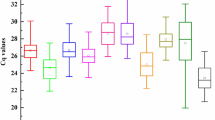
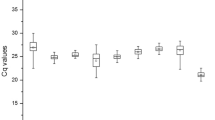
Abstract
Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction is the most commonly used method to accurately detect gene expression patterns. The method requires stable internal reference genes to standardize the data. However, studies have shown that there is no stable expression of internal reference genes in different tissues and under different treatments. Therefore, in order to study the optimal reference genes of quinoa under different hormones and abiotic stress, leaves and stems from quinoa seedlings treated with low temperature (4 °C), salt (200 mmol/L) and abscisic acid (200 mmol/L) were used as experimental materials. Using ACT-1, eIF, EF1α, GAPDH, TUA, TUB-9, TUB-1, H2A and L8-1 as candidate reference genes, the expression stability of these 9 quinoa candidate reference genes under different hormone treatment and abiotic stress was evaluated by using geNorm, NormFinder and BestKeeper software. The results showed that TUB-1 gene under salt stress, L8-1 gene under low temperature stress, EF-1α gene induced by ABA. PLIM2c WLIM1and WLIM2b were selected to verify the candidate internal reference genes, and finally the expression of GAPDH was most unstable under the three treatments, which was not suitable to be the internal reference gene of quinoa under specific conditions, while EF1α showed good stability under the three different treatments and was suitable to be used as the internal reference gene. In conclusion, the results of this study could provide an important reference for quantifying the expression level of reference genes in quinoa.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Orntoft TF (2004) Normalizaion of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res 64(15):5245–5250
Annapaula G, Lut O, Dirk V, Brigitte D, Roger B, Chantal M (2001) An overview of real-time quantitative PCR: applications to quantify cytokine gene expression. Methods 25(4):386–401
Bao W, Qu Y, Shan X, Wan Y (2016) Screening and validation of housekeeping genes of the root and cotyledon of cunninghamia lanceolata under abiotic stresses by using quantitative real-time PCR. Int J Mol Sci 17:1198
Bustin SA (2000) Absolute quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays. J Mol Endocrinol 25(2):169–193
Bustin SA, Benes V, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW (2005) Quantitative real-time RT-PCR–a perspective. J Mol Endocrinol 34(3):597–601
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW, Shipley GL, Vandesompele J, Wittwer CT (2009) The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem 55(4):611–622
Bustin SA, Beaulieu JF, Huggett J, Jaggi R, Kibenge FS, Olsvik PA, Penning LC, Toegel S (2010) MIQE précis: practical implementation of minimum standard guidelines for fluorescence-based quantitative real-time PCR experiments. BMC Mol Biol 11:74
Chao Z, Jian F, Yi W, Zhi B, Hong Z (2015) Identification of suitable reference genes for gene expression normalization in the quantitative real-time PCR analysis of sweet Osmanthus. PLoS ONE 10(8):e0136355
Cui B, Smooker PM, Rouch DA, Deighton MA (2016) Selection of suitable reference genes for gene expression studies in Staphylococcus capitis during growth under erythromycin stress. Mol Genet Genom 291(4):1795–1811
Die JV, Román B, Nadal S, González-V CI (2010) Evaluation of candidate reference genes for expression studies in Pisum sativum under different experimental conditions. Planta 232:145–153
Fan CJ, Ma JM, Guo Q, Li XT, Wang H, Lu MZ (2013) Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR in bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). PLoS ONE 8(2):e56573
Filipe P, Catarina CP, Daniela F, Pedro MF, Paula T (2012) Selection of suitable reference genes for RT-qPCR analyses incyanobacteria. PLoS ONE 7(4):e34983
Guo J, Ling H, Wu Q, Xu L, Que Y (2014) The choice of reference genes for assessing gene expression in sugarcane under salinity and drought stresses. Sci Rep 4:7042
Hu RB, Fan CM, Li HY, Zhang QZ, Fu YF (2009) Evaluation of putative reference genes for gene expression normalization in soybean by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. BMC Mol Biol 10:93
Huang LK, Yan HD, Jiang XM, Yin GH, Zhang XQ, Qi X, Zhang Y, Yan YH, Ma X, Peng Y (2014) Identification of candidate reference genes in perennial ryegrass for quantitative RT-PCR under various abiotic stress conditions. PLoS ONE 9:e93724
Jo V, Katleen DP, Filip P, Bruce P, Nadine VR, Anne DP, Frank S (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3(7):467–470
José VD, Belén R, Salvador N, Clara I (2010) Evaluation of candidate reference genes for expression studies in Pisum sativum under different experimental conditions. Planta 232(1):145–153
Kai S, Qian C, Yao W, Rui L, Hua Z, Peng W, Yan L (2016) ABI4 mediates antagonistic effects of abscisic acid and gibberellins at transcript and protein levels. Plant J 85(3):348–361
Koo YM, Heo AY, Choi HW (2020) Salicylic acid as a safe plant protector and growth regulator. Plant Pathol J 36(1):1–10
Le DT, Aldrich DL, Valliyodan B, Watanabe Y, Ha CV, Nishiyama R, Guttikonda SK, Quach TN, Gutierrez-Gonzalez JJ, Tran LS, Nguyen HT (2012) Evaluation of candidate reference genes for normalization of quantitative RT-PCR in soybean tissues under various abiotic stress conditions. PLoS ONE 7(9):e46487
Li HY, Dong YY, Yang J, Liu XM, Wang YF, Yao N, Guan LL, Wang N, Wu JY, Li XK (2012) De novo transcriptome of safflower and the identification of putative genes for oleosin and the biosynthesis of flavonoids. PLoS ONE 7(2):e30987
Long XY, Wang JR, Ouellet T, Rocheleau H, Wei YM, Pu ZE, Jiang QT, Lan XJ, Zheng YL (2010) Genome-wide identification and evaluation of novel internal control genes for Q-PCR based transcript normalization in wheat. Plant Mol Biol 74:307–311
Long XY, He B, Gao XS, Qin YX, Yang JH, Fang YJ, Qi JY, Tang CR (2015) Validation of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR during latex regeneration in rubber tree. Gene 563:190–195
Mascia T, Santovito E, Gallitelli D, Cillo F (2010) Evaluation of reference genes for quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction normalization in infected tomato plants. Mol Plant Pathol 11:805–816
Michael WP, Ales T, Christian P, Tanja PN (2004) Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper – Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotech Lett 26(6):509–515
Milena P, Francesco M, Luigi Z, Marco S (2015) Reference gene selection for normalization of RT-qPCR gene expression data from Actinidia deliciosa leaves infected with Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae. Sci Rep 5(1):329–369
Mukesh J, Aashima N, Akhilesh KT, Jitendra PK (2006) Validation of housekeeping genes as internal control for studying gene expression in rice by quantitative real-time PCR. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 345(2):646–651
Nicot N, Hausman JF, Hoffmann L, Lucien H, Danièle E (2005) Housekeeping gene selection for real-time RT-PCR normalization in potato during biotic and abiotic stress. J Exp Bot 56(421):12387
Oliveira LA, Breton MC, Bastolla FM, Camargo SS, Margis R, Frazzon J, Pasquali G (2012) Reference genes for the normalization of gene expression in Eucalyptus species. Plant Cell Physiol 53(2):405–422
Paolacci AR, Tanzarella OA, Porceddu E, Ciaffi M (2009) Identification and validation of reference genes for quantitative RT-PCR normalization in wheat. BMC Mol Biol 10(10):11–37
Pfaffl MW, Tichopad A, Prgomet C, Neuvians TP (2004) Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: bestkeeper–excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotech Lett 26:509–524
Raquel LP, Enrique R (2013) Selection of housekeeping genes for qRT-PCR analysis in potato tubers under cold stress. Mol Breed 31(1):39–45
Reid KE, Olsson N, Schlosser J, Peng F, Lund ST (2006) An optimized grapevine RNA isolation procedure and statistical determination of reference genes for real-time RT-PCR during berry development. BMC Plant Biol 6:27
Ren GX, Yang XS, Yao Y (2015) Current situation of quinoa industry in China. Crops 5:1–5
Saad-allah KM, Youssef MS (2018) Phytochemical and genetic characterization of five quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) geno-types introduced to Egypt. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 24(4):617–629
Schmid H, Cohen CD, Henger A, Irrgang S, Schlöndorff D, Kretzler M (2003) Validation of endogenous controls for gene expression analysis in micro dissected human renal biopsies. Kidney Int 64:356–360
Shu K, Liu XD, Xie Q, He ZH (2016) Two faces of one seed: hormonal regulation of dormancy and germination. Mol Plant 9(1):34–45
Sinara A, Sarah MN, Osmundo B, Maria FG, Marcio AF (2010) Identification and evaluation of new reference genes in Gossypium hirsutum for accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data. BMC Plant Biol 10(1):49–60
Tu Z, Hao Z, Zhong W, Li H (2019) Identification of suitable reference genes for RT-qPCR assays in Liriodendron chinense. Forests 10:441
Vandesompele J, De PK, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van RN, De PA (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3:H34
Wang SB, Liu KW, Zhi L, Ge W, Liu JB, Pan BG, Wan HJ, Chen JF (2012) Evaluation of appropriate reference genes for gene expression studies in pepper by quantitative real-time PCR. Mol Breed 30(3):1393–1400
Wei LB, Miao HM, Zhao RH, Han XH, Zhang T, Zhang HY (2013) Identification and testing of reference genes for sesame gene expression analysis by quantitative real-time PCR. Planta 237(3):873–889
Xiao Z, Sun XB, Liu XQ, Li C, He LS, Chen SP, Su JL (2016) Selection of reliable reference genes for gene expression studies on Rhododendron molle. Front Plant Sci 7:1547–1552
Yang H, Liu J, Huang S, Guo T, Deng L, Hua W (2014a) Selection and evaluation of novel reference genes for quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) based on genome and transcriptome data in Brassica napus L. Gene 538:113–122
Yang Q, Yin J, Qi L, Yang F, Wang R, Li G (2014b) Reference gene selection for qRT-PCR in Caragana korshinskii Kom. under different stress conditions. Mol Biol Rep 41:2325–2334
Yu M, Liu D, Li YC, Sui C, Chen GD, Tang ZK, Yang CM, Hou DB, Wei JH (2018) Validation of reference genes for expression analysis in three Bupleurum species. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 33(1):154–161
Zhang X, Xu Z C, Xu J, Ji AJ, Luo HM, Song JY, Sun C, Hu YL, Chen SL (2016) Selection and validation of reference genes for normalization of quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR analysis in Poria cocos Wolf. Chin Med 11(1):1–17
Zhu PH, Ma YY, Zhu LZ, Chen Y, Li R, Ji KS (2019) Selection of Suitable Reference Genes in Pinus massoniana Lamb. Under Different Abiotic Stresses for qPCR Normalization. Forests 10(8):462–478
Zhuang HH, Fu YP, He W, Wang L, Wei YH (2015) Selection of appropriate reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR in Oxytropis ochrocephala Bunge using transcriptome datasets under abiotic stress treatments. Front Plant Sci 6:475–483
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all contributors to this research for their help. The research was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (32060401), Gansu Provincial Key Laboratory of Aridland Crop Science, Fostering Foundation for the Excellent Ph.D. Dissertation of Gansu Agricultural University [YB2021001].
Funding
The research was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 32060401), Fostering Foundation for the Excellent Ph.D. Dissertation of Gansu Agricultural University [YB2021001], Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province (21JR7RA808).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Data curation, XW; Funding acquisition, XW and CZ; Methodology, CZ, XW, and XZ; Project administration, XW; Resources, LH; Supervision, XZ and XW; Writing—original draft, BW; Writing—review and editing, XZ and XW.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Wang, B., Wang, X. et al. Screening of stable internal reference gene of Quinoa under hormone treatment and abiotic stress. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 27, 2459–2470 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-021-01094-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-021-01094-z