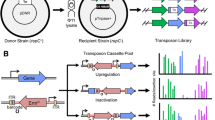
Abstract
Transposon mutant libraries are an important resource to study bacterial metabolism and pathogenesis. The fitness analysis of mutants in the libraries under various growth conditions provides important clues to study the physiology and biogenesis of structural components of a bacterial cell. A transposon library in conjunction with next-generation sequencing techniques, collectively named transposon sequencing (Tn-seq), enables high-throughput genome profiling and synthetic lethality analysis. Tn-seq has also been used to identify essential genes and to study the mode of action of antibacterials. To construct a high-density transposon mutant library, an efficient delivery system for transposition in a model bacterium is essential. Here, I describe a detailed protocol for generating a high-density phage-based transposon mutant library in a Staphylococcus aureus strain, and this protocol is readily applicable to other S. aureus strains including USA300 and MW2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badarinarayana, V., Estep, P.W.3rd, Shendure, J., Edwards, J., Tavazoie, S., Lam, F., and Church, G.M. 2001. Selection analyses of insertional mutants using subgenic-resolution arrays. Nat. Biotechnol. 19, 1060–1065.
Carver, T., Harris, S.R., Berriman, M., Parkhill, J., and McQuillan, J.A. 2012. Artemis: an integrated platform for visualization and analysis of high-throughput sequence-based experimental data. Bioinformatics 28, 464–469.
Chao, M.C., Abel, S., Davis, B.M., and Waldor, M.K. 2016. The design and analysis of transposon insertion sequencing experiments. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 14, 119–128.
Chao, M.C., Pritchard, J.R., Zhang, Y.J., Rubin, E.J., Livny, J., Davis, B.M., and Waldor, M.K. 2013. High-resolution definition of the Vibrio cholerae essential gene set with hidden Markov model-based analyses of transposon-insertion sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 41, 9033–9048.
Cho, H. 2021. Transposon insertion site sequencing (TIS) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Microbiol. 59, 1067–1074.
Coe, K.A., Lee, W., Stone, M.C., Komazin-Meredith, G., Meredith, T.C., Grad, Y.H., and Walker, S. 2019. Multi-strain Tn-Seq reveals common daptomycin resistance determinants in Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS Pathog. 15, e1007862.
Fey, P.D., Endres, J.L., Yajjala, V.K., Widhelm, T.J., Boissy, R.J., Bose, J.L., and Bayles, K.W. 2013. A genetic resource for rapid and comprehensive phenotype screening of nonessential Staphylococcus aureus genes. mBio 4, e00537–12.
Goodman, A.L., McNulty, N.P., Zhao, Y., Leip, D., Mitra, R.D., Lozupone, C.A., Knight, R., and Gordon, J.I. 2009. Identifying genetic determinants needed to establish a human gut symbiont in its habitat. Cell Host Microbe 6, 279–289.
Karash, S. and Yahr, T.L. 2022. Genome-wide identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa genes important for desiccation tolerance on inanimate surfaces. mSystems 7, e0011422.
Koo, B.M., Kritikos, G., Farelli, J.D., Todor, H., Tong, K., Kimsey, H., Wapinski, I., Galardini, M., Cabal, A., Peters, J.M., et al. 2017. Construction and analysis of two genome-scale deletion libraries for Bacillus subtilis. Cell Syst. 4, 291–305.
Lampe, D.J., Akerley, B.J., Rubin, E.J., Mekalanos, J.J., and Robertson, H.M. 1999. Hyperactive transposase mutants of the Himar1 mariner transposon. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 11428–11433.
Langridge, G.C., Phan, M.D., Turner, D.J., Perkins, T.T., Parts, L., Haase, J., Charles, I., Maskell, D.J., Peters, S.E., Dougan, G., et al. 2009. Simultaneous assay of every Salmonella Typhi gene using one million transposon mutants. Genome Res. 19, 2308–2316.
Lee, W., Do, T., Zhang, G., Kahne, D., Meredith, T.C., and Walker, S. 2018. Antibiotic combinations that enable one-step, targeted mutagenesis of chromosomal genes. ACS Infect. Dis. 4, 1007–1018.
Lee, W., VanderVen, B.C., Fahey, R.J., and Russell, D.G. 2013. Intracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis exploits host-derived fatty acids to limit metabolic stress. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 6788–6800.
Murry, J.P., Sassetti, C.M., Lane, J.M., Xie, Z., and Rubin, E.J. 2008. Transposon site hybridization in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. In Osterman, A.L. and Gerdes, S.Y. (eds) Microbial Gene Essentiality: Protocols and Bioinformatics. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol. 416, pp. 45–59. Humana Press, Totowa, New Jersey, USA.
Nazarova, E.V., Montague, C.R., La, T., Wilburn, K.M., Sukumar, N., Lee, W., Caldwell, S., Russell, D.G., and VanderVen, B.C. 2017. Rv3723/LucA coordinates fatty acid and cholesterol uptake in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. eLife 6, e26969.
Pasquina, L., Santa Maria, J.P.Jr., McKay Wood, B., Moussa, S.H., Matano, L.M., Santiago, M., Martin, S.E.S., Lee, W., Meredith, T.C., and Walker, S. 2016. A synthetic lethal approach for compound and target identification in Staphylococcus aureus. Nat. Chem. Biol. 12, 40–45.
Price, M.N., Wetmore, K.M., Waters, R.J., Callaghan, M., Ray, J., Liu, H., Kuehl, J.V., Melnyk, R.A., Lamson, J.S., Suh, Y., et al. 2018. Mutant phenotypes for thousands of bacterial genes of unknown function. Nature 557, 503–509.
Reznikoff, W.S. 2008. Transposon Tn5. Annu. Rev. Genet. 42, 269–286.
Rubin, E.J., Akerley, B.J., Novik, V.N., Lampe, D.J., Husson, R.N., and Mekalanos, J.J. 1999. In vivo transposition of mariner-based elements in enteric bacteria and mycobacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 1645–1650.
Salama, N.R., Shepherd, B., and Falkow, S. 2004. Global transposon mutagenesis and essential gene analysis of Helicobacter pylori. J. Bacteriol. 186, 7926–7935.
Santa Maria, J.P.Jr., Sadaka, A., Moussa, S.H., Brown, S., Zhang, Y.J., Rubin, E.J., Gilmore, M.S., and Walker, S. 2014. Compound-gene interaction mapping reveals distinct roles for Staphylococcus aureus teichoic acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111, 12510–12515.
Santiago, M., Lee, W., Fayad, A.A., Coe, K.A., Rajagopal, M., Do, T., Hennessen, F., Srisuknimit, V., Müller, R., Meredith, T.C., et al. 2018. Genome-wide mutant profiling predicts the mechanism of a Lipid II binding antibiotic. Nat. Chem. Biol. 14, 601–608.
Santiago, M., Matano, L.M., Moussa, S.H., Gilmore, M.S., Walker, S., and Meredith, T.C. 2015. A new platform for ultra-high density Staphylococcus aureus transposon libraries. BMC Genomics 16, 252.
Sassetti, C.M., Boyd, D.H., and Rubin, E.J. 2001. Comprehensive identification of conditionally essential genes in mycobacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 12712–12717.
Siegrist, M.S. and Rubin, E.J. 2009. Phage transposon mutagenesis. In Parish, T. and Brown, A. (eds) Mycobacteria Protocols. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 465, pp. 311–323. Humana Press, Totowa, New Jersey, USA.
Stryjewski, M.E. and Corey, G.R. 2014. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: an evolving pathogen. Clin. Infect. Dis. 58, S10–S19.
van Opijnen, T., Bodi, K.L., and Camilli, A. 2009. Tn-seq: high-throughput parallel sequencing for fitness and genetic interaction studies in microorganisms. Nat. Methods 6, 767–772.
van Opijnen, T., Lazinski, D.W., and Camilli, A. 2014. Genome-wide fitness and genetic interactions determined by Tn-seq, a high-throughput massively parallel sequencing method for microorganisms. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 106, 7.16.1–7.16.24.
Wang, H., Claveau, D., Vaillancourt, J.P., Roemer, T., and Meredith, T.C. 2011. High-frequency transposition for determining antibacterial mode of action. Nat. Chem. Biol. 7, 720–729.
Zhang, Y.J., Ioerger, T.R., Huttenhower, C., Long, J.E., Sassetti, C.M., Sacchettini, J.C., and Rubin, E.J. 2012. Global assessment of genomic regions required for growth in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PLoS Pathog. 8, e1002946.
Acknowledgements
We thank all Wonsik Lee’s lab members for discussion and comments. This work was supported by a grant from the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea, funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (grant numbers NRF-2020M3A9H5104234 and NRF-2020R1C1C1014695).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, W. Construction of high-density transposon mutant library of Staphylococcus aureus using bacteriophage ϕ11. J Microbiol. 60, 1123–1129 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-022-2476-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-022-2476-2