Abstract
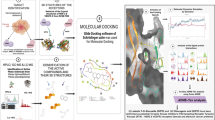
Neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) is a transmembrane glycoprotein receptor whose distinct sites bind semaphorins and vascular endothelial growth factor family members to mediate the role of these ligands in neuronal axon guidance and angiogenesis, respectively. Similarly, Eph receptors and ephrin ligands play critical roles in various biological functions, and deregulated activation of Eph/ephrin signaling in humans is thought to lead to tumorigenesis. Therefore, in this paper, an attempt was made to elucidate the inhibition potential of nine bioactive compounds from four different native spices of Bangladesh against this couple of receptors via molecular docking study. The molecular docking study was carried out using Vina docking protocol. Finally, the receptor–ligand interaction analysis was carried out using the Discovery Studio Client package. Quercetin and diosgenin of onion showed favorable binding with NRP-1 with low binding energy of −7.8 and −7.2 kcal/mol, respectively, in comparison with the control inhibitor (−6.1 kcal/mol). The study suggests that ligand interaction with the residues Asp 48, Thr 44, Thr 77, Tyr 81, Trp29, Ile 143 of NRP-1 and Lys 653, Phe 765, Ser 763, Thr 699, Ile 683 of Eph might be critical for the inhibitory activity of these receptors. The study provides evidence for consideration of quercetin and diosgenin of onion as valuable small ligand molecules for targeting NRP-1 receptor in treatment and prevention of neurological disorders as well as cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tessier-Lavigne M, Goodman CS (1996) The molecular biology of axon guidance. Science 274:1123–1133
Lin L, Lesnick TG, Maraganore DM, Isacson O (2009) Axon guidance and synaptic maintenance: preclinical markers for neurodegenerative disease and therapeutics. Trends Neurosci 32:142–149
Hinck L (2004) The versatile roles of “axon guidance” cues in tissue morphogenesis. Dev Cell 7:783–793
Maglott D, Ostell J, Pruitt KD, Tatusova T (2011) Entrez Gene: gene-centered information at NCBI. Nucleic Acids Res 39:D52–D57
Moret F, Renaudot C, Bozon M, Castellani V (2007) Semaphorin and neuropilin co-expression in motoneurons sets axon sensitivity to environmental semaphorin sources during motor axon pathfinding. Development 134:4491–4501
Soker S, Takashima S, Miao HQ, Neufeld G, Klagsbrun M (1998) Neuropilin-1 is expressed by endothelial and tumor cells as an isoform-specific receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. Cell 92:735–745
Bachelder RE, Lipscomb EA, Lin X, Wendt MA, Chadborn NH, Eickholt BJ, Mercurio AM (2003) Competing autocrine pathways involving alternative neuropilin-1 ligands regulate chemotaxis of carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 63:5230–5233
Marquardt T, Shirasaki R, Ghosh S, Andrews SE, Carter N, Hunter T, Pfaff SL (2005) Coexpressed EphA receptors and ephrin-A ligands mediate opposing actions on growth cone navigation from distinct membrane domains. Cell 121:127–139
Pasquale EB (2010) Eph receptors and ephrins in cancer: bidirectional signalling and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer 10:165–180
Mathew M, Subramanian S (2014) In vitro evaluation of anti-Alzheimer effects of dry ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) extract. Indian J Exp Biol 52:606–612
Yun H-M, Ban JO, Park K-R, Lee CK, Jeong H-S, Han SB, Hong JT (2014) Potential therapeutic effects of functionally active compounds isolated from garlic. Pharmacol Ther 142:183–195
Hwang IK, Lee CH, Yoo K-Y, Choi JH, Park OK, Lim SS, Kang I-J, Kwon DY, Park J, Yi J-S (2009) Neuroprotective effects of onion extract and quercetin against ischemic neuronal damage in the gerbil hippocampus. J Med Food 12:990–995
Klein A, Joe C, Davoodi A, Takechi K, Carstens M, Carstens E (2014) Eugenol and carvacrol excite first-and second-order trigeminal neurons and enhance their heat-evoked responses. Neuroscience 271:45–55
Leeson P (2012) Drug discovery: chemical beauty contest. Nature 481:455–456
Olboyle NM, Banck M, James CA, Morley C, Vandermeersch T, Hutchison GR (2011) Open Babel: an open chemical toolbox. J Cheminf 3:33
Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF, Belew RK, Goodsell DS, Olson AJ (2009) AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem 30:2785–2791
Binkowski TA, Naghibzadeh S, Liang J (2003) CASTp: computed atlas of surface topography of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3352–3355
Trott O, Olson AJ (2010) AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem 31:455–461
Zhao J, Gu L, Li C, Ma W, Ni Z (2014) Investigation of a novel biomarker, neuropilin-1, and its application for poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia patients. Tumor Biol 35:6919–6924
Ben Q, Zheng J, Fei J, An W, Li P, Li Z, Yuan Y (2014) High neuropilin 1 expression was associated with angiogenesis and poor overall survival in resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 43:744–749
Zhu H, Cai H, Tang M, Tang J (2014) Neuropilin-1 is overexpressed in osteosarcoma and contributes to tumor progression and poor prognosis. Clin Transl Oncol 16:732–738
Boyd AW, Bartlett PF, Lackmann M (2014) Therapeutic targeting of EPH receptors and their ligands. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 13:39–62
Benzie IF, Wachtel-Galor S (2011) Herbal medicine: biomolecular and clinical aspects. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Reddy L, Odhav B, Bhoola K (2003) Natural products for cancer prevention: a global perspective. Pharmacol Ther 99:1–13
Penta A, Chander S, Ganguly S, Murugesan S (2014) De novo design and in silico studies of novel 1-phenyl-2, 3, 4, 9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido [3, 4-b] indole-3-carboxylic acid derivatives as HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Med Chem Res 23:3662–3670
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest among the authors of this study.
Additional information
Tahirah Yasmin and Mohammad Tuhin Ali have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yasmin, T., Ali, M.T., Haque, S. et al. Interaction of Quercetin of Onion with Axon Guidance Protein Receptor, NRP-1 Plays Important Role in Cancer Treatment: An In Silico Approach. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci 9, 184–191 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-015-0137-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-015-0137-4