Abstract
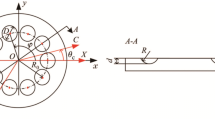
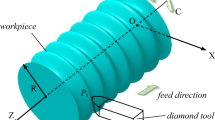
In micro pattern machining, rectangular channel structures having high aspect ratio can be easily deformed because the cutting force perpendicular to the moving direction of the diamond tool pushes the channel structure. In order to prevent such deformation, conservative cutting conditions that can reduce the cutting force are applied, but make great sacrifices in productivity. Therefore, it is necessary to study the deformation behavior of micro channels to determine optimum cutting conditions. This paper presents a theoretical prediction solution for the deformation of the micro rectangular channels. To obtain maximum principle stress and deflection of micro rectangular pattern, the used model was a cantilever beam with a distributed load. Furthermore, for verifying this solution, FEM analysis and experiments have been carried out to rectangular patterns by diamond machining. The maximum error between the predicted deformation and experimental deformation was approximately 5mm, which means that this prediction solution works well.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, Y., Zhao, Q., Shang, Y., Lv, P., Guo, B., and Zhao, L., “Ultra-Precision Machining of Fresnel Microstructure on Die Steel Using Single Crystal Diamond Tool,” Journal of Materials Processing Technology, Vol. 211, No. 12, pp. 2152–2159, 2011.
Abou-El-Hossein, K., Olufayo, O., and Mkoko, Z., “Diamond Tool Wear during Ultra-High Precision Machining of Rapidly Solidified Aluminium RSA 905,” Wear, Vol. 302, No. 1, pp. 1105–1112, 2013.
Jiang, S., Wang, Z., Zhou, G., and Yang, W., “An Implicit Control-Volume Finite Element Method and Its Time Step Strategies for Injection Molding Simulation,” Computers & Chemical Engineering, Vol. 31, No. 11, pp. 1407–1418, 2007.
Vancoliie, E., Xiangdong, L., Ling, Y., and Annergren, I., “Materials Selection for Durable Optical Inserts Used in Plastic Lens Moulding,” Technical Report (DD/00/009/OTC), SIMTech, Singapore, 2000.
Venkata Rao, R. and Kalyankar, V., “Parameter Optimization of Machining Processes using a New Optimization Algorithm,” Materials and Manufacturing Processes, Vol. 27, No. 9, pp. 978–985, 2012.
Dhananchezian, M., Kumar, M. P., and Sornakumar, T., “Cryogenic Turning of AISI 304 Stainless Steel with Modified Tungsten Carbide Tool Inserts,” Materials and Manufacturing Processes, Vol. 26, No. 5, pp. 781–785, 2011.
DeVries, W. R., “Analysis of Material Removal Processes,” Springer, 1st Ed., pp. 43–54, 1991.
Duong, T. H., Kim, H. C., Lee, D. Y., Lee, S. W., Park, E. S., and Je, T. J., “A Theoretical Deformation Prediction of Micro Channels in Ultra-Precision Machining,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 14, No. 2, pp. 173–181, 2013.
Lubliner, J., “Plasticity Theory,” Courier Dover Publications, pp. 239–245, 2008.
Gere, J. M. and Timoshenko, S. P., “Mechanics of Materials,” PWS, pp. 306–315, 1997.
Klamecki, B. E., “Incipient Chip Formation in Metal Cutting-a Three-Dimension Finite Element Analysis,” Ph.D. Thesis, Deparment of Mechanical Engineering, University of Illinois, 1973.
El-Hossainy, T., El-Zoghby, A., Badr, M., Maalawi, K., and Nasr, M., “Cutting Parameter Optimization when Machining Different Materials,” Materials and Manufacturing Processes, Vol. 25, No. 10, pp. 1101–1114, 2010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duong, TH., Kim, HC. Deformation analysis of rectangular channel structures in micro pattern machining. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 16, 619–627 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-015-0083-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-015-0083-4