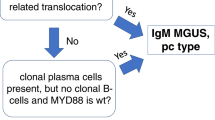
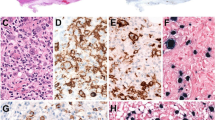
Abstract
Posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder is an extremely fatal complication arising in transplant recipients as a side effect of immunosuppression. PTLDs are seen after both solid organ and hematopoietic stem cell transplants though the incidence is much higher in the former. Primary Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) infection or reactivation due to a state of immune dysregulation along with intensity of immunosuppression used are of paramount importance in pathogenesis of PTLD. EBV associated PTLDs occur early in the post transplant period whereas late onset lymphomas are usually EBV negative. The uncontrolled B cell proliferation can create a spectrum of histological patterns from nondestructive lesions to destructive polymorphic or more aggressive monomorphic PTLDs. Early detection of seropositivity by serial monitoring in the recipient can prevent PTLD development by starting pre-emptive therapy. The mainstay treatment in established cases remains reduction of immunosuppression. Chemotherapeutic and immunomodulatory agents are added sequentially based on the type of PTLD and based on its response to initial therapy. Despite various treatment options available, the morbidity remains high and achieving state of disease remission without causing graft rejection can be quite challenging. Hence, a better understanding in pathobiology of EBV+ versus EBV− PTLDS may help prevent lymphomagenesis in transplant recipients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doak PB, Montgomerie JZ, North JD, Smith F (1968) Reticulum cell sarcoma after renal homotransplantation and azathioprine and prednisone therapy. Br Med J 4:746–748
Penn I, Hammond W, Brettschneider L, Starzl TE (1969) Malignant lymphomas in transplantation patients. Transpl Proc 1:106–112
Ghobrial IM, Habermann TM, Macon WR et al (2005) Differences between early and late posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders in solid organ transplant patients: are they two different diseases? Transplantation 79:244–247
Johnson LR, Nalesnik MA, Swerdlow SH (2006) Impact of Epstein–Barr virus in monomorphic B cell posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders: a histogenetic study. Am J Surg Pathol 30(12):1604–1612
Nourse JP, Jones K, Gandhi MK (2011) Epstein–Barr Virus-related post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders: pathogenetic insights for targeted therapy. Am J Transpl 11(5):888–895
Knight JS, Tsodikov A, Cibrik DM, Ross CW, Kaminski MS, Blayney DW (2009) Lymphoma after solid organ transplantation: risk, response to therapy, and survival at a transplantation center. J Clin Oncol 27(20):3354–3362
Taylor AL, Marcus R, Bradley JA (2005) Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders (PTLD) after solid organ transplantation. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 56:155–167
Cockfield SM (2001) Identifying the patient at risk for post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder. Transpl Infect Dis 3:70–78
Bates WD, Gray DW, Dada MA et al (2003) Lymphoproliferative disorders in oxford renal transplant recipients. J Clin Pathol 56:439–446
Leblond V, Dhedin N, Mamzer Bruneel MF, Choquet S, Hermine O, Porcher R et al (2001) Identification of prognostic factors in 61 patients with posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorders. J Clin Oncol 19(3):772–778
Ghobrial IM, Habermann TM, Maurer MJ, Geyer SM, Ristow KM, Larson TS et al (2005) Prognostic analysis for survival in adult solid organ transplant recipients with post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorders. J Clin Oncol 23(30):7574–7582
Dotti G, Fiocchi R, Motta T, Mammana C, Gotti E, Riva S et al (2002) Lymphomas occurring late after solid-organ transplantation: influence of treatment on the clinical outcome. Transplantation 74(8):1095–1102
Buell JF, Gross TG, Hanaway MJ, Trofe J, Roy-Chaudhury P, First MR et al (2005) Posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder: significance of central nervous system involvement. Transpl Proc 37(2):954–955
Penn I, Porat G (1995) Central nervous system lymphomas in organ allograft recipients. Transplantation 59(2):240–244
Cavaliere R, Petroni G, Lopes MB, Schiff D, International Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma Collaborative G (2010) Primary central nervous system post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorder: an International Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma Collaborative Group report. Cancer 116(4):863–870
Boubenider S, Hiesse C, Goupy C, Kriaa F, Marchand S, Charpentier B (1997) Incidence and consequences of post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorders. J Nephrol 10(3):136–145
Caillard S, Lelong C, Pessione F, Moulin B, French PTLD Working Group (2006) Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders occurring after renal transplantation in adults: report of 230 cases from the French registry. Am J Transpl 6:2735–2742
Oton AB, Wang H, Leleu X et al (2008) Clinical and pathological prognostic markers for survival in adult patients with post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders in solid transplant. Leuk Lymphoma 49:1738–1744
Kinch A et al (2014) Donor or recipient origin of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders following solid organ transplantation. Am J Transpl 14:2838–2845
Sanz J et al (2014) EBV-associated post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder after umbilical cord blood transplantation in adults with hematological diseases. Bone Marrow Transpl 49:397–402
Doycheva I, Amer S, Watt KD (2016) De novo malignancies after transplantation: risk and surveillance strategies. Med Clin North Am 100(3):551–567
Euvrard S, Kanitakis J, Claudy A (2003) Skin cancers after organ transplantation. N Engl J Med 348(17):1681–1691
Mihalov ML, Gattuso P, Abraham K, Holmes EW, Reddy V (1996) Incidence of post-transplant malignancy among 674 solid-organ-transplant recipients at a single center. Clin Transpl 10(3):248–255
Sundin M, Le Blanc K, Ringden O et al (2006) The role of HLA mismatch, splenectomy and recipient Epstein–Barr virus seronegativity as risk factors in post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica 91:1059–1067
Landgren O, Gilbert ES, Rizzo JD et al (2009) Risk factors for lymphoproliferative disorders after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood 113:4992–5001
Juvonen E, Aalto SM, Tarkkanen J et al (2003) High incidence of PTLD after non-T-cell-depleted allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation as a consequence of intensive immunosuppressive treatment. Bone Marrow Transpl 32:97–102
Trofe J et al (2005) Analysis of factors that influence survival with post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder in renal transplant recipients: the Israel Penn International Transplant Tumor Registry experience. Am J Transpl 5:775–780
Sampaio MS, Cho YW, Shah T, Bunnapradist S, Hutchinson I (2012) Impact of Epstein–Barr virus donor and recipient serostatus on the incidence of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder in kidney transplant recipients. Nephrol Dial Transpl 27:2971–2979
Allen U, Hébert D, Moore D, Dror Y, Wasfy S, the Canadian PTLD Survey Group—1998 (2001) Epstein–Barr virus-related post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease in solid organ transplant recipient, 1988–97: a Canadian multi-centre experience. Pediatr Transpl 5:198–203
Opelz G, Dohler B (2004) Lymphomas after solid organ transplantation: a collaborative transplant study report. Am J Transpl 4(2):222–230
Lange A, Klimczak A, Dlubek D, Dybko J (2003) B-cell lymphoproliferative syndrome and peripheral blood CD20+ cells expansion after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: association with fludarabine and anti-thymocyte globulin containing conditioning regimen. Transpl Proc 35(8):3093–3095
Schubert S, Renner C, Hammer M et al (2008) Relationship of immunosuppression to Epstein–Barr viral load and lymphoproliferative disease in pediatric heart transplant patients. J Heart Lung Transpl 27(1):100–105
Caillard S, Dharnidharka V, Agodoa L, Bohen E, Abbott K (2005) Posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders after renal transplantation in the United States in era of modern immunosuppression. Transplantation 80(9):1233–1243
Duvoux C, Pageaux GP, Vanlemmens C et al (2002) Risk factors for lymphoproliferative disorders after liver transplantation in adults: an analysis of 480 patients. Transplantation 74(8):1103–1109
Opelz G, Naujokat C, Daniel V, Terness P, Dohler B (2006) Disassociation between risk of graft loss and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma with induction agents in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation 81(9):1227–1233
Krams SM, Martinez OM (2008) Epstein–Barr virus, rapamycin, and host immune responses. Curr Opin Organ Transpl 13(6):563–568
Cao S, Cox KL, Berquist W et al (1999) Long-term outcomes in pediatric liver recipients: comparison between cyclosporin A and tacrolimus. Pediatr Transpl 3(1):22–26
Uhlin M et al (2014) Risk factors for Epstein–Barr virus-related post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica 99:346–352
Babcock GJ, Hochberg D, Thorley-Lawson AD (2000) The expression pattern of Epstein–Barr virus latent genes in vivo is dependent upon the differentiation stage of the infected B cell. Immunity 13:497–506
Langerak AW, Moreau E, van Gastel-Mol EJ, van der Burg M, van Dongen JJ (2002) Detection of clonal EBV episomes in lymphoproliferations as a diagnostic tool. Leukemia 16:1572–1573
Middeldorp JM, Brink AA, van den Brule AJ, Meijer CJ (2003) Pathogenic roles for Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) gene products in EBV-associated proliferative disorders. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 45:1–36
Delecluse HJ, Bartnizke S, Hammerschmidt W, Bullerdiek J, Bornkamm GW (1993) Episomal and integrated copies of Epstein–Barr virus coexist in Burkitt lymphoma cell lines. J Virol 67:1292–1299
Ohshima K, Suzumiya J, Kanda M, Kato A, Kikuchi M (1998) Integrated and episomal forms of Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) in EBV associated disease. Cancer Lett 122:43–50
Reisinger J, Rumpler S, Lion T, Ambros PF (2006) Visualization of episomal and integrated Epstein–Barr virus DNA by fiber fluorescence in situ hybridization. Int J Cancer 118:1603–1608
Chaganti S et al (2009) Epstein–Barr virus colonization of tonsillar and peripheral blood B-cell subsets in primary infection and persistence. Blood 113:6372–6381
Petrara MR, Giunco S, Serraino D, Dolcetti R, De Rossi A (2015) Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders: from epidemiology to pathogenesis-driven treatment. Cancer Lett 369(1):37–44
Luskin MR, Heil DS, Tan KS et al (2015) The impact of EBV status on characteristics and outcomes of posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorder. Am J Transpl 15(10):2665–2673
Shimizu N, Tanabe-Tochikura A, Kuroiwa Y, Takada K (1994) Isolation of Epstein–Barr virus (EBV)-negative cell clones from the EBV-positive Burkitt’s lymphoma (BL) line Akata: malignant phenotypes of BL cells are dependent on EBV. J Virol 68(9):6069–6073
Ambinder RF (2000) Gammaherpesviruses and “hit-and-run” oncogenesis. Am J Pathol 156(1):1–3
Capello D, Rossi D, Gaidano G (2005) Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders: molecular basis of disease histogenesis and pathogenesis. Hematol Oncol 23(2):61–67
Nelson BP, Nalesnik MA, Bahler DW, Locker J, Fung JJ, Swerdlow SH (2000) Epstein–Barr virus-negative post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders: a distinct entity? Am J Surg Pathol 24(3):375–385
Rinaldi A, Capello D, Scandurra M et al (2010) Single nucleotide polymorphism-arrays provide new insights in the pathogenesis of post-transplant diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol 149(4):569–577
Swerdlow SH (2017) World Health Organization. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 5th, Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer. International Agency for Research on Cancer
Parker A, Bowles K, Bradley JA, Emery V, Featherstone C, Gupte G et al (2010) Diagnosis of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder in solid organ transplant recipients—BCSH and BTS Guidelines. Br J Haematol 149(5):675–692
Carpentier L, Tapiero B, Alvarez F et al (2003) Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) early-antigen serologic testing in conjunction with peripheral blood EBV DNA load as a marker for risk of posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disease. J Infect Dis 188:1853–1864
Young L, Alfieri C, Hennessy K et al (1989) Expression of Epstein–Barr virus transformation-associated genes in tissues of patients with EBV lymphoproliferative disease. N EngI J Med 321:1080–1085
Fanaian N, Cohen C, Waldrop S et al (2009) EBER: automated in situ hybridization (ISH) vs. manual ISH and immunohistochemistry (IHC) for detection of EBV in pediatric lymphoproliferative disorders. Pediatr Dev Pathol 12:195–199
Hayden RT, Hokanson KM, Pounds SB et al (2008) Multicenter comparison of different real-time PCR assays for quantitative detection of Epstein–Barr virus. J Clin Microbiol 46:157–163
Preiksaitis JK, Pang XL, Fox JD et al (2009) Inter-laboratory comparison of Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) viral load assays. Am J Transpl 9:269–279
Hakim H, Gibson C, Pan J et al (2007) Comparison of various blood compartments and reporting units for the detection and quantification of Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) in peripheral blood. J Clin Microbiol 45:2151–2155
De Paoli P, Pratesi C, Bortolin MT (2007) The Epstein Barr virus DNA levels as a tumor marker in EBV-associated cancers. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 133:809–815
Ghobrial IM, Habermann TM, Ristow KM, Ansell SM, Macon W, Geyer SM et al (2005) Prognostic factors in patients with post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders (PTLD) in the rituximab era. Leuk Lymphoma 46(2):191–196
Swinnen LJ, Mullen GM, Carr TJ, Costanzo MR, Fisher RI (1995) Aggressive treatment for postcardiac transplant lymphoproliferation. Blood 86(9):3333–3340
Reshef R, Vardhanabhuti S, Luskin MR, Heitjan DF, Hadjiliadis D, Goral S et al (2011) Reduction of immunosuppression as initial therapy for posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorder. Am J Transpl 11(2):336–347
Evens AM, David KA, Helenowski I, Nelson B, Kaufman D, Kircher SM et al (2010) Multicenter analysis of 80 solid organ transplantation recipients with post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disease: outcomes and prognostic factors in the modern era. J Clin Oncol 28(6):1038–1046
Trappe R, Oertel S, Leblond V, Mollee P, Sender M, Reinke P et al (2012) Sequential treatment with rituximab followed by CHOP chemotherapy in adult B cell post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD): the prospective international multicentre phase 2 PTLD-1 trial. Lancet Oncol 13(2):196–206
Ramanarayanan Jeyanthi, Krishnan Ganapathy S, Czuczman Myron S, Hernandez-Ilizaliturri Francisco J (2007) Efficacy and safety of rituximab in post transplant lymphoproliferative disorders (PTLD): pooled analysis and review of literature. Blood 110:1084
Evens AM, David KA, Helenowski I et al (2010) Multicenter analysis of 80 solid organ transplantation recipients with post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disease: outcomes and prognostic factors in the modern era. J Clin Oncol 28:1038–1046
Haque T, Wilkie GM, Jones MM, Higgins CD, Urquhart G, Wingate P et al (2007) Allogeneic cytotoxic T cell therapy for EBV-positive posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disease: results of a phase 2 multicenter clinical trial. Blood 110(4):1123–1131
Rooney CM, Smith CA, Ng CY, Loftin SK, Sixbey JW, Gan Y et al (1998) Infusion of cytotoxic T cells for the prevention and treatment of Epstein–Barr virus-induced lymphoma in allogeneic transplant recipients. Blood 92(5):1549–1555
Gustafsson A, Levitsky V, Zou JZ, Frisan T, Dalianis T, Ljungman P et al (2000) Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) load in bone marrow transplant recipients at risk to develop posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease: prophylactic infusion of EBV-specific cytotoxic T cells. Blood 95(3):807–814
Gottschalk Stephen, Rooney Cliona (2015) Adoptive T-cell immunotherapy. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 391:427–454
Haddad E, Paczesny S, Leblond V, Seigneurin JM, Stern M, Achkar A et al (2001) Treatment of B-lymphoproliferative disorder with a monoclonal anti-interleukin-6 antibody in 12 patients: a multicenter phase 1–2 clinical trial. Blood 97(6):1590–1597
Davis CL, Wood BL, Sabath DE, Joseph JS, Stehman-Breen C, Broudy VC (1998) Interferon-alpha treatment of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder in recipients of solid organ transplants. Transplantation 66(12):1770–1779
Komrokji RS, Oliva JL, Zand M, Felgar R, Abboud CN (2005) Mini-BEAM and autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant for treatment of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders. Am J Hematol 79(3):211–215
Williams KM, Higman MA, Chen AR, Schwartz CL, Wharam M, Colombani P et al (2008) Successful treatment of a child with late-onset T cell post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder/lymphoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer 50(3):667–670
Cavaliere R, Petroni G, Lopes MB, Schiff D, The International Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma Collaborative Group (2010) Primary central nervous system post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorder. Cancer 116:863–870
Patrick A, Wee A, Hedderman A, Wilson D, Weiss J, Govani M (2011) High-dose intravenous rituximab for multifocal, monomorphic primary central nervous system posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder. J Neuro Oncol 103:739–743
Daan D, Habermann TM (2018) Post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorders in adults. N Engl J Med 378:549–562
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, D., Mendonca, S., Chakraborty, S. et al. Post Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus 36, 229–237 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-019-01182-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-019-01182-x