Abstract
Introduction
Despite improvements in surgical techniques and treatments introduced into clinical practice, the overall survival of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma remains low. Several epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors are being evaluated in the context of clinical trials, but there is little evidence of effectiveness in real-world conditions. This study aimed at assessing the effectiveness of nimotuzumab combined with onco-specific treatment in Cuban real-life patients with locally advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Methods
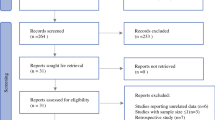
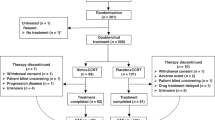
A comparative and retrospective effectiveness study was performed. The 93 patients treated with nimotuzumab were matched, with use of propensity score matching, with patients who received a diagnosis of locally advanced or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus in three Cuban provinces reported between 2011 and 2015 to the National Cancer Registry. The Kaplan–Meier method was used to estimate event–time distributions. Log-rank statistics were used for comparisons of overall survival between groups. A two-component mixture model assuming a Weibull distribution was fitted to assess the effect of nimotuzumab on short-term and long-term survival populations.
Results
There was an increase in median overall survival in patients treated with nimotuzumab (11.9 months versus 6.5 months without treatment) and an increase in the 1-year survival rate (54.0% versus 21.9% without treatment). The 2-year survival rates were 21.1% for patients treated with nimotuzumab and 0% in the untreated cohort. There were statistically significant differences in survival between groups treated and not treated with nimotuzumab, both in the short-term survival population (6.0 months vs 4.0 months, p = 0.009) and in the long-term survival population (18.0 months vs 11.0 months, p = 0.001).
Conclusions
Our study shows that nimotuzumab treatment concurrent with chemoradiotherapy increases the survival of real-world patients with locally advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Further prospective studies are required to confirm the therapeutic effectiveness of nimotuzumab in esophageal cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(1):5–29.
Mehta K, Bianco V, Awais O, Luketich JD, Pennathur A. Minimally invasive staging of esophageal cancer. Ann Cardiothorac Surg. 2017;6(2):110–8.
Murphy AG, Lynch D, Kelly RJ. State of the art management of metastatic gastroesophageal cancer. Ann Transl Med. 2015;3(16):236.
Conroy T, Galais MP, Raoul JL, Bouche O, Gourgou-Bourgade S, Douillard JY, et al. Definitive chemoradiotherapy with FOLFOX versus fluorouracil and cisplatin in patients with oesophageal cancer (PRODIGE5/ACCORD17): final results of a randomised, phase 2/3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(3):305–14.
Herskovic A, Russell W, Liptay M, Fidler MJ, Al-Sarraf M. Esophageal carcinoma advances in treatment results for locally advanced disease: review. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(5):1095–103.
Dhupar R, Van Der Kraak L, Pennathur A, Schuchert MJ, Nason KS, Luketich JD, et al. Targeting immune checkpoints in esophageal cancer: a high mutational load tumor. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017;103(4):1340–9.
Han X, Lu N, Pan Y, Xu J. Nimotuzumab combined with chemotherapy is a promising treatment for locally advanced and metastatic esophageal cancer. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:412–8.
Berger ML, Mamdani M, Atkins D, Johnson ML. Good research practices for comparative effectiveness research: defining, reporting and interpreting nonrandomized studies of treatment effects using secondary data sources: the ISPOR good research practices for retrospective database analysis task force report—part I. Value Health. 2009;12(8):1044–52.
Crosby T, Hurt CN, Falk S, Gollins S, Mukherjee S, Staffurth J, et al. Chemoradiotherapy with or without cetuximab in patients with oesophageal cancer (SCOPE1): a multicentre, phase 2/3 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14(7):627–37.
Lorenzen S, Schuster T, Porschen R, Al-Batran SE, Hofheinz R, Thuss-Patience P, et al. Cetuximab plus cisplatin-5-fluorouracil versus cisplatin-5-fluorouracil alone in first-line metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: a randomized phase II study of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie. Ann Oncol. 2009;20(10):1667–73.
Ford HE. Gefitinib for oesophageal cancer: a cog in need of a wheel? Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(8):790–1.
Garrido G, Tikhomirov IA, Rabasa A, Yang E, Gracia E, Iznaga N, et al. Bivalent binding by intermediate affinity of nimotuzumab: a contribution to explain antibody clinical profile. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011;11(4):373–82.
Lage A. Immunotherapy and complexity: overcoming barriers to control of advanced cancer. MEDICC Rev. 2014;16(3–4):65–72.
Ramos-Suzarte M, Lorenzo-Luaces P, Lazo NG, Perez ML, Soriano JL, Gonzalez CE, et al. Treatment of malignant, non-resectable, epithelial origin esophageal tumours with the humanized anti- epidermal growth factor antibody nimotuzumab combined with radiation therapy and chemotherapy. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012;13(8):600–5.
Hershman DL, Wright JD. Comparative effectiveness research in oncology methodology: observational data. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(34):4215–22.
Austin PC. An introduction to propensity score methods for reducing the effects of confounding in observational studies. Multivar Behav Res. 2011;46(3):399–424.
Marín JM, Rodríguez-Bernal MT, Wiper P. Using weibull mixture distributions to model heterogeneous survival data. Commun Stat Simul Comput. 2005;34(3):673–84.
Mahajan R. Real world data: additional source for making clinical decisions. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2015;5(2):82.
Austin PC. The performance of different propensity score methods for estimating marginal hazard ratios. Stat Med. 2013;32(16):2837–49.
Suntharalingam M, Winter K, Ilson D, Dicker AP, Kachnic L, Konski A et al. Effect of the addition of cetuximab to paclitaxel, cisplatin, and radiation therapy for patients with esophageal cancer: the NRG oncology RTOG 0436 phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.1598.
Liang J, Mingyan E, Wu G, Zhao L, Li X, Xiu X, et al. Nimotuzumab combined with radiotherapy for esophageal cancer: preliminary study of a phase II clinical trial. Onco Targets Ther. 2013;6:1589–96.
Kato K, Tahara M, Hironaka S, Muro K, Takiuchi H, Hamamoto Y, et al. A phase II study of paclitaxel by weekly 1-h infusion for advanced or recurrent esophageal cancer in patients who had previously received platinum-based chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011;67(6):1265–72.
Lu M, Wang X, Shen L, Jia J, Gong J, Li J, et al. Nimotuzumab plus paclitaxel and cisplatin as the first line treatment for advanced esophageal squamous cell cancer: a single centre prospective phase II trial. Cancer Sci. 2016;107(4):486–90.
Castro G, Skare NG, Andrade CJ, Segalla J, Jobim De Azevedo S, Silva ID et al. Chemoradiation with or without nimotuzumab in locally advanced esophageal cancer (LAEC): a randomized phase II study (NICE trial). J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(15):4078. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2014.32.15_suppl.4078.
Xu S, Ramos-Suzarte M, Bai X, Xu B. Treatment outcome of nimotuzumab plus chemotherapy in advanced cancer patients: a single institute experience. Oncotarget. 2016;7(22):33391–407.
Perez R, Moreno E. EGFR-targeting therapy as an evolving concept: learning from nimotuzumab clinical development. Chin Clin Oncol. 2014;3(1):5.
Wang C, Fu X, Cai X, Wu X, Hu X, Fan M, et al. High-dose nimotuzumab improves the survival rate of esophageal cancer patients who underwent radiotherapy. Onco Targets Ther. 2016;9:117–22.
Acknowledgements
The study and the article processing charges were funded by the Center of Molecular Immunology. We gratefully thank the cancer registry staff of the three provinces’ statistical health departments. We thank two anonymous referees and an associate editor for useful comments. All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors criteria for authorship for the manuscript, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given final approval for the version to be published.
Disclosures
Yaimarelis Saumell, Lizet Sanchez, Sandra González, Ramón Ortiz, Edadny Medina, Yaima Galán and Agustin Lage declare that they have nothing to disclose.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
This article used data from the National Cancer Registry of Cuba and does not involve any new studies of humans or animals performed by any of the authors.
Data Availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Enhanced content
To view enhanced content for this article go to http://www.medengine.com/Redeem/E7CCF0600774D0A9.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saumell, Y., Sanchez, L., González, S. et al. Overall Survival of Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated with Nimotuzumab in the Real World. Adv Ther 34, 2638–2647 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-017-0631-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-017-0631-7