Abstract
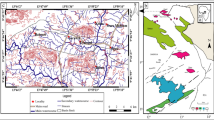
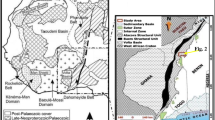
The northern Ethiopian Kingdom of Axum (ca. 100–700 AD) is known for its underground royal tombs and monolithic obelisks, which were probably carved and erected before/during the fourth century A.D. Most or almost all of these structures have been sculpted or made from only the phonolitic and trachytic rocks, which are part of the Ethiopian post-trap volcanic sequences. The post-trap volcanic suites have two end-members, the basalts and the nephelinites. Based on geochemistry, the nephelinites cover a wide spectrum of alkaline rocks. Our new 40Ar/39Ar dates for samples of phonolite and trachyte sampled at various levels of the sequence show that the Axum phonolites and trachytes erupted in the mid-Miocene, between 19.5 and 15.0 Ma. The rocks from which the monuments were sculpted correspond to the 19.29 ± 0.22 Ma old Gobo-Dura phonolites. Other stone-made artifacts have geochemical signatures similar to the 15.04 ± 0.53 Ma Adi-Tsehafi phonolitic trachyte. Despite the large numbers of quarry sites in the Axum area, most of the Axum relics were mined from three local quarries: two of the quarry sites are found at the flanks of the Gobo-Dura ridge, whereas the third quarry site is located at the Adi-Tsehafi village.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beyth M (1972) The geology of central and western Tigray. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms Universität, Bonn, Germany, pp 200
Butzer K (1981) Rise and fall of Axum, Ethiopia: a geo-archaeological interpretation. Am Antiq 46:471–495
Croci G (2001) Dismantling the stelae of Axum. J Cult Herit 2:173–178
Fattovich R, Bard KA, Petrassi L, Pisano V (2000) The Aksum archaeological area: a preliminary assessment. Isituto Universitario Orientale Centro Interdipartimentale di Servizi per l'Archeologia, Naples, p. 102
Ferrari G, Ciampalini R, Billi P, Migon P (2015) Geomorphology of the archaeological area of Axum. In: Billi P (ed) Landscapes and landforms of Ethiopia, world geomorphological landscapes. Springer, Berlin, pp. 147–161
Govindaraju K (1989) 1989 compilation of working values and sample description for 272 geostandards. Geostand Newslett 13:1–113
Hagege A (2000) The churches of Tigrai (in Amharic). Efita 4:232–241
Hagos M, Koeberl C, Kabeto K, Koller F (2010) Geochemical characteristics of the alkaline basalts and the phonolite–trachyte plugs of the Axum area, northern Ethiopia. Austrian Journal of Earth Sciences 103:153–170
Hofmann C, Courtillot V, Feraud G, Rochette P, Yirgu G, Ketefo E, Pik R (1997) Timing of the Ethiopian flood basalt event and implications for plume birth and environmental change. Nature 389:838–841
Hofmann C, Feraud G, Courtillot V (2000) 40Ar/39Ar dating of mineral separates and whole rocks from the Western Ghats lava pile: further constraints on duration and age of the Deccan traps. Earth Planet Sci Lett 180:13–27
Jarosewich E, Clarke RSJ, Barrows JN (1987) The Allende meteorite reference sample. Smithson Contrib Earth Sci 27:1–49
Jourdan F, Verati C, Feraud G (2006) Intercalibration of the Hb3gr 40Ar/39Ar dating standard. Chem Geol 231:177–189
Jourdan F, Feraud G, Bertrand H, Watkeys MK, Renne PR (2007) Distinct brief major events in the Karoo large igneous province clarified by new 40Ar/39Ar ages on the Lesotho basalts. Lithos 98:195–209
Jourdan F, Renne PR (2007) Age calibration of the Fish Canyon sanidine 40Ar/39Ar dating standard using primary K-Ar standards. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 71:387–402
Jourdan F, Renne PR, Reimold WU (2009) An appraisal of the ages of terrestrial impact structures. Earth Planet Sci Lett 286:1–13
Kieffer B, Arndt N, Lapierre H, Bastien F, Bosch D, Pecher A, Yirgu G, Ayalew D, Weis D, Jerram AD, Keller F, Meugniot C (2004) Flood and shield basalts from Ethiopia: magmas from the African superswell. Jouranl of Petrology 45:793–834
Koeberl C (1993) Instrumental neutron activation analysis of geochemical and cosmochemical samples: a fast and reliable method for small sample analysis. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 168:47–60
Koppers AAP (2002) ArArCALC-software for 40Ar/39Ar age calculations. Comput Geosci 28:605–619
Le Bas ML, Le Maitre RW, Streckeisen A, Zanettin B (1986) A chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkali—silica diagram. J Petrol 27:745–750
Mader D, Koeberl C (2009) Using instrumental neutron activation analysis for geochemical analyses of terrestrial impact structures: current analytical procedures at the laboratory. Appl Radiat Isot 67:2100–2103
Merla G, Abbate E, Azzaroli A, Bruni P, Canuti P, Fazzuoli M, Sagri M, Tacconi P (1979) Comments to the geological map of Ethiopia and Somalia. Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche, Firenze, p. 95
Michels JW (2005) Changing settlement patterns in the Aksum–Yeha region of Ethiopia: 700 BC–AD 850; Cambridge monographs in African archaeology, 64, British archaeological reports international series 1446. Archaeopress, UK, Oxford, p. 256
Renne PR, Swisher CC, Deino AL, Karner DB, Owens T, Depaolo DJ (1998) Intercalibration of standards, absolute ages and uncertainties in 40Ar/39Ar dating. Chem Geol 145:117–152
Renne PR, Mundil R, Balco G, Min K, Ludwig KR (2010) Joint determination of 4K decay constants and 40Ar*/4K for the Fish Canyon sanidine standard, and improved accuracy for 40Ar/39Ar geochronology. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 74:5349–5367
Schmid T, Koch M, DiBlasi M, Hagos M (2008) Spatial and spectral analysis of soil surface properties for an archaeological area in Aksum, Ethiopia, applying high and medium resolution data. Catena 75:93–101
Son TH, Koeberl C (2005) Chemical variations within fragments of Australasian tektites. Meteoritics and Planetary Sciences 40:805–815
Sun S, McDonough WF (1989) Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders A.D. and Norry M.J. (Eds.), Magmatism in the ocean basins. Special Publication of Volcanology. Geological Society of London 42: 313–345
Tadesse T (1997) The geology of Axum area (ND 37-6). Memoir no. 9. Ethiopia Institute of Geological Survey, Ethiopia
Taylor SR, McLennan SM (1985) The continental crust: its composition and evolution. Blackwell, Oxford, p. 312
Verati C, Jourdan F (2014) Effect of sericitization of plagioclase on the 4K/40Ar and 40Ar/39Ar chronometers: implication for dating basaltic rocks and mineral deposits. In: Jourdan, F., Mark, D., and Verati, C. Eds., Advances in 40Ar/39Ar Dating: from Archaeology to Planetary Sciences; Geological Society, London, Special Publication 378: 155–174
Zanettin B, Bellieni G, Visentin JE (2006a) New radiometric age of volcanic rocks in the central Eritrean plateau (from Asmara to Adi Quala): considerations on stratigraphy and correlations. J Afr Earth Sci 45:156–161
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Axum tourism office for access to samples from the Axum quarry and stelae sites. The authors gratefully acknowledge comments from K. Bheemalingeswar, Mekelle University, Ethiopia. We appreciate the assistance of the staff of the “Atominstitut” of the Technical University of Vienna for the neutron irradiation. The manuscript benefited greatly from thoughtful reviews by anonymous referees. M.H. was supported by an ÖAD scholarship while in Austria.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hagos, M., Koeberl, C. & Jourdan, F. Geochemistry and Geochronology of Phonolitic and Trachytic Source Rocks of the Axum Obelisks and Other Stone Artifacts, Axum, Ethiopia. Geoheritage 9, 479–494 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12371-016-0199-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12371-016-0199-7