Abstract
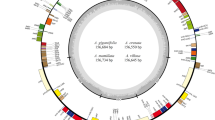
Arabis paniculata Franch (Brassicaceae) has been widely used for the phytoremediation of heavy mental, owing to its hyper tolerance of extreme Pb, Zn, and Cd concentrations. However, studies on its genome or plastid genome are scarce. In the present study, we obtained the complete chloroplast (cp) genome of A. paniculata via de novo assembly through the integration of Illumina reads and PacBio subreads. The cp genome presents a typical quadripartite cycle with a length of 153,541 bp, and contains 111 unigenes, with 79 protein-coding genes, 28 tRNAs and 4 rRNAs. Codon usage analysis showed that the codons for leucine were the most frequent codons and preferentially ended with A/U. Synonymous (Ks) and non-synonymous (Ka) substitution rate analysis indicated that the unigenes, ndhF and rpoC2, related to “NADH-dehydrogenase” and “RNA polymerase” respectively, underwent the lowest purifying selection pressure. Phylogenetic analysis demonstrated that Arabis flagellosa and A. hirsuta are more similar to each other than to A. paniculata, and Arabis is the closest relative of Draba among all Brassicaceae genera. These findings provide valuable information for the optimal exploitation of this model species as a heavy-metal hyperaccumulator.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Cp:
-
Chloroplast
- IR:
-
Inverted repeat
- LSC:
-
Large single copy
- SSC:
-
Small single copy
- rRNA:
-
Ribosomal RNA
- tRNA:
-
Transfer RNA
- NJ:
-
Neighbor-joining
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeat
- RSCU:
-
The relative synonymous codon usage
- ML:
-
Maximum likelihood
- BI:
-
Bayesian inference
- Ka:
-
Non-synonymous
- Ks:
-
Synonymous
- Pb:
-
Lead
- Zn:
-
Zinc
- Cd:
-
Cadmium
References
Beier S, Thiel T, Munch T, Scholz U, Mascher M (2017) MISA-web: a web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 33:2583–2585. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btx198
Booker TR, Jackson BC, Keightley PD (2017) Detecting positive selection in the genome. BMC Biol 15:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-017-0434-y
Chaisson MJ, Tesler G (2012) Mapping single molecule sequencing reads using basic local alignment with successive refinement (BLASR): application and theory. BMC Bioinformatics 13:238. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-13-238
Chalhoub B, Denoeud F, Liu S, Parkin IAP, Tang HB, Wang XY et al (2014) Early allopolyploid evolution in the post-Neolithic Brassica napus oilseed genome. Science 345:950–953. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1253435
Chen S, Zhou Y, Chen Y et al (2018) Fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34:884–890. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560
Choi KS, Park S (2015) The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Aster spathulifolius (Asteraceae), genomic features and relationship with Asteraceae. Gene 572:214–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2015.07.020
Downie SR, Palmer JD (1992) Use of chloroplast DNA rearrangements in reconstructing plant phylogeny. In: Molecular systematics of plants. Springer, pp 14–35, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-3276-7_2
Du X, Zeng T, Feng Q, Hu L, Luo X, Weng Q et al (2020) The complete chloroplast genome sequence of yellow mustard (Sinapis alba L.) and its phylogenetic relationship to other Brassicaceae species. Gene 2020(731):144340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2020.144340
English AC, Richards S, Han Y, Wang M, Vee V, Qu J et al (2012) Mind the gap: upgrading genomes with Pacific Biosciences RS long-read sequencing technology. PLoS ONE 7:e47768. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0047768
Frazer KA, Pachter L, Poliakov A, Rubin EM, Dubchak I (2004) VISTA: computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 2004(32):273–279. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh458
Gao H, Roston RL, Jouhet J, Yu F (2019) Structure and Function of Chloroplasts. Frontiers Media SA 9:1–2. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01656
Hebert PDN, Braukmann TWA, Prosser SWJ, Ratnasingham S, dewaard JR, Ivanova NV, et al (2018) A Sequel to Sanger: amplicon sequencing that scales. BMC Genomics 19:219. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-4611-3
Huotari T, Korpelainen H (2012) Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Elodea canadensis and comparative analyses with other monocot plastid genomes. Gene 508:96–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2012.07.020
Jeong YM, Chung WH, Mun JH, Kim N, Yu HJ (2014) De novo assembly and characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Gene 551:39–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2014.08.038
Jian HY, Zhang YH, Yan HJ, Qiu XQ, Wang QG, Li SB et al (2018) The complete chloroplast genome of a key ancestor of modern roses, Rosa chinensis var. spontanea, and a comparison with congeneric species. Molecules 23:389. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020389
Jordon-Thaden I, Hase I, Al-Shehbaz I (2010) Molecular phylogeny and systematics of the genus Draba (Brassicaceae) and identification of its most closely related genera. Mol Phylogenet Evol 55:524–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2010.02.012
Karl R, Koch MA (2014) Phylogenetic signatures of adaptation: The Arabis hirsuta species aggregate (Brassicaceae) revisited. Perspect Plant Ecology Evol 2014(16):247–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ppees.2014.06.001
Kawabe A, Nukii H, Furihata HY (2018) Exploring the history of chloroplast capture in Arabis using whole chloroplast genome sequencing. Internat J Mol Sci 2018(19):602. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020602
Kim HS, Moon BC, Yang S, Song JH, Chun JM, Kwon BI et al (2019) Determination of fatty acids in the seeds of Lepidium apetalum Willdenow, Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl, and Draba nemorosa L. by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography equipped with a charged aerosol detector. J Liq Chromatogr R 42:128–136. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826076.2019.1571509
Kimura M (2020) The neutral theory and molecular evolution. In: My thoughts on biological evolution. Springer, Singapore, pp 119–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-6165-8_8
Koch M, Bishop J, Mitchell-Olds T, Koch M (1999) Molecular systematics and evolution of Arabidopsis and Arabis. Plant Biol 1:529–537. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1438-8677.1999.tb00779.x
Koren S, Schatz MC, Walenz BP, Martin J, Howard JT, Ganapathy G et al (2012) Hybrid error correction and de novo assembly of single-molecule sequencing reads. Nat Biotechnol 30:693–700. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2280
Kurtz S, Choudhuri JV, Ohlebusch E, Schleiermacher C, Stoye J, Giegerich R (2001) REPuter: the manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res 29:4633–4642. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.22.4633
Lee SB, Kaittanis C, Jansen RK, Hostetler JB, Tallon LJ, Town CD et al (2006) The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Gossypium hirsutum: organization and phylogenetic relationships to other angiosperms. BMC Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-7-61
Lgloi G, Kössel H (1992) The transcriptional apparatus of chloroplasts. Criti Rev Plant Sci 10:525–558. https://doi.org/10.1080/0735268920938232664
Liu L, Qin MZ, Yang L, Song ZZ, Luo L, Bao HY et al (2017) A genome-wide analysis of simple sequence repeats in Apis cerana and its development as polymorphism markers. Gene 599:53–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2016.11.016
Lohse M, Drechsel O, Bock R (2007) OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW): a tool for the easy generation of high-quality custom graphical maps of plastid and mitochondrial genomes. Curr Genet 52:267–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-007-0161-y
Machado HE, Lawrie DS, Petrov DA (2020) Pervasive strong selection at the level of codon usage bias in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 214:511–528. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.119.302542
Makałowski W, Boguski MS (1998) Evolutionary parameters of the transcribed mammalian genome: an analysis of 2,820 orthologous rodent and human sequences. P Natl Acad Sci USA 95:9407–9412. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.16.9407
McPherson H, Vander Merwe M, Delaney SK, Edwards MA, Henry RJ, McIntosh E et al (2013) Capturing chloroplast variation for molecular ecology studies: a simple next generation sequencing approach applied to a rainforest tree. BMC Ecol 13:8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6785-13-8
Melodelima C, Lobréaux S (2013) Complete Arabis alpina chloroplast genome sequence and insight into its polymorphism. Meta Gene 1:65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mgene.2013.10.004
Nie X, Lv S, Zhang Y, Du X, Wang L, Biradar SS et al (2012) Complete chloroplast genome sequence of a major invasive species, crofton weed (Ageratina adenophora). PLoS ONE 7:e36869. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0036869
Peden JF (2000) Analysis of codon usage. University of Nottingham, UK,. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystems.2011.06.005
Qian J, Song J, Gao H, Zhu Y, Xu J, Pang X et al (2013) The complete chloroplast genome sequence of the medicinal plant Salvia miltiorrhiza. PLoS ONE 8:e57607. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0057607
Qiu RL, Zhao X, Tang YT, Yu FM, Hu PJ (2008) Antioxidative response to Cd in a newly discovered cadmium hyperaccumulator, Arabis paniculata F. Chemosphere 74:6–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.09.069
Rajput V, Minkina T, Semenkov I, Klink G, Tarigholizadeh S, Sushkova S (2020) Phylogenetic analysis of hyperaccumulator plant species for heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ Geochem Health 2020:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00527-0
Raman G, Park V, Kwak M, Lee B, Park S (2017) Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of Arabis stellari and comparisons with related species. PLoS ONE 2017(12):e0183197. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0183197
Rambaut A (2012) FigTree v1.4. Edinburgh: University of Edinburgh. http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/
Rhoads A, Au KF (2015) PacBio sequencing and its applications. Genom Proteom Bioinf 13:278–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2015.08.002
Ronquist F, Teslenko M, Van-Der Mark P, Ayres DL, Darling A, Höhna S et al (2012) MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst Biol 61:539–542. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029
Saina JK, Gichira AW, Li ZZ, Hu GW, Wang QF, Liao K (2018) The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Dodonaea viscosa: comparative and phylogenetic analyses. Genetica 146:101–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-017-0003-x
Schattner P, Brooks AN, Lowe TM (2005) The tRNAscan-SE, snoscan and snoGPS web servers for the detection of tRNAs and snoRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 33:686–689. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki366
Shen X, Wu M, Liao B, Liu Z, Bai R, Xiao S et al (2017) Complete chloroplast genome sequence and phylogenetic analysis of the medicinal plant Artemisia annua. Molecules 22:1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22081330
Shimada H, Fukuta M, Ishikawa M, Sugiura M (1990) Rice chloroplast RNA polymerase genes: the absence of an intron in rpoC1 and the presence of an extra sequence in rpoC2. Mol Gen Genet 221:395–402. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00259404
Sun M, Zhang M, Singh J, Song B, Tang Z, Liu Y et al (2020) Contrasting genetic variation and positive selection followed the divergence of NBS-encoding genes in Asian and European pears. BMC Genomics 21:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-07226-1
Tang YT, Qiu RI, Zeng XW, Fang XH (2005) A New Found Pb/Zn/Cd Hyperaccumulator——Arabis Panieulata L. Acta Sci Natur Univ Sunyatseni 44:135–136 ((in Chinese))
Tang YT, Qiu RL, Zeng XW, Ying RR, Yu FM, Zhou XY (2008) Lead, zinc, cadmium hyperaccumulation and growth stimulation in Arabis paniculata Franch. Environ Exp Bot 2009(66):126–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2008.12.016
Todd RT, Wikoff TD, Forche A, Selmecki A (2019) Genome plasticity in Candida albicans is driven by long repeat sequences. Elife 8:e45954. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45954.001
Wang D, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Zhu J, Yu J (2010) KaKs_Calculator 2.0: a toolkit incorporating gamma-series methods and sliding window strategies. Genom Proteom & Bioinf 8:77–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1672-0229(10)60008-3
Wang M, Wang X, Sun J, Wang Y, Ge Y, Dong W et al (2021) Phylogenomic and evolutionary dynamics of inverted repeats across Angelica plastomes. BMC Plant Biol 21(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02801-w
Warwick SI, Al-Shehbaz IA, Sauder CA (2006) Phylogenetic position of Arabis arenicola and generic limits of Aphragmus and Eutrema (Brassicaceae) based on sequences of nuclear ribosomal DNA. Botany 84:269–281. https://doi.org/10.3100/1043-4534-13.2.289
Wicke S, Schneeweiss GM, dePamphilis CW, Muller KF, Quandt D (2011) The evolution of the plastid chromosome in land plants: gene content, gene order, gene function. Plant Mol Biol 76:273–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-011-9762-4
Wyman SK, Jansen RK, Boore JL (2004) Automatic annotation of organellar genomes with DOGMA. Bioinformatics 2004(20):3252–3255. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bth352
Xie Y, Wu G, Tang J, Luo R, Patterson J, Liu S et al (2014) SOAPdenovo-Trans: de novo transcriptome assembly with short RNA-Seq reads. Bioinformatics 2014(30):1660–1666. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu077
Yan C, Du JC, Gao L, Li Y, Hou XL (2019) The complete chloroplast genome sequence of watercress (Nasturtium officinale R. Br.): Genome organization, adaptive evolution and phylogenetic relationships in Cardamineae. Gene 699:24–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2019.02.075
Yang Z, Nielsen R (2000) Estimating synonymous and nonsynonymous substitution rates under realistic evolutionary models. Mol Biol Evol 17:32–43. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026236
Yang Z, Wang G, Ma Q, Liang L, Zhao T (2019) The complete chloroplast genomes of three Betulaceae species: Implications for molecular phylogeny and historical biogeography. Peer J 7:e6320. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.6320
Yu CH, Dang Y, Zhou Z, Wu C, Zhao F, Sachs MS (2015) Codon usage influences the local rate of translation elongation to regulate co-translational protein folding. Mol Cell 59:744–754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.07.018
Zeng X, Ma LQ, Qiu R, Tang Y (2009) Responses of non-protein thiols to Cd exposure in Cd hyperaccumulator Arabis paniculata Franch. Environ Exp Bot 66:242–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2009.03.003
Zeng XW, Qiu RL, Ying RR, Tang YT, Tang L, Fang XH (2011) The differentially-expressed proteome in Zn/Cd hyperaccumulator Arabis paniculata Franch. in response to Zn and Cd. Chemosphere 82:321–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.10.030
Zhang GJ, Hu HH, Zhang CF, Tian XJ, Peng H, Gao TG (2015) Inaccessible biodiversity on limestone cliffs: Aster tianmenshanensis (Asteraceae), a new critically endangered species from China. PLoS ONE 10:e0134895. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0134895
Zhou T, Yang Y, Hu Y (2017) Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome sequence of Lepidium meyenii (Brassicaceae). Conserv Genet Resour 9:405–408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-017-0695-3
Zhu B, Gao ZM, Luo X, Feng Q, Du XY, Weng QB et al (2019) The complete chloroplast genome sequence of garden cress (Lepidium sativum L.) and its phylogenetic analysis in Brassicaceae family. Mitochondrial DNA B 4:3601–3602. https://doi.org/10.1080/23802359.2019.1677527
Zhu B, Feng Q, Yu J, Yu Y, Zhu XX, Wang Y et al (2020) Chloroplast genome features of an important medicinal and edible plant: Houttuynia cordata (Saururaceae). PLoS ONE 15:e0239823. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0239823
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the by the Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Foundation under Grant ([2020]1Y102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.Z.: Writing—original draft; X.L. and C.G.: Data curation and Formal analysis; C.D.: Resources; S.Z. and Q.X.: Software; Q.W.: Validation; X.H. and X.D.: Writing—review & editing; B.Z.: Project administration and Funding acquisition. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12298_2022_1151_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Figure S1. The ka/ks ratios of 71 protein-coding genes of the A. paniculata cp genome versus five closed related species. The X and Y axis represents the ka/ks ratios and 71 protein-coding genes, respectively. The different color boxes represent different comparisons at the top right corner
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Gan, C., Luo, X. et al. Complete chloroplast genome features of the model heavy metal hyperaccumulator Arabis paniculata Franch and its phylogenetic relationships with other Brassicaceae species. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 28, 775–789 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-022-01151-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-022-01151-1