Abstract
Cancer metastasis results from a multi-step cascading process that includes: 1) vascularization of the primary tumor; 2) detachment and invasion of cancer cells; 3) intravasation into lymphatic and blood vessels; 4) survival and arrest in the circulation; 5) extravasation into distant organs; and 6) colonization and growth of metastatic tumors. microRNAs (miRNAs) play critical roles in this multi-step process, both promoting and suppressing metastasis. This review updates the progress made in understanding the roles of miRNAs for invasion and metastasis during cancer progression. A specific miRNA signature of cancer metastasis is also reviewed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fidler IJ (2003) The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: the ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev Cancer 3:453–458
Bockhorn M, Jain RK, Munn LL (2007) Active versus passive mechanisms in metastasis: do cancer cells crawl into vessels, or are they pushed? Lancet Oncol 8:444–448
Weinberg RA (2007) The biology of cancer, 1st edn. Garland Science, Taylor & Francis Group, New York
Ambros V (2001) microRNAs: tiny regulators with great potential. Cell 107:823–826
He L, Hannon GJ (2004) MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet 5:522–531
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Schickel R, Boyerinas B, Park SM, Peter ME (2008) MicroRNAs: key players in the immune system, differentiation, tumorigenesis and cell death. Oncogene 27:5959–5974
Zorio E, Medina P, Rueda J et al (2009) Insights into the role of microRNAs in cardiac diseases: from biological signalling to therapeutic targets. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem 7:82–90
Bushati N, Cohen SM (2007) microRNA functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 23:175–205
Rana TM (2007) Illuminating the silence: understanding the structure and function of small RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:23–36
Shivdasani RA (2006) MicroRNAs: regulators of gene expression and cell differentiation. Blood 108:3646–3653
Spizzo R, Nicoloso MS, Croce CM, Calin GA (2009) SnapShot: MicroRNAs in cancer. Cell 137:586
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Weinberg RA (2007) Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature 449:682–688
Yu F, Yao H, Zhu P et al (2007) let-7 regulates self renewal and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells. Cell 131:1109–1123
Hurst DR, Edmonds MD, Welch DR (2009) Metastamir: the field of metastasis-regulatory microRNA is spreading. Cancer Res 69:7495–7498
Bracken CP, Gregory PA, Khew-Goodall Y, Goodall GJ (2009) The role of microRNAs in metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:1682–1699
Ma L, Weinberg RA (2008) Micromanagers of malignancy: role of microRNAs in regulating metastasis. Trends Genet 24:448–456
Nicoloso MS, Spizzo R, Shimizu M, Rossi S, Calin GA (2009) MicroRNAs-the micro steering wheel of tumour metastases. Nat Rev Cancer 9:293–302
Poliseno L, Tuccoli A, Mariani L et al (2006) MicroRNAs modulate the angiogenic properties of HUVECs. Blood 108:3068–3071
le Sage C, Nagel R, Egan DA et al (2007) Regulation of the p27(Kip1) tumor suppressor by miR-221 and miR-222 promotes cancer cell proliferation. EMBO J 26:3699–3708
Felli N, Fontana L, Pelosi E et al (2005) MicroRNAs 221 and 222 inhibit normal erythropoiesis and erythroleukemic cell growth via kit receptor down-modulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:18081–18086
Gramantieri L, Fornari F, Callegari E et al (2008) MicroRNA involvement in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Mol Med 12:2189–2204
Besson A, Hwang HC, Cicero S et al (2007) Discovery of an oncogenic activity in p27Kip1 that causes stem cell expansion and a multiple tumor phenotype. Genes Dev 21:1731–1746
Hua Z, Lv Q, Ye W et al (2006) MiRNA-directed regulation of VEGF and other angiogenic factors under hypoxia. PLoS ONE 1:e116
Bonci D, Coppola V, Musumeci M et al (2008) The miR-15a-miR-16-1 cluster controls prostate cancer by targeting multiple oncogenic activities. Nat Med 14:1271–1277
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M et al (2005) miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:13944–13949
Roccaro AM, Sacco A, Thompson B et al (2009) MicroRNAs 15a and 16 regulate tumor proliferation in multiple myeloma. Blood 113:6669–6680
Tsai WC, Hsu PW, Lai TC et al (2009) MicroRNA-122, a tumor suppressor microRNA that regulates intrahepatic metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 49:1571–1582
Fish JE, Santoro MM, Morton SU et al (2008) miR-126 regulates angiogenic signaling and vascular integrity. Dev Cell 15:272–284
Wang S, Aurora AB, Johnson BA et al (2008) The endothelial-specific microRNA miR-126 governs vascular integrity and angiogenesis. Dev Cell 15:261–271
Crawford M, Brawner E, Batte K et al (2008) MicroRNA-126 inhibits invasion in non-small cell lung carcinoma cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 373:607–612
Guo C, Sah JF, Beard L, Willson JK, Markowitz SD, Guda K (2008) The noncoding RNA, miR-126, suppresses the growth of neoplastic cells by targeting phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling and is frequently lost in colon cancers. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 47:939–946
Zhang J, Du YY, Lin YF et al (2008) The cell growth suppressor, mir-126, targets IRS-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 377:136–140
Wurdinger T, Tannous BA, Saydam O et al (2008) miR-296 regulates growth factor receptor overexpression in angiogenic endothelial cells. Cancer Cell 14:382–393
Hayashita Y, Osada H, Tatematsu Y et al (2005) A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res 65:9628–9632
Rinaldi A, Poretti G, Kwee I et al (2007) Concomitant MYC and microRNA cluster miR-17-92 (C13orf25) amplification in human mantle cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 48:410–412
Sylvestre Y, De Guire V, Querido E et al (2007) An E2F/miR-20a autoregulatory feedback loop. J Biol Chem 282:2135–2143
Aguda BD, Kim Y, Piper-Hunter MG, Friedman A, Marsh CB (2008) MicroRNA regulation of a cancer network: consequences of the feedback loops involving miR-17-92, E2F, and Myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:19678–19683
Dews M, Homayouni A, Yu D et al (2006) Augmentation of tumor angiogenesis by a Myc-activated microRNA cluster. Nat Genet 38:1060–1065
Bonauer A, Carmona G, Iwasaki M, et al (2009) MicroRNA-92a controls angiogenesis and functional recovery of ischemic tissues in mice. Science 2009 324:1710–1713
Lee DY, Deng Z, Wang CH, Yang BB (2007) MicroRNA-378 promotes cell survival, tumor growth, and angiogenesis by targeting SuFu and Fus-1 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:20350–20355
Pola R, Ling LE, Silver M et al (2001) The morphogen Sonic hedgehog is an indirect angiogenic agent upregulating two families of angiogenic growth factors. Nat Med 7:706–711
Kulshreshtha R, Ferracin M, Wojcik SE et al (2007) A microRNA signature of hypoxia. Mol Cell Biol 27:1859–1867
Hebert C, Norris K, Scheper MA, Nikitakis N, Sauk JJ (2007) High mobility group A2 is a target for miRNA-98 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer 6:5
Pulkkinen K, Malm T, Turunen M, Koistinaho J, Yla-Herttuala S (2008) Hypoxia induces microRNA miR-210 in vitro and in vivo ephrin-A3 and neuronal pentraxin 1 are potentially regulated by miR-210. FEBS Lett 582:2397–2401
Fasanaro P, D’Alessandra Y, Di Stefano V et al (2008) MicroRNA-210 modulates endothelial cell response to hypoxia and inhibits the receptor tyrosine kinase ligand Ephrin-A3. J Biol Chem 283:15878–15883
Kong W, Yang H, He L et al (2008) MicroRNA-155 is regulated by the transforming growth factor beta/Smad pathway and contributes to epithelial cell plasticity by targeting RhoA. Mol Cell Biol 28:6773–6784
Parmacek MS (2009) MicroRNA-modulated targeting of vascular smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest 119:2526–2528
Gabriely G, Wurdinger T, Kesari S et al (2008) MicroRNA 21 promotes glioma invasion by targeting matrix metalloproteinase regulators. Mol Cell Biol 28:5369–5380
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal K, Jacob ST, Patel T (2007) MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology 133:647–658
Zhu S, Si ML, Wu H, Mo YY (2007) MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J Biol Chem 282:14328–14336
Lu Z, Liu M, Stribinskis V et al (2008) MicroRNA-21 promotes cell transformation by targeting the programmed cell death 4 gene. Oncogene 27:4373–4379
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA et al (2008) MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 27:2128–2136
Papagiannakopoulos T, Shapiro A, Kosik KS (2008) MicroRNA-21 targets a network of key tumor-suppressive pathways in glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 68:8164–8172
Sayed D, Rane S, Lypowy J et al (2008) MicroRNA-21 targets Sprouty2 and promotes cellular outgrowths. Mol Biol Cell 19:3272–3282
Zhang D, Fan GC, Zhou X et al (2008) Over-expression of CXCR4 on mesenchymal stem cells augments myoangiogenesis in the infarcted myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol 44:281–292
Li T, Li D, Sha J, Sun P, Huang Y (2009) MicroRNA-21 directly targets MARCKS and promotes apoptosis resistance and invasion in prostate cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 383:280–285
Li Y, Li W, Yang Y et al (2009) MicroRNA-21 targets LRRFIP1 and contributes to VM-26 resistance in glioblastoma multiforme. Brain Res 1286:13–18
Tang YF, Zhang Y, Li XY, Li C, Tian W, Liu L (2009) Expression of miR-31, miR-125b-5p, and miR-326 in the adipogenic differentiation process of adipose-derived stem cells. OMICS 13:331–336
Wang P, Zou F, Zhang X et al (2009) microRNA-21 negatively regulates Cdc25A and cell cycle progression in colon cancer cells. Cancer Res 69:8157–8165
Xiao B, Guo J, Miao Y et al (2009) Detection of miR-106a in gastric carcinoma and its clinical significance. Clin Chim Acta 400:97–102
Lin SL, Chiang A, Chang D, Ying SY (2008) Loss of mir-146a function in hormone-refractory prostate cancer. RNA 14:417–424
Marhaba R, Zoller M (2004) CD44 in cancer progression: adhesion, migration and growth regulation. J Mol Histol 35:211–231
Wang CH, Lee DY, Deng Z et al (2008) MicroRNA miR-328 regulates zonation morphogenesis by targeting CD44 expression. PLoS ONE 3:e2420
Huang Q, Gumireddy K, Schrier M et al (2008) The microRNAs miR-373 and miR-520c promote tumour invasion and metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 10:202–210
Li Y, Guessous F, Zhang Y et al (2009) MicroRNA-34a inhibits glioblastoma growth by targeting multiple oncogenes. Cancer Res 69:7569–7576
Horst D, Kriegl L, Engel J, Kirchner T, Jung A (2009) Prognostic significance of the cancer stem cell markers CD133, CD44, and CD166 in colorectal cancer. Cancer Invest 27:844–850
Ji Q, Hao X, Zhang M et al (2009) MicroRNA miR-34 inhibits human pancreatic cancer tumor-initiating cells. PLoS ONE 4:e6816
Lin EH, Jiang Y, Deng Y, Lapsiwala R, Lin T, Blau CA (2008) Cancer stem cells, endothelial progenitors, and mesenchymal stem cells: “seed and soil” theory revisited. Gastrointest Cancer Res 2:169–174
Palapattu GS, Wu C, Silvers CR et al (2009) Selective expression of CD44, a putative prostate cancer stem cell marker, in neuroendocrine tumor cells of human prostate cancer. Prostate 69:787–798
Takaishi S, Okumura T, Tu S et al (2009) Identification of gastric cancer stem cells using the cell surface marker CD44. Stem Cells 27:1006–1020
Zhu Z, Hao X, Yan M, et al (2009) Cancer stem/progenitor cells are highly enriched in CD133(+)CD44(+) population in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer 2009. doi:10.1002/ijc.24868
Voorhoeve PM, le Sage C, Schrier M et al (2006) A genetic screen implicates miRNA-372 and miRNA-373 as oncogenes in testicular germ cell tumors. Cell 124:1169–1181
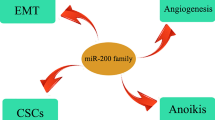
Hurteau GJ, Carlson JA, Spivack SD, Brock GJ (2007) Overexpression of the microRNA hsa-miR-200c leads to reduced expression of transcription factor 8 and increased expression of E-cadherin. Cancer Res 67:7972–7976
Christoffersen NR, Silahtaroglu A, Orom UA, Kauppinen S, Lund AH (2007) miR-200b mediates post-transcriptional repression of ZFHX1B. RNA 13:1172–1178
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL et al (2008) The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol 10:593–601
Korpal M, Lee ES, Hu G, Kang Y (2008) The miR-200 family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer cell migration by direct targeting of E-cadherin transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Biol Chem 283:14910–14914
Park SM, Gaur AB, Lengyel E, Peter ME (2008) The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes Dev 22:894–907
Burk U, Schubert J, Wellner U et al (2008) A reciprocal repression between ZEB1 and members of the miR-200 family promotes EMT and invasion in cancer cells. EMBO Rep 9:582–589
Gandellini P, Folini M, Longoni N et al (2009) miR-205 Exerts tumor-suppressive functions in human prostate through down-regulation of protein kinase Cepsilon. Cancer Res 69:2287–2295
Gebeshuber CA, Zatloukal K, Martinez J (2009) miR-29a suppresses tristetraprolin, which is a regulator of epithelial polarity and metastasis. EMBO Rep 10:400–405
Tavazoie SF, Alarcon C, Oskarsson T et al (2008) Endogenous human microRNAs that suppress breast cancer metastasis. Nature 451:147–152
Harris TA, Yamakuchi M, Ferlito M, Mendell JT, Lowenstein CJ (2008) MicroRNA-126 regulates endothelial expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:1516–1521
Sengupta S, den Boon JA, Chen IH et al (2008) MicroRNA 29c is down-regulated in nasopharyngeal carcinomas, up-regulating mRNAs encoding extracellular matrix proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:5874–5878
Valastyan S, Reinhardt F, Benaich N et al (2009) A pleiotropically acting microRNA, miR-31, inhibits breast cancer metastasis. Cell 137:1032–1046
Evangelisti C, Florian MC, Massimi I, et al (2009) MiR-128 up-regulation inhibits Reelin and DCX expression and reduces neuroblastoma cell motility and invasiveness. FASEB J 2009 23:4276–4287
Huang ZM, Yang J, Shen XY et al (2009) MicroRNA expression profile in non-cancerous colonic tissue associated with lymph node metastasis of colon cancer. J Dig Dis 10:188–194
Weiss L, Orr FW, Honn KV (1988) Interactions of cancer cells with the microvasculature during metastasis. FASEB J 2:12–21
Kim J, Yu W, Kovalski K, Ossowski L (1998) Requirement for specific proteases in cancer cell intravasation as revealed by a novel semiquantitative PCR-based assay. Cell 94:353–362
Salvi A, Sabelli C, Moncini S et al (2009) MicroRNA-23b mediates urokinase and c-met downmodulation and a decreased migration of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. FEBS J 276:2966–2982
Dangi-Garimella S, Yun J, Eves EM et al (2009) Raf kinase inhibitory protein suppresses a metastasis signalling cascade involving LIN28 and let-7. EMBO J 28:347–358
Zijlstra A, Lewis J, Degryse B, Stuhlmann H, Quigley JP (2008) The inhibition of tumor cell intravasation and subsequent metastasis via regulation of in vivo tumor cell motility by the tetraspanin CD151. Cancer Cell 13:221–234
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120:15–20
Repesh LA, Fitzgerald TJ (1984) Interactions of tumor cells with intact capillaries: a model for intravasation. Clin Exp Metastasis 2:139–150
Li C, Feng Y, Coukos G, Zhang L (2009) Therapeutic microRNA strategies in human cancer. AAPS J 2009 11:747–757
Lu LF, Liston A (2009) MicroRNA in the immune system, microRNA as an immune system. Immunology 127:291–298
Rhee KJ, Wu S, Wu X et al (2009) Induction of persistent colitis by a human commensal, enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis, in wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Infect Immun 77:1708–1718
Tili E, Croce CM, Michaille JJ (2009) miR-155: on the crosstalk between inflammation and cancer. Int Rev Immunol 28:264–284
Johnnidis JB, Harris MH, Wheeler RT et al (2008) Regulation of progenitor cell proliferation and granulocyte function by microRNA-223. Nature 451:1125–1129
Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ, Baltimore D (2006) NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:12481–12486
Dykxhoorn DM, Wu Y, Xie H et al (2009) miR-200 enhances mouse breast cancer cell colonization to form distant metastases. PLoS ONE 4:e7181
Wicha MS, Liu S, Dontu G (2006) Cancer stem cells: an old idea—a paradigm shift. Cancer Res 66:1883–1890, discussion 1895–1886
Nguyen DX, Bos PD, Massague J (2009) Metastasis: from dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat Rev Cancer 9:274–284
Al-Hajj M, Clarke MF (2004) Self-renewal and solid tumor stem cells. Oncogene 23:7274–7282
Welm AL, Kim S, Welm BE, Bishop JM (2005) MET and MYC cooperate in mammary tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:4324–4329
Bernstein E, Kim SY, Carmell MA et al (2003) Dicer is essential for mouse development. Nat Genet 35:215–217
Lujambio A, Calin GA, Villanueva A et al (2008) A microRNA DNA methylation signature for human cancer metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:13556–13561
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J et al (2005) RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell 120:635–647
Mayr C, Hemann MT, Bartel DP (2007) Disrupting the pairing between let-7 and Hmga2 enhances oncogenic transformation. Science 315:1576–1579
Garzia L, Andolfo I, Cusanelli E et al (2009) MicroRNA-199b-5p impairs cancer stem cells through negative regulation of HES1 in medulloblastoma. PLoS ONE 4:e4998
Park IK, Qian D, Kiel M et al (2003) Bmi-1 is required for maintenance of adult self-renewing haematopoietic stem cells. Nature 423:302–305
Liu S, Dontu G, Mantle ID et al (2006) Hedgehog signaling and Bmi-1 regulate self-renewal of normal and malignant human mammary stem cells. Cancer Res 66:6063–6071
Godlewski J, Nowicki MO, Bronisz A et al (2008) Targeting of the Bmi-1 oncogene/stem cell renewal factor by microRNA-128 inhibits glioma proliferation and self-renewal. Cancer Res 68:9125–9130
Ferretti E, De Smaele E, Miele E et al (2008) Concerted microRNA control of Hedgehog signalling in cerebellar neuronal progenitor and tumour cells. EMBO J 27:2616–2627
Northcott PA, Fernandez LA, Hagan JP et al (2009) The miR-17/92 polycistron is up-regulated in sonic hedgehog-driven medulloblastomas and induced by N-myc in sonic hedgehog-treated cerebellar neural precursors. Cancer Res 69:3249–3255
Uziel T, Karginov FV, Xie S et al (2009) The miR-17∼92 cluster collaborates with the Sonic Hedgehog pathway in medulloblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:2812–2817
Bos PD, Zhang XH, Nadal C et al (2009) Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to the brain. Nature 459:1005–1009
Mueller DW, Rehli M, Bosserhoff AK (2009) miRNA expression profiling in melanocytes and melanoma cell lines reveals miRNAs associated with formation and progression of malignant melanoma. J Invest Dermatol 129:1740–1751
Olson P, Lu J, Zhang H et al (2009) MicroRNA dynamics in the stages of tumorigenesis correlate with hallmark capabilities of cancer. Genes Dev 23:2152–2165
Baffa R, Fassan M, Volinia S et al (2009) MicroRNA expression profiling of human metastatic cancers identifies cancer gene targets. J Pathol 219:214–221
Budhu A, Jia HL, Forgues M et al (2008) Identification of metastasis-related microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 47:897–907
Duursma AM, Kedde M, Schrier M, le Sage C, Agami R (2008) miR-148 targets human DNMT3b protein coding region. RNA 14:872–877
Melhuish TA, Gallo CM, Wotton D (2001) TGIF2 interacts with histone deacetylase 1 and represses transcription. J Biol Chem 276:32109–32114
Laios A, O’Toole S, Flavin R et al (2008) Potential role of miR-9 and miR-223 in recurrent ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer 7:35
Guo LM, Pu Y, Han Z et al (2009) MicroRNA-9 inhibits ovarian cancer cell growth through regulation of NF-kappaB1. FEBS J 276:5537–5546
Hsu PY, Deatherage DE, Rodriguez BA et al (2009) Xenoestrogen-induced epigenetic repression of microRNA-9-3 in breast epithelial cells. Cancer Res 69:5936–5945
Bazzoni F, Rossato M, Fabbri M et al (2009) Induction and regulatory function of miR-9 in human monocytes and neutrophils exposed to proinflammatory signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:5282–5287
Foekens JA, Sieuwerts AM, Smid M et al (2008) Four miRNAs associated with aggressiveness of lymph node-negative, estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:13021–13026
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Milena Nicoloso for drawing the Fig. 1 and Sherri De Jesus for her technical editing expertise. George A. Calin, a Fellow, is supported by The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Research Trust, The University of Texas System Regents Research Scholar Program, and by the Ladjevardian Regents Research Scholar Fund. This study was supported in part by a grant from the Anne and Henry Zarrow Foundation and by NIH grant 1R01CA135444. The authors acknowledge that all related articles are not cited in this article due to the space limit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le, XF., Merchant, O., Bast, R.C. et al. The Roles of MicroRNAs in the Cancer Invasion-Metastasis Cascade. Cancer Microenvironment 3, 137–147 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12307-010-0037-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12307-010-0037-4