Abstract
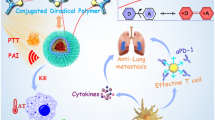
Programmed death 1 (PD-1) and its ligand PD-L1 are two typical immune checkpoints. Antibody-based immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) strategy targeting PD-1/PD-L1 achieved a significant therapeutic effect on cancer. However, due to the impenetrability of antibody drugs and the occurrence of immune-related adverse events, only a minority of patients benefit from this treatment. Peptides multimerization has been widely proved to be an effective method to improve receptor binding affinity through a multivalent synergistic effect. In this study, we report a novel peptide-aggregation-induced emission (AIE) hybrid supramolecular TAP, which can self-assemble into nanofibers through non-covalent interactions such as hydrogen bonds, with a specific nanomolar affinity to PD-L1 in vivo and in vitro. Combined with near-infrared agents, it can be used for tumor imaging and photothermal therapy, which enables photothermal ablation of cancer cells for generating tumor-associated antigen (TAA) and triggering a series of immunological events. Collectively, our work suggests that synthetic self-assembled peptide nanofibers can be developed as attractive platforms for active photothermal immunotherapies against cancer.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keir, M. E.; Butte, M. J.; Freeman, G. J.; Sharpe, A. H. PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 677–704.
Tumeh, P. C.; Harview, C. L.; Yearley, J. H.; Shintaku, I. P.; Taylor, E. J. M.; Robert, L.; Chmielowski, B.; Spasic, M.; Henry, G.; Ciobanu, V. et al. PD-1 blockade induces responses by inhibiting adaptive immune resistance. Nature 2014, 515, 568–571.
Iwai, Y.; Ishida, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Okazaki, T.; Honjo, T.; Minato, N. Involvement of PD-L1 on tumor cells in the escape from host immune system and tumor immunotherapy by PD-L1 blockade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12293–12297.
Pardoll, D. M. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264.
Postow, M. A.; Callahan, M. K.; Wolchok, J. D. Immune checkpoint blockade in cancer therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1974–1982.
Sharma, P.; Allison, J. P. The future of immune checkpoint therapy. Science 2015, 348, 56–61.
Muttenthaler, M.; King, G. E.; Adams, D. J.; Alewood, P. F. Trends in peptide drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 309–325.
Cooper, B. M.; Iegre, J.; O’Donovan, D. H.; Halvarsson, M. O.; Spring, D. R. Peptides as a platform for targeted therapeutics for cancer: Peptide-drug conjugates (PDCs). Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 52, 1480–1494.
Xing, P. Y.; Zhao, Y. L. Multifunctional nanoparticles self-assembled from small organic building blocks for biomedicine. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 7304–7339.
Qi, G. B.; Gao, Y. J.; Wang, L.; Wang, H. Self-assembled peptide-based nanomaterials for biomedical imaging and therapy. Adv. Mater. 2018, 32, 1703444.
Habibi, N.; Kamaly, N.; Memic, A.; Shafiee, H. Self-assembled peptide-based nanostructures: Smart nanomaterials toward targeted drug delivery. Nano Today 2016, 11, 41–60.
Li, J.; Wang, J. Q.; Zhao, Y. R.; Zhou, P.; Carter, J.; Li, Z. Y.; Waigh, T. A.; Lu, J. R.; Xu, H. Surfactant-like peptides: From molecular design to controllable self-assembly with applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 421, 213418.
Fleming, S.; Ulijn, R. V. Design of nanostructures based on aromatic peptide amphiphiles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 8150–8177.
Moore, A. N.; Hartgerink, J. D. Self-assembling multidomain peptide nanofibers for delivery of bioactive molecules and tissue regeneration. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 52, 714–722.
Wang, Y.; An, Y. X.; Shmidov, Y.; Bitton, R.; Deshmukh, S. A.; Matson, J. B. A combined experimental and computational approach reveals how aromatic peptide amphiphiles self-assemble to form ion-conducting nanohelices. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 3022–3031.
Li, S. K.; Zhang, W. J.; Xing, R. R.; Yuan, C. Q.; Xue, H. D.; Yan, X. H. Supramolecular nanofibrils formed by coassembly of clinically approved drugs for tumor photothermal immunotherapy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2100595.
Li, X. S.; Lovell, J. F.; Yoon, J.; Chen, X. Y. Clinical development and potential of photothermal and photodynamic therapies for cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 657–674.
Huang, X. Y.; Lu, Y.; Guo, M. X.; Du, S. Y.; Han, N. Recent strategies for nano-based PTT combined with immunotherapy: From a biomaterial point of view. Theranostics 2021, 11, 7546–7569.
Xu, P.; Liang, F. Nanomaterial-based tumor photothermal immunotherapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 9159–9180.
Delfi, M.; Sartorius, R.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Sharifi, E.; Zhang, Y. P.; De Berardinis, P.; Zarrabi, A.; Varma, R. S.; Tay, F. R.; Smith, B. R. et al. Self-assembled peptide and protein nanostructures for anticancer therapy: Targeted delivery, stimuli-responsive devices and immunotherapy. Nano Today 2021, 38, 101119.
Shang, T. Y.; Yu, X. Y.; Han, S. S.; Yang, B. Nanomedicine-based tumor photothermal therapy synergized immunotherapy. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 5241–5259.
Zhang, R. Y.; Duan, Y. K.; Liu, B. Recent advances of AIE dots in NIR imaging and phototherapy. Nanoscale 2019, 77, 19241–19250.
Chen, C.; Ni, X.; Jia, S. R.; Liang, Y.; Wu, X. L.; Kong, D. L.; Ding, D. Massively evoking immunogenic cell death by focused mitochondrial oxidative stress using an AIE luminogen with a twisted molecular structure. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1904914.
Li, J.; Gao, H. Q.; Liu, R. H.; Chen, C.; Zeng, S.; Liu, Q.; Ding, D. Endoplasmic reticulum targeted AIE bioprobe as a highly efficient inducer of immunogenic cell death. Sci. China Chem. 2020, 63, 1428–1434.
Liao, Y. H.; Wang, R. L.; Wang, S. Z.; Xie, Y. F.; Chen, H. H.; Huang, R. J.; Shao, L. Q.; Zhu, Q. H.; Liu, Y. S. Highly efficient multifunctional organic photosensitizer with aggregation-induced emission for in vivo bioimaging and photodynamic therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 54783–54793.
Dai, J.; Li, Y. H.; Long, Z.; Jiang, R. M.; Zhuang, Z. Y.; Wang, Z. M.; Zhao, Z. J.; Lou, X. D.; Xia, F.; Tang, B. Z. Efficient near-infrared photosensitizer with aggregation-induced emission for imaging-guided photodynamic therapy in multiple xenograft tumor models. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 854–866.
Li, X. S.; Kim, J.; Yoon, J.; Chen, X. Y. Cancer-associated, stimuli-driven, turn on theranostics for multimodality imaging and therapy. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606857.
Qian, Y. X.; Wang, W. Z.; Wang, Z. H.; Han, Q. J.; Jia, X. Q.; Yang, S.; Hu, Z. Y. Switchable probes: pH-triggered and VEGFR2 targeted peptides screening through imprinting microarray. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 5690–5693.
Wang, A. H.; Cui, L. Y.; Debnath, S.; Dong, Q. Q.; Yan, X. H.; Zhang, X.; Ulijn, R. V.; Bai, S. Tuning supramolecular structure and functions of peptide bola-amphiphile by solvent evaporation-dissolution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 21390–21396.
Wang, J.; Liu, K.; Yan, L. Y.; Wang, A. H.; Bai, S.; Yan, X. H. Trace solvent as a predominant factor to tune dipeptide self-assembly. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 2138–2143.
Yang, Y. P. Cancer immunotherapy: Harnessing the immune system to battle cancer. J. Clin. Invest. 2015, 125, 3335–3337.
Etezadi, D.; Warner IV, J. B.; Ruggeri, F. S.; Dietler, G.; Lashuel, H. A.; Altug, H. Nanoplasmonic mid-infrared biosensor for in vitro protein secondary structure detection. Light Sci. Appl. 2017, 6, e17029.
Raymond, D. M.; Nilsson, B. L. Multicomponent peptide assemblies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 3659–3720.
Castelletto, V.; Kirkham, S.; Hamley, I. W.; Kowalczyk, R.; Rabe, M.; Reza, M.; Ruokolainen, J. Self-assembly of the toll-like receptor agonist macrophage-activating lipopeptide MALP-2 and of its constituent peptide. Biomacromolecules 2016, 77, 631–640.
Zhou, X. M.; Zuo, C.; Li, W. Q.; Shi, W. W.; Zhou, X. W.; Wang, H. F.; Chen, S. M.; Du, J. F.; Chen, G. Y.; Zhai, W. J. et al. A novel D-peptide identified by mirror-image phage display blocks TIGIT/PVR for cancer immunotherapy. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 15114–15118.
Xu, X. L.; Deng, G. J.; Sun, Z. H.; Luo, Y.; Liu, J. K.; Yu, X. H.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, P.; Liu, G. Z.; Zhang, P. F. et al. A biomimetic aggregation-induced emission photosensitizer with antigen-presenting and hitchhiking function for lipid droplet targeted photodynamic immunotherapy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2102322.
Guo, J. C.; An, Q.; Guo, M. Y.; Xiao, Y. T.; Li, B.; Gao, F. E.; Wang, Y. Q.; Li, J. Y.; Wang, Y. L.; Liu, Y. et al. Oxygen-independent free radical generation mediated by core-shell magnetic nanocomposites synergizes with immune checkpoint blockade for effective primary and metastatic tumor treatment. Nano Today 2021, 36, 101024.
Qian, Y. X.; Wang, Y. H.; Jia, F.; Wang, Z. H.; Yue, C. Y.; Zhang, W. K.; Hu, Z. Y.; Wang, W. Z. Tumor-microenvironment controlled nanomicelles with AIE property for boosting cancer therapy and apoptosis monitoring. Biomaterials 2019, 188, 96–106.
Conde, J.; Oliva, N.; Zhang, Y.; Artzi, N. Local triple-combination therapy results in tumour regression and prevents recurrence in a colon cancer model. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 1128–1138.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported financially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 32027801, 81801766, 21775031, and 31870992), the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Nos. XDB36000000 and XDB38010400), Foundation of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (No. HZ2021006), CAS-JSPS (No. GJHZ2094), Fujian Medical University Foundation for the Introduction of Talents (Nos. XRCZX2017020, XRCZX2019005, and XRCZX2019018), and the Joint Funds for the innovation of science and Technology Fujian Province (No. 2019Y9001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2022_4331_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
A novel PD-L1 targeting peptide self-assembled nanofibers for sensitive tumor imaging and photothermal immunotherapy in vivo
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, L., Zhang, J., Wu, C. et al. A novel PD-L1 targeting peptide self-assembled nanofibers for sensitive tumor imaging and photothermal immunotherapy in vivo. Nano Res. 15, 7286–7294 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4331-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4331-5