Abstract
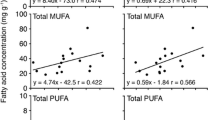
The present study provides the first comparative fatty acid profiling of the three Indian seabuckthorn species, collected from varying altitudes (2900–4300 masl) of Trans-Himalayas (Hippophae rhamnoides, H. tibetana) and Sikkim Himalayas (H. salicifolia) regions. Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis showed variability in fatty acid composition of different seabuckthorn populations. Sikkim populations showed higher (1.28–1.6 folds) palmitic acid than Trans-Himalayan populations which possess higher linoleic (1.3–1.5 folds) and linolenic (1.6–1.8 folds) acids. Interestingly, a strong altitudinal gradient associated positive correlation was observed with the degree of unsaturation and PUFA content while negative correlation was observed with saturated fatty acids content of different seabuckthorn populations. H. salicifolia collected from Sikkim showed healthy ω-6:ω-3 ratio (closer to 1:1) of functional lipids exhibiting its better nutraceutical potential than other commonly used seed oils. Interestingly, H. tibetana from Losar showed higher (5.81) degree of unsaturation than Sikkim populations (3.5) suggesting its better stress tolerance trait. Chemo-taxonomic diversity analysis also formed two broad clusters of Trans-Himalayan and Sikkim populations which correlated with earlier taxonomic studies.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alabdulkarim B, Bakeet ZAN, Arzoo S (2012) Role of some functional lipids in preventing diseases and promoting health. J King Saud Univ Sci 24:319–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2012.03.001
Bakht J, Bano A, Dominy P (2006) The role of abscisic acid and low temperature in chickpea (Cicer arietinum) cold tolerance. II. Effects on plasma membrane structure and function. J Exp Bot 57:3707–3715. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erl120
Barrero-Sicilia C, Silvestre S, Haslam RP, Michaelson LV (2017) Lipid remodelling: unravelling the response to cold stress in Arabidopsis and its extremophile relative Eutrema salsugineum. Plant Sci 263:194–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2017.07.017
Burčová Z, Kreps F, Schmidt Š, Jablonský M (2017) Composition of fatty acids and tocopherols in peels, seeds and leaves of Sea buckthorn. Acta Chim Slovaca 10:29–34. https://doi.org/10.1515/acs-2017-0005
Choudhary Kumar A, Sunojkumar P, Mishra G (2017) Phytochemistry fatty acid profiling and multivariate analysis in the genus Leucas reveals its nutritional, pharmaceutical and chemotaxonomic significance. Phytochemistry 143:72–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2017.07.007
Ding J, Ruan C, Guan Y, Krishna P (2018) Identification of microRNAs involved in lipid biosynthesis and seed size in developing sea buckthorn seeds using high-throughput sequencing. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-22464-w
Dolkar P, Dolkar D, Angmo S, Kumar B, Stobdan T (2017a) Variability in phenolics, flavonoids and antioxidants in Seabuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) seed from nine trans-Himalayan natural population. J Berry Res 7:109–116. https://doi.org/10.3233/JBR-170149
Dolkar P, Dolkar D, Kant A, Chaurasia OP, Stobdan T (2017b) Gender-specific seasonal pattern and altitudinal variation in freeze tolerance response of Seabuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.). J Berry Res 7:291–297. https://doi.org/10.3233/JBR-170165
Dolkar P, Dolkar D, Kant A, Chaurasia OP, Stobdan T (2019) Gender differences in phenotypic and adaptive response of Seabuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) along an altitudinal gradient in trans-Himalaya. J Berry Res 9:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3233/JBR-170294
Dulf FV (2012) Fatty acids in berry lipids of six sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L., subspecies carpatica) cultivars grown in Romania. Chem Cent J 6:1–12
Erasmus U (1993) Fats that heal, fats that kill: the complete guide to fats, oils, cholesterol, and human health. In: Health & fitness. Summertown, Tennessee
Falcone DL, Ogas JP, Somerville CR (2004) Regulation of membrane fatty acid composition by temperature in composition. BMC Plant Biol 4:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-4-17
Fatima T, Snyder CL, Schroeder WR et al (2013) Fatty acid composition of developing sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) berry and the transcriptome of the mature seed. PlosOne 7:e34099. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0034099
Graham SA, Coelho GP, Murad AM et al (2016) Patterns of fatty acid composition in seed oils of Cuphea, with new records from Brazil and Mexico. Ind Crop Prod 87:379–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.04.008
Gulfraz M, Kasuar R, Arshad G, Mehmood S et al (2009) Isolation and characterization of edible oil from wild olive. Afr J Biotechnol 8:3734–3738
Gupta R, Deswal R (2012) Low temperature stress modulated secretome analysis and purification of antifreeze protein from Hippophae rhamnoides, a Himalayan wonder plant. J Proteome Res 11:2684–2696. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr200944z
Hou G, Ablett GR, Pauls KP, Rajcan I (2006) Environment effects on fatty acid levels in soybean oil. J Am Oil Chem Soc 83:759–763
Johansson A, Laine T, Linna MM, Kallio H (2000) Variability in oil content and fatty acid composition in wild northern currants. Eur Food Res Technol 211:277–283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002170000151
Kaushal M, Sharma PC (2011) Nutritional and antimicrobial property of seabuckthorn (Hippophae sp.) seed oil. J Sci Ind Res (India) 70:1033–1036
Raina SN, Jain S, Sehgal D et al (2011) Diversity and relationships of multipurpose seabuckthorn (Hippophae L.) germplasm from the Indian Himalayas as assessed by AFLP and SAMPL markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 59:1033–1053. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-011-9742-1
Ranjith A, Kumar KS, Venugopalan VV (2006) Fatty acids, tocols, and carotenoids in pulp oil of three sea buckthorn species (Hippophae rhamnoides, H. salicifolia, and H. tibetana). JAOCS 83:359–364
Saikia M, Handique PJ (2013) Antioxidant and antibacterial activity of leaf, bark, pulp and seed extracts of seabuckthorn (Hippophae salicifolia D. Don) of Sikkim Himalayas. J Med Plant Res 7:1330–1338. https://doi.org/10.5897/JMPR12.1123
Sakamoto T, Murata N (2002) Regulation of the desaturation of fatty acids and its role in tolerance to cold and salt stress. Curr Opin Microbiol 5:206–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-5274(02)00306-5
Sharma B, Deswal R (2019) Ecophysiolomic analysis of stress tolerant Himalayan shrub Hipppophae rhamnoides shows multifactorial acclimation strategies induced by diverse environmental conditions. Physiol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12942
Shukla S, Hegde S, Kumar A, Chaudhary G (2017) Fatty acid composition and antibacterial potential of Cassia tora (leaves and stem) collected from different geographic areas of India. J Food Drug Anal 26:107–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2016.12.010
Stobdan T, Dolkar P, Chaurasia OP, Kumar B (2017) Seabuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) in trans-Himalayan. Def Life Sci J 2:46–53
Suryakumar G, Gupta A (2011) Medicinal and therapeutic potential of Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.). J Ethnopharmacol 138:268–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2011.09.024
Upchurch RG (2008) Fatty acid unsaturation, mobilization, and regulation in the response of plants to stress. Biotechnol Lett 30:967–977. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-008-9639z
Yang B, Kallio HP (2001) Fatty acid composition of lipids in sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) berries of different origins. J Agric Food Chem 49:1939–1947. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf001059s
Zheng G, Tian B, Zhang F et al (2014) Plant adaptation to frequent alterations between high and low temperatures: remodeling of membrane lipids and maintenance of unsaturation levels. Plant Cell Environ 34:1431–1442. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2011.02341.x.Plant
Zheng L, Shi L, Zhao C et al (2017) Fatty acid, phytochemical, oxidative stability and in vitro antioxidant property of sea buckthorn (Hippophaë rhamnoides L.) oils extracted by supercritical and subcritical technologies. LWT Food Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2017.08.042
Zielińska A, Nowak I (2017) Abundance of active ingredients in sea-buckthorn oil. Lipids Health Dis 16:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-017-0469-7
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by financial assistance from Department of Biotechnology (IBSD/A1/P(PH-2)/4), Government of India to RD. BS is thankful to UGC and DBT for providing fellowship. Authors are thankful to Dr. Girish Mishra for kindly extending GC–MS facility for FAMEs analysis and critical suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, B., Arora, S., Sahoo, D. et al. Comparative fatty acid profiling of Indian seabuckthorn showed altitudinal gradient dependent species-specific variations. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26, 41–49 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-019-00720-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-019-00720-1