Abstract
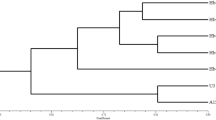
Cauliflower mushroom (Sparassis latifolia or S. crispa) is popular for food and medicine. Importance of new varieties of Sparassis was raised and studied widely by protection system of UPOV. In this study, 10 crossbred strains of Sparassis latifolia that specifically expressed distinctive features during basidiocarp formation and mycelium growth were applied to sawdust medium inoculated with S. latifolia mycelia. The 10 crossbred strains were divided into 3 groups on the basis of morphological (size of marginal wave and basidiocarp color) and genetic characteristics. Each phenotype of the parent and crossbred strains represented 3 marginal wave-sizes (large, medium, and small) and 3 color notations (NN155D, 163C, and 8D). Our result suggests that morphological characteristics of cauliflower mushroom can be affected by various environmental and genetic stimuli under artificial conditions such as crossbreed. Also this research showed genetic differences among breeding isolates and their morphological characteristics were correlated with the molecular data within parent and crossed strain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burdsall, H.H. Jr. and Miller, O.K. Jr. 1988a. Type studies and nomenclatural considerations in the genus Sparassis. Mycotaxon 31, 199–206.
Burdsall, H.H. Jr. and Miller, O.K. Jr. 1988b. Neotypification of Sparassis crispa. Mycotaxon 31, 591–593.
Dai, Y.C., Wang, Z., Binder, M., and Hibbett, D.S. 2006. Phylogeny and a new species of Sparassis (Polyporales, Basidiomycota): evidence from mitochondrial atp6, nuclear rDNA and rpb2 genes. Mycologia 98, 584–592.
Desjardin, D.E., Wang, Z., Binder, M., and Hibbett, D.S. 2004. Sparassis cystidiosa sp. nov. from Thailand is described using morphological and molecular data. Mycologia 96, 1010–1014.
Harada, T., Miura, N.N., Adachi, Y., Nakajima, M., Yadomae, T., and Ohno, N. 2002. IFN-γ introduction by SCG, 1, 3-β-D-glucan from Sparassis crispa, in DBA/2 mice in vitro. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 22, 1227–1239.
Jordens, R. 2005. Progress of plant variety protection based on the International Convention for the Protection of New Varieties of Plants (UPOV Convention). World Patent Informat. 27, 232–243.
Jukes, T.H. and Cantor, C.R. 1969. Evolution of protein molecules. In Munro, H.N. (ed.), Mammalian Protein Metabolism, pp. 21–132, Academic Press, New York, N.Y., USA.
Kurosumi, A., Kobayasi, F., Mtui, G., and Nakamura, Y. 2006. Development of optimal culture method of Sparassis crispa mycelia and a new extraction method of antineoplastic constituent. Biochem. Engineer. J. 30, 109–113.
Lee, S.B. and Taylor, J.W. 1990. Isolation of DNA from fungal mycelia and single spores, pp. 282–287. In Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J., and White, T.J. (eds.). PCR protocols. Academic Press. San Diego, California, USA.
Park, H., Lee, B.H., Oh, D.S., Ka, K.H., Bak, W.C., and Lee, H.J. 2005. Cultivation of cauliflower mushroom (Sparassis crispa) using coniferous sawdust-based media with barley flours. Kor. J. Forest Energy 24, 31–36.
Park, H., Ryu, S.R., and Ka, K.H. 2011. Cultivation of Sparassis crispa on several kinds of medium density and particle size of sawdust-based medium made of Larix kaempferi. Mokchae Konghak 39, 68–74.
Ryoo, R., Sou, H.D., Ka, K.H., and Park, H. 2013. Phylogenetic relationships of Korean Sparassis latifolia based on morphological and ITS rDNA characteristics. J. Microbiol. 51, 43–48.
Ryu, S.R., Ka, K.H., Park, H., Bak, W.C., and Lee, B.H. 2009. Cultivation characteristics of Sparassis crispa strains using sawdust medium of Larix kaempferi. Kor. J. Mycol. 37, 49–54.
Tada, R., Harada, T., Nagi-Miura, N., Adachi, Y., Nakajima, M., Yadomae, T., and Ohno, N. 2007. NMR characterization of the structure of a β-(1→3)-D-glucan isolate from cultured fruit bodies of Sparassis crispa. Carbohydrate Res. 342, 2611–2618.
Tamura, K., Peterson, D., Peterson, N., Stecher, G., Nei, M., and Kumar, S. 2011. MEGA5: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis using Maximum Likelihood, Evolutionary Distance, and Maximum Parsimony Methods. Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Uhart, M. and Albertó, E. 2009. Mating tests in Agrocybe cylindracea sensu lato. Recognition of Agrocybe wrightii as a novel species. Mycol. Progress 8, 337–349.
Wang, Z., Binder, M., Dai, Y.C., and Hibbett, D.S. 2004. Phylogenetic relationships of Sparassis inferred from nuclear and mitochondrial ribosomal DNA and RNA polymerase sequences. Mycologia 96, 1015–1029.
Williams, J.G., Kubelik, A.R., Livak, K.J., Rafalski, J.A., and Tingey, S.V. 1990. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 18, 6531–6535.
Woodward, S., Sultan, H.Y., Barrett, D.K., and Pearce, R.B. 1993. Two new antifungal metabolites produced by Sparassis crispa in culture and in decayed trees. J. Gen. Microbiol. 139, 153–159.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sou, HD., Ryoo, R., Ryu, SR. et al. Morphological and genetic characteristics of newly crossbred cauliflower mushroom (Sparassis latifolia). J Microbiol. 51, 552–557 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-013-2666-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-013-2666-z