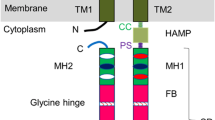
Abstract
Using yeast two-hybrid assay, we investigated protein-protein interactions between all orthologous histidine kinase (HK)/response regulator (RR) pairs of M. tuberculosis H37Rv and identified potential protein-protein interactions between a noncognate HK/RR pair, DosT/NarL. The protein interaction between DosT and NarL was verified by phosphotransfer reaction from DosT to NarL. Furthermore, we found that the DosT and DosS HKs, which share considerable sequence similarities to each other and form a two-component system with the DosR RR, have different cross-interaction capabilities with NarL: DosT interacted with NarL, while DosS did not. The dimerization domains of DosT and DosS were shown to be sufficient to confer specificity for DosR, and the different cross-interaction abilities of DosS and DosT with NarL were demonstrated to be attributable to variations in the amino acid sequences of the α2-helices of their dimerization domains.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhattacharya, M., Biswas, A., and Das, A.K. 2010. Interaction analysis of TcrX/Y two component system from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochimie92, 263–272.
Casino, P., Rubio, V., and Marina, A. 2009. Structural insight into partner specificity and phosphoryl transfer in two-component signal transduction. Cell139, 325–336.
Cho, H.Y., Cho, H.J., Kim, Y.M., Oh, J.I., and Kang, B.S. 2009. Structural insight into the heme-based redox sensing by DosS from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Biol. Chem.284, 13057–13067.
Dasgupta, N., Kapur, V., Singh, K.K., Das, T.K., Sachdeva, S., Jyothisri, K., and Tyagi, J.S. 2000. Characterization of a twocomponent system, devR-devS, of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuber Lung Dis.80, 141–159.
Drepper, T., Wiethaus, J., Giaourakis, D., Gross, S., Schubert, B., Vogt, M., Wiencek, Y., McEwan, A.G., and Masepohl, B. 2006. Cross-talk towards the response regulator NtrC controlling nitrogen metabolism in Rhodobacter capsulatus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett.258, 250–256.
Dutta, R., Qin, L., and Inouye, M. 1999. Histidine kinases: diversity of domain organization. Mol. Microbiol.34, 633–640.
Ewann, F., Locht, C., and Supply, P. 2004. Intracellular autoregulation of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis PrrA response regulator. Microbiology150, 241–246.
Gupta, S., Sinha, A., and Sarkar, D. 2006. Transcriptional autoregulation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis PhoP involves recognition of novel direct repeat sequences in the regulatory region of the promoter. FEBS Lett.580, 5328–5338.
Guthrie, C. and Fink, G.R. 1991. Guide to yeast genetics and molecular biology. Methods Enzymology194, 1–932.
Haydel, S.E., Benjamin, W.H.Jr., Dunlap, N.E., and Clark-Curtiss, J.E. 2002. Expression, autoregulation, and DNA binding properties of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis TrcR response regulator. J. Bacteriol.184, 2192–2203.
Himpens, S., Locht, C., and Supply, P. 2000. Molecular characterization of the mycobacterial SenX3-RegX3 two-component system: evidence for autoregulation. Microbiology146Pt 12, 3091–3098.
Honaker, R.W., Leistikow, R.L., Bartek, I.L., and Voskuil, M.I. 2009. Unique roles of DosT and DosS in DosR regulon induction and Mycobacterium tuberculosis dormancy. Infect. Immun.77, 3258–3263.
Ioanoviciu, A., Yukl, E.T., Moenne-Loccoz, P., and de Montellano, P.R. 2007. DevS, a heme-containing two-component oxygen sensor of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochemistry46, 4250–4260.
James, P., Halladay, J., and Craig, E.A. 1996. Genomic libraries and a host strain designed for highly efficient two-hybrid selection in yeast. Genetics144, 1425–1436.
Kim, M.J., Park, K.J., Ko, I.J., Kim, Y.M., and Oh, J.I. 2010. Different roles of DosS and DosT in the hypoxic adaptation of Mycobacteria. J. Bacteriol.192, 4868–4875.
Kumar, A., Toledo, J.C., Patel, R.P., Lancaster, J.R.Jr., and Steyn, A.J. 2007. Mycobacterium tuberculosis DosS is a redox sensor and DosT is a hypoxia sensor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA104, 11568–11573.
Laub, M.T. and Goulian, M. 2007. Specificity in two-component signal transduction pathways. Annu. Rev. Genet.41, 121–145.
Lee, J.M., Cho, H.Y., Cho, H.J., Ko, I.J., Park, S.W., Baik, H.S., Oh, J.H., Eom, C.Y., Kim, Y.M., Kang, B.S., andet al. 2008. O2-and NO-sensing mechanism through the DevSR two-component system in Mycobacterium smegmatis. J. Bacteriol.190, 6795–6804.
Marina, A., Waldburger, C.D., and Hendrickson, W.A. 2005. Structure of the entire cytoplasmic portion of a sensor histidine-kinase protein. Embo J.24, 4247–4259.
Martinez-Argudo, I., Martin-Nieto, J., Salinas, P., Maldonado, R., Drummond, M., and Contreras, A. 2001. Two-hybrid analysis of domain interactions involving NtrB and NtrC two-component regulators. Mol. Microbiol.40, 169–178.
Martinez-Argudo, I., Salinas, P., Maldonado, R., and Contreras, A. 2002. Domain interactions on the ntr signal transduction pathway: two-hybrid analysis of mutant and truncated derivatives of histidine kinase NtrB. J. Bacteriol.184, 200–206.
Morth, J.P., Gosmann, S., Nowak, E., and Tucker, P.A. 2005. A novel two-component system found in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. FEBS Lett.579, 4145–4148.
Noriega, C.E., Lin, H.Y., Chen, L.L., Williams, S.B., and Stewart, V. 2010. Asymmetric cross-regulation between the nitrate-responsive NarX-NarL and NarQ-NarP two-component regulatory systems from Escherichia coli K-12. Mol. Microbiol.75, 394–412.
Ohta, N. and Newton, A. 2003. The core dimerization domains of histidine kinases contain recognition specificity for the cognate response regulator. J. Bacteriol.185, 4424–4431.
Podust, L.M., Ioanoviciu, A., and Ortiz de Montellano, P.R. 2008. 2.3 A X-ray structure of the heme-bound GAF domain of sensory histidine kinase DosT of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochemistry47, 12523–12531.
Roberts, D.M., Liao, R.P., Wisedchaisri, G., Hol, W.G., and Sherman, D.R. 2004. Two sensor kinases contribute to the hypoxic response of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Biol. Chem.279, 23082–23087.
Saini, D.K., Malhotra, V., Dey, D., Pant, N., Das, T.K., and Tyagi, J.S. 2004a. DevR-DevS is a bona fide two-component system of Mycobacterium tuberculosis that is hypoxia-responsive in the absence of the DNA-binding domain of DevR. Microbiology150, 865–875.
Saini, D.K., Malhotra, V., and Tyagi, J.S. 2004b. Cross talk between DevS sensor kinase homologue, Rv2027c, and DevR response regulator of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. FEBS Lett.565, 75–80.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F., and Maniatis, T. 2001. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y., USA.
Sardiwal, S., Kendall, S.L., Movahedzadeh, F., Rison, S.C., Stoker, N.G., and Djordjevic, S. 2005. A GAF domain in the hypoxia/NO-inducible Mycobacterium tuberculosis DosS protein binds haem. J. Mol. Biol.353, 929–936.
Schneider, S., Buchert, M., and Hovens, C.M. 1996. An in vitro assay of beta-galactosidase from yeast. Biotechniques20, 960–962.
Seok, J.S., Kaplan, S., and Oh, J.I. 2006. Interacting specificity of a histidine kinase and its cognate response regulator: the PrrBA system of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Microbiology152, 2479–2490.
Shrivastava, R., Ghosh, A.K., and Das, A.K. 2007. Probing the nucleotide binding and phosphorylation by the histidine kinase of a novel three-protein two-component system from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. FEBS Lett.581, 1903–1909.
Shrivastava, R., Ghosh, A.K., and Das, A.K. 2009. Intra- and intermolecular domain interactions among novel two-component system proteins coded by Rv0600c, Rv0601c and Rv0602c of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Microbiology155, 772–779.
Skerker, J.M., Perchuk, B.S., Siryaporn, A., Lubin, E.A., Ashenberg, O., Goulian, M., and Laub, M.T. 2008. Rewiring the specificity of two-component signal transduction systems. Cell133, 1043–1054.
Sousa, E.H., Tuckerman, J.R., Gonzalez, G., and Gilles-Gonzalez, M.A. 2007. DosT and DevS are oxygen-switched kinases in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Protein Sci.16, 1708–1719.
Stock, A.M., Robinson, V.L., and Goudreau, P.N. 2000. Two-component signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem.69, 183–215.
Tomomori, C., Tanaka, T., Dutta, R., Park, H., Saha, S.K., Zhu, Y., Ishima, R., Liu, D., Tong, K.I., Kurokawa, H., andet al. 1999. Solution structure of the homodimeric core domain of Escherichia coli histidine kinase EnvZ. Nat. Struct. Biol.6, 729–734.
Via, L.E., Curcic, R., Mudd, M.H., Dhandayuthapani, S., Ulmer, R.J., and Deretic, V. 1996. Elements of signal transduction in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: in vitro phosphorylation and in vivo expression of the response regulator MtrA. J. Bacteriol.178, 3314–3321.
West, A.H. and Stock, A.M. 2001. Histidine kinases and response regulator proteins in two-component signaling systems. Trends Biochem. Sci.26, 369–376.
Yamada, S., Sugimoto, H., Kobayashi, M., Ohno, A., Nakamura, H., and Shiro, Y. 2009. Structure of PAS-linked histidine kinase and the response regulator complex. Structure17, 1333–1344.
Yamamoto, K., Hirao, K., Oshima, T., Aiba, H., Utsumi, R., and Ishihama, A. 2005. Functional characterization in vitro of all two-component signal transduction systems from Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem.280, 1448–1456.
Zahrt, T.C., Wozniak, C., Jones, D., and Trevett, A. 2003. Functional analysis of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis MprAB two-component signal transduction system. Infect. Immun.71, 6962–6970.
Zapf, J., Sen, U., Madhusudan, Hoch, J.A., and Varughese, K.I. 2000. A transient interaction between two phosphorelay proteins trapped in a crystal lattice reveals the mechanism of molecular recognition and phosphotransfer in signal transduction. Structure Fold Des.8, 851–862.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://www.springerlink.com/content/120956.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, HN., Jung, KE., Ko, IJ. et al. Protein-protein interactions between histidine kinases and response regulators of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. J Microbiol. 50, 270–277 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-012-2050-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-012-2050-4