Abstract
Background
This study was undertaken to explore the clinical outcome and prognosis of subclinical hypothyroidism detected by newborn screening.
Methods
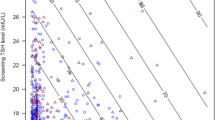
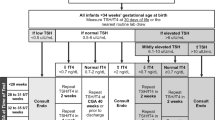
Newborn screening was conducted at 1156 health care institutions in Zhejiang Province from October 1999 to September 2006. Included were (1) infants who had thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) ≥20 mU/L, and normal or lower normal levels of triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) and (2) infants with TSH between 5.6 mU/L and 20 mU/L at a confirmatory examination and follow-up showing TSH levels ≥20 mU/L or delayed reduction in T4 levels. These infants were considered as having subclinical hypothyroidism and levothyroxine (L-T4) at an initial dose of 3–5 μg/kg per day was administered. The levels of TSH and T4, developmental quotient (DQ), and index of growth were evaluated.
Results
A total of 204 infants met our criteria for subclinical hypothyroidism, with an incidence of 1/8809. After 2–4 weeks of standard therapy, serum TSH level dropped to normal and T4 reached a higher normal level in all the 204 infants. Evaluations of 60 patients after 2 years of therapy showed that their average DQ was 101±14.61, and body weight and height were within the normal ranges. Bone age test for 54 patients revealed normal development in 44, slightly retarded development in 7, and advanced development in 3.
Conclusions
Newborns with high TSH levels should be given particular attention to ensure early diagnosis. A L-T4 dose of 3–5 μg/kg per day was effective in the initial treatment of subclinical hypothyroidism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kohler B, Schnabel D, Biebermann H, Gruters A. Transient congenital hypothyroidism and hyperthyrotropinemia: normal thyroid function and physical development at the ages of 6–14 years. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1996;81:1563–1567.
Paoli-Valeri M, Maman-Alvarado D, Jimenez-Lopez V, Arias-Ferreira A, Bianchi G, Arata-Bellabarba G. Frequency of subclinical hypothyroidism among healthy children and those with neurological conditions in the state of Merida, Venezuela. Invest Clin 2003;44:209–218.
Reiterer E, Borkenstein MH. Disorders of the thyroid gland in neonates and youth: latent hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Acta Med Austriaca 2003;30:107–109.
Teofoli F, Camilot M, Tato L. Lack of association between thyrotropin receptor gene polymorphisms and subclinical hypothyroidism in children. J Endocrinol Invest 2007;30:163–166.
Motta RM, Gullio D, Fichera G. Children with neonatal short lasting hyper-TSH frequently have subclinical hypothyroidism in early infancy. 4th Meeting of the International Society for Neonatal Screening. Stockholm, Sweden: 1999, 82.
Paoli-Valeri M, Guzman M, Jimenez-Lopez V, Arias-Ferreira A, Briceno-Fernandez M, Arata-Bellabarba G. Atherogenic lipid profile in children with subclinical hypothyroidism. An Pediatr (Barc) 2005;62:128–134.
Waldhauser F, Frisch H, Schober E. Subclinical hypothyroidism in infancy (author’s transl). Monatsschr Kinderheilkd 1981;129:364–366.
Clemens PC. Subclinical hypothyroidism in the neonate: not to treat. Am J Med Sci 1989;297:132–133.
Alemzadeh R, Friedman S, Fort P, Recker B, Lifshitz F. Is there compensated hypothyroidism in infancy? Pediatrics 1992;90:207–211.
American Academy of Pediatrics AAP Section on Endocrinology and Committee on Genetics, American Thyroid Association Committee on Public Health. Newborn screening for congenital hypothyroidism: recommended guidelines. Pediatrics 1993;91:1203–1209.
American Academy of Pediatrics, Section on Endocrinologyan, Committee on Genetics, American Thyroid Association, Committee on Public Health. Update of newborn screening and therapy for congenital hypothyroidism. Pediatrics 2006;117:2290–2303.
Voigt RG, Jensen CL, Fraley JK, Rozelle JC, Brown FR 3rd, Heird WC. Relationship between omega3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid status during early infancy and neurodevelopmental status at 1 year of age. J Hum Nutr Diet 2002;15:111–120.
Knobloch H, Stevens F, Malone AF. Manual of Developmental Diagnosis. Hagerstown: Harper & Row, 1980.
Staub JJ, Althaus BU, Engler H, Ryff AS, Trabucco P, Marquardt K, et al. Spectrum of subclinical and overt hypothyroidism: effect on thyrotropin, prolactin, and thyroid reserve, and metabolic impact on peripheral target tissues. Am J Med 1992;92:631–642.
Teng WP. Subclinical hypothyroidism. Foreign Med Sci Sec Endocrinology 2003;23:370–372. [In Chinese]
Calaciura F, Motta RM, Miscio G, Fichera G, Leonardi D, Carta A, et al. Subclinical hypothyroidism in early childhood: a frequent outcome of transient neonatal hyperthyrotropinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002;87:3209–3214.
Moore DC. Natural course of ’subclinical’ hypothyroidism in childhood and adolescence. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1996;150:293–297.
Chen XX, Yang RL, Shi YH, Cao LP, Zhou XL, Mao HQ, et al. Screening for congenital hypothyroidism in neonates of Zhejiang Province during 1999–2004. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2005;34:304–307. [In Chinese]
Tian GL, Cao X, Dong QY. Neonatal screening and clinical analysis for congenital hypothyroidism. Chin J Endocrinol Metab 2001;17:90–92. [In Chinese]
Ehrlich RM. Thyroxin dose for congenital hypothyroidism. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1995;34:521–522.
He YF, Zhang LQ, Yu SY, Xu N, Liu ML, Song Y. A study on initial L-T4 dose application in congenital hypothyroid children. J Clin Pediatr 2003;21:410–412.
Bongers-Schokking JJ, de Muinck Keizer-Schrama SM. Influence of timing and dose of thyroid hormone replacement on mental, psychomotor, and behavioral development in children with congenital hypothyroidism. J Pediatr 2005;147:768–774.
Rovet JF. In search of the optimal therapy for congenital hypothyroidism. J Pediatr 2004;144:698–700.
Michalopoulou G, Alevizaki M, Piperingos G, Mitsibounas D, Mantzos E, Adamopoulos P, et al. High serum cholesterol levels in persons with ‘high-normal’ TSH levels: should one extend the definition of subclinical hypothyroidism? Eur J Endocrinol 1998;138:141–145.
McDermott MT, Ridgway EC. Subclinical hypothyroidism is mild thyroid failure and should be treated. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001;86:4585–4590.
Cooper DS. Clinical practice. Subclinical hypothyroidism. N Engl J Med 2001;345:260–265.
Alberti L, Proverbio MC, Costagliola S, Romoli R, Boldrighini B, Vigone MC, et al. Germline mutations of TSH receptor gene as cause of nonautoimmune subclinical hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002;87:2549–2555.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, XX., Qin, YF., Zhou, XL. et al. Diagnosis and treatment of subclinical hypothyroidism detected by neonatal screening. World J Pediatr 7, 350–354 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-011-0314-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-011-0314-4