Sahu, J.: Computations of supersonic flow over a missile afterbody containing an exhaust jet. J. Spacecr. 24(5), 403–410 (1987)
Venkatakrishnan, L., Suriyanarayanan, P., Mathur, N.B.: Bos density measurements in afterbody flows with shock and jet effects. In: 37th AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference and Exhibit, 25–28 June 2007, Miami, AIAA 2007-4223 (2007)
Peters, W.L., Kennedy, T.L.: Jet simulation techniques - Simulation of aerodynamic effects of jet temperature by altering gas composition. In: AIAA-1979-327 (1979)
Peters, W.L., Kennedy, T.L.: An evaluation of jet simulation parameters for nozzle/afterbody testing at transonic mach number. In: AIAA-1977-106 (1977)
Deck, S., Thorigny, P.: Unsteadiness of an axisymmetric separating-reattaching flow: numerical investigation. Phys. Fluids 19, 065103 (2007)
Stephan, S., Wu, J., Radespiel, R.: Propulsive jet influence on generic launcher base flow. CEAS Space J. (2015). doi:10.1007/s12567-015-0098-9
Wong, H., Meijer, J., Schwane, R.: Theoretical and experimental investigations on Ariane 5 base-flow buffeting. In: Proceedings of the Fifth European Symposium on Aerothermodynamics for Space Vehicles, 8–11 November, Cologne (ESA SP-563) (2005)
Reijasse, P., Delery, J.: Experimental analysis of the flow past the afterbody of the Ariane 5 European launcher. In: AIAA-91-2897 (1991)
Pain, R., Weiss, P.-E., Deck, S.: Zonal detached eddy simulation of the flow around a simplified launcher afterbody. AIAA J. 52(9) (2014)
Schwane, R.: Numerical prediction and experimental validation of unsteady loads on Ariane 5 and Vega. J. Spacecr. Rockets 52(1) (2015)
Weiss, P.-E., Deck, S., Robinet, J.-C., Sagaut, P.: On the dynamics of axisymmetric turbulent separating/reattaching flows. Phys. Fluids 21 (2009)
Bitter, M., Scharnowski, S., Hain, R., Kähler, C.J.: High-repetition-rate PIV investigations on a generic rocket model in sub- and supersonic flows. Exp. Fluids 50, 1019–1030 (2011)
Weiss, P.-E., Deck, S., Sagaut, P.: Zonal-detached-eddy-simulation of a two-dimensional and axisymmetric separating, reattaching flow. In: 38th Fluid Dynamics Conference and Exhibit, 23–26 June 2008, Seattle, AIAA 2008-4377 (2008)
Statnikov, V., Sayadi, T., Meinke, M., Schmid, P., Schröder, W.: Analysis of pressure perturbation sources on a generic space launcher after-body in supersonic flow using zonal RANS/LES and dynamic mode decomposition. Phys. Fluids 27(1) (016103), 1–22 (2015)
Saile, D., Gülhan, A., Henckels, A., Glatzer, C., Statnikov, V., Meinke, M.: Investigation on the turbulent wake of a generic space launcher geometry in the hypersonic flow regime. In: EUCASS Proceedings Series—Advances in AeroSpace Sciences, Progress in Flight Physics 5, 209–234 (2013)
Saile, D., Guelhan, A.: Plume-induced effects on the near-wake region of a generic space launcher geometry. In: 32nd AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference, AIAA Aviation and Aeronautics Forum and Exposition, 16–20 June, Atlanta (2014)
Estorf, M., Wolf, T., Radespiel, R.: Experimental and numerical investigations on the operation of the hypersonic Ludwieg tube Braunschweig (2005)
Wu, J., Radespiel, R.: Tandem nozzle supersonic wind tunnel design. Int. J. Eng. Syst. Model. Simul. Proc. 5(1), 8–18 (2013). doi:10.1504/IJESMS.2013.052369
Wu, J., Radespiel, R., Zamre, P.: Disturbance characterization and flow quality improvement in a tandem nozzle Mach 3 wind tunnel. Exp Fluids 56 doi:10.1007/s00348-014-1887-1 (2015)
Gruemmer, K.: Ein Rechenprogramm für den Entwurf ebener und rotationssymmetrischer Überschallwindkanaldüsen. In: DFVLR-FB 76-59, Deutsches Zentrum für Luft und Raumfahrt (1976)
Morgan, W.V., Young, K.J.: Studies of rocket noise simulation with substitute gas jets and the effect of vehicle motion on jet noise. In: Technical Documentary Report No. ASD-TDR-62-787 (1963)
Panda, J., Burnside, N.J., Fong, R.K., Ross, J.C., James, G.H., Fogt, V.A.: Heated helium to simulate surface pressure fluctuations created by rocket motor plumes. AIAA J. 51(2), 302–314 (2013). doi:10.2514/1.J051485
Kinzie, K.W., McLaughlin, D.K.: Measurements of supersonic helium/air mixture jets. AIAA J. 37(11), 1363–1369 (1999). doi:10.2514/2.634
Schrijer, F.F.J., Sciacchitano, A., Scarano, F.: Spatio-temporal and modal analysis of unsteady fluctuations in a high-subsonic base flow. Phys. Fluids 26. doi:10.1063/1.4891257 (2014)
Hannemann, K., Lüdecke, H., Pallegoix, J.-F., Ollivier, A., Lambare, H., Maseland, H., Geurts, E.G.M., Frey, M., Deck, S., Schrijer, F.F.J., Scarano, F., Schwane, R.: Launcher vehicle base buffeting—recent experimental and numerical investigations. In: Proceedings of the 7th European Symposium on Aerothermodynamics for Space Vehicles, Brugge, 9–12 May (2011)
Reijasse, P., Délery, J.: Investigation of the flow past the Ariane 5 launcher afterbody. J. Spacecr. Rockets 31(2) (1994)
David, C., Radulovic, S.: Prediction of buffet loads on the Ariane 5 afterbody. In: 6th International Symposium on Launcher Technologies, Munich (2005)
Statnikov, V., Stephan, S., Pausch, K., Meinke, M., Radespiel, R., Schrder, W.: Experimental and numerical investigations of the turbulent wake flow of a generic space launcher at \(M_\infty =3 \, {\rm and} \, M_\infty =6\). CEAS Space J. 8(2), 101116 (2016). doi:10.1007/s12567-016-0112-x
Ponton, M.K., Seiner, J.M.: The effects of initial jet exit conditions on plume resonance. In: AIAA 12th Aeroacoustics Conference, 10–12 April, San Antonio, AlAA 89-1054 (1989)
Ponton, M.K., Seiner, J.M.: The effects of nozzle exit lip thickness on plume resonance. J. Sound Vib. 154(3), 531–554 (1992)
Acknowledgements
Financial support has been provided by the German Research Foundation (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft—DFG) in the framework of the Sonderforschungsbereich Transregio 40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stephan, S., Radespiel, R. Propulsive jet simulation with air and helium in launcher wake flows. CEAS Space J 9, 195–209 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12567-016-0142-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12567-016-0142-4